Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1. Put a tick mark (✓) against the correct alternative in the following statements
(1) Pollen is produced in the:
(a) Filament
(b) Style
(c) Pistil
(d) Anther
Solution: (d) Anther
(2) Reproductive whorls of a flower are:
(a) Stamens and carpels
(b) Sepals and petals
(c) Sepals and stamens
(d) Petals and carpels
Solution: (a) Stamens and carpels
(3) Grafting is a method of:
(a) Artificial vegetative propagation
(b) Sexual reproduction
(c) Artificial pollination
(d) Cross-pollination
Solution: (a) Artificial vegetative propagation
(4) Which one of the following is a false fruit?
(a) Tomato
(b) Apple
(c) Potato
(d) Pea
Solution: (b) Apple
Short Answer Questions:
Question 1. Write two ways in which pollination may occur in plants.
Solution:
Plants can be pollinated in two different ways:
(a) Self-pollination.
(b) Cross-pollination.
Question 2. Name the three agents of pollination.
Solution:
Below are the three pollination agents are:
(a) Insect
(b) Wind
(c) Water
Question 3. Give two features of flowers which favour pollination by insects.
Solution:
Specialties of flowers pollinated by insects:-
(a) To draw insects, these flowers have large, colourful petals.
(b) Insects may find the blooms by smell thanks to them being scented.
Question 4. Name two characteristics of flowers in which pollination occur by wind.
Solution:
The following traits are specific to flowers that are pollinated by the wind:
(a) They generate light pollen that is readily carried away.
(b) They generate a lot of pollen.
Question 5. What is a “false fruit”? Give one example:
Solution:
The ovary is reduced to a little seed-storing component in false fruits, while the fruit’s major fleshy section develops from the thalamus, the base of the flowers. For instance: – Apple and pears.
Question 6. Name any three agencies for dispersal of seeds.
Solution:
Below are the three agencies for dispersal of seeds:-
a. Wind
b. Water
c. Man and animals, birds, bats, squirrels.
Question 7. Fill in the blanks by selecting suitable words:
(Unisexual, fertilization, fruit, stamen, anther, bisexual, pollination, seed, ovary)
1. A flower that bears both the male and the female parts is known as __________ flower.
2. A flower bearing only male or female parts is known as __________ flower.
3. Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma is known as______________.
4. Fusion of male cell with the female cell is called ___________.
5. The ovule develops into a ______.
6. The ovary of the flower develops into a _______.
Solution:
1. A flower that bears both the male and the female parts is known as bisexual flower.
2. A flower bearing only male or female parts is known as unisexual flower.
3. Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma is known as pollination .
4. Fusion of male cell with the female cell is called fertilization .
5. The ovule develops into a seed .
6. The ovary of the flower develops into a fruit .
Long Answer Questions:
Question 1. What is vegetative reproduction?
Solution:
Vegetative reproduction: In this process, the plant’s vegetative components create new plants. The leaf, stem, and root are considered to be vegetative. This method can replicate foods like potato, mint, ginger, and banana. Both natural and artificial methods can be used to propagate vegetation. Reproduction in nature can also occur through the stem, the roots, and the leaves. Artificial methods of reproduction include tissue culture, grafting, layering, and cutting.
Question 2. Briefly explain why a gardener prefers to grow certain plants vegetatively?
Solution:
Some plants are preferred by gardeners to be grown vegetative. The following are some benefits of doing this:
1.) Vegetative components’ reproduction occurs more quickly.
2.) The resulting new plants spread quickly in a small space.
3.) It’s a safer approach.
4.) The daughter plants have all of the traits of the mother plant.
Question 3. Why is it disadvantageous to grow plants?
Solution:
The following reasons make vegetative plant growth unhealthy:
1. If a disease spreads throughout the farm, since all plants produced through vegetative propagation are the same, they are likely to be affected at the same time.
2. Plant dispersal does not happen on its own. Daughter plants that have grown to this level prefer to stick close by and are confined to a specific area, which creates competition for resources.
Question 4. What is meant by pollination? Explain the structure of germinating pollen grain with the help of a labelled diagram.
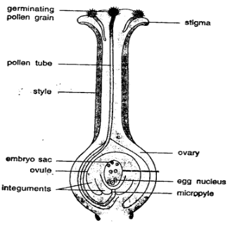
Solution:
The act of transferring pollen grains from the stems to the stigma is known as pollination. Grain structure of the pollen: Pollen grains are left on the stigma of the carpel after pollination. Pollen grains create a tube known as a pollen tube when the best conditions are present. This tube runs from the ovary downward through the stigma and style.
Through mitosis, the pollen grain nucleus separates into two male gametes. The two male gametes are released into the embryo sac by the pollen tube’s tip when it enters the ovary. The fertilization is created when one of the male gametes unites with the egg. Fertilization is the term for this union. The endosperm, a food-storing structure, is created when a second male gamete unites with the double secondary nucleus.
Question 5. Imagine all the seeds produced by a plant happen to fall under the same plant and sprout into new plants. Mention any two problems that will be faced by the new plants.
Solution:
In the event when all of a plant’s seeds sprout into new plants from the same parent plant, the following issues will arise for the plants:
1. A lot of plants can grow in a tiny, restricted area. Both the water and There won’t be as many minerals in the soil for them to use.
2. There won’t be enough air around them, and there won’t be as much sunlight. Therefore, the most of these budding plants will die.
Question 6. What is a flower? Draw a neat labelled diagram showing the L.S. of a typical flower.
Solution:
A flower is a plant’s reproductive organ. Given that it has both male and female components, it aids in sexual reproduction.
The following components make to a fully opened flower:

Stalk – A flower is attached to the shoot by means of stalk or pedicel stalk. The tip of the stalk is swollen or flattened. This is called torus or thalamus or receptacle. The different parts of a flower are inserted on the thalamus. There are usually four whorls as:
1. Sepals (Calyx): These are the outermost part of the flower. These are leaf like and green in colour. This is the outer covering of the flower and form outer whorl in a flower. The Calyx (sepals) enclose the inner parts of the flower when it is a bud. It is protective in function.
2. Corolla (Petals): Petals form the second whorl inner to the sepals. These are usually coloured, gaudy, or white in colour and scented and give sweet smell. The value of a flower is due to the attractive colour of the petals. These attract the insects for pollination.
3. Stamens (Androecium): The third whorls inner to the petals are stamens. This third whorl is called Androecium. These are the male parts of the flower. Each stamen is formed of a long narrow, hair like structure called filament. On its tip it bears, a rounded broad sac like structure called anther. Each anther has two anther lobes. Each anther lobe has two pollen sacs which have powdery mass called pollen grains.
4. Carpels (Gynoecium): Carpels are the inner most or fourth whorl in a flower. It is lodged on the thalamus and forms the female part of a flower. This whorl of carpels is called gynoecium. Each carpel or pistil has three parts.
(a) The lower most, swollen part is ovary. It is attached to the thalamus.
(b) The middle part is style which is narrow, thread like.
(c) Stigma: The style ends in a knob like, rounded structure which is sticky in nature to receive the pollen grains. The ovaries contain ovules which later turn into seeds after fertilization and the ovary wall forms the fruit sometimes the thalamus also becomes a part of the fruit as in apple.
Question 7. Write short notes on the following:
(a) Micro propagation
(b) Bryophyllum
(c) Vegetative reproduction
(d) Grafting
Solution:
(a) Micro propagation: This technique for growing plants involves the cultivation of cells and tissues. Buds, the shoot apex, or any other portion of the plant can be utilised as an explant for micropropagation if vegetative propagation is not possible in a crop.
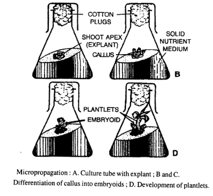
1. To stop microbial growth, the explants are first sterilised using chemicals before being cultivated in a specific feeding medium.
2. Cells multiply and grow to produce a callus, which is a mass of cells. Plant hormones, or growth regulators, are included.
3. The callus separates into plant parts that resemble plant parts (plantlet). The plantlets were put to the soil after 4-6 weeks.
(b) Bryophyllum: This beautiful plant can thrive in any kind of soil or container and is an associated with group plant. It needs sunlight. When a leaf accidently falls to the ground or is dropped from the parent plant. In the leaf notches, it begins to produce buds. When these buds come into contact with moist soil, they begin to grow. Small aerial shoots that go into the air and adventitious roots that penetrate the earth are produced by them. Therefore, from a single plant, these accidental buds produce several plants. This allows us to grow several plants from a single leaf. These little plants may be grown in separate pots to become independent plants. One of the vegetative modes of reproduction is this one.

(c) Vegetative reproduction: The vegetative parts of the plant are used in this method to produce new plants. The leaf, stem, and root are referred to as “vegetative.” Potatoes, mint, ginger, bananas, sugar beets, gul-e-daudi, asparagus, and sugar cane are all grown using this method.
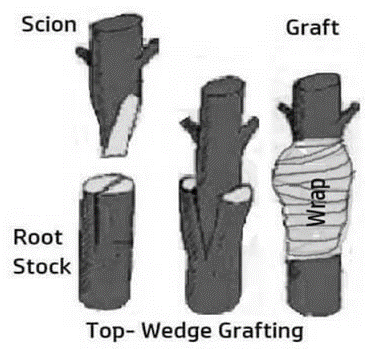
(d) Grafting: A little bud is connected to the stem of plants including mango, zizyphus (ber), guava, apples, fruits, and roses. A little orchard on a single plant with a variety of apple varieties. Consequently, we are able to grow many rose and chrysanthemum varieties on a single plant.
Question 8. How artificial pollination is useful to plant breeders? Discuss briefly.
Solution:
Artificial pollination entails the artificial introduction of pollen to the stigma. It was customary in the past to sprinkle “male blossoms of palms” over “female flowers.” Modern plant breeders, however, use artificial pollination to create new types. Breeders take off the anthers from immature flowers and wrap them in plastic bags. The pollen from the plants of the chosen variety is then used to fertilize these blooms.
Question 9. With the help of suitable diagrams, describe
(a) Binary fission in plants
(b) Budding in yeast cell
Solution:
(a) Binary fission: This method of reproduction is asexual. This process increases reproduction in lower plants, such as bacteria. The cell’s nucleus divides into two during this procedure. The cell wall then separates in the centre of the cell. Each component, thus, has a nucleus. Each component is a separate bacterium as a result. Later, these two cell components become separated from one another and develop into two independent individuals known as daughter cells, which live separate lives.

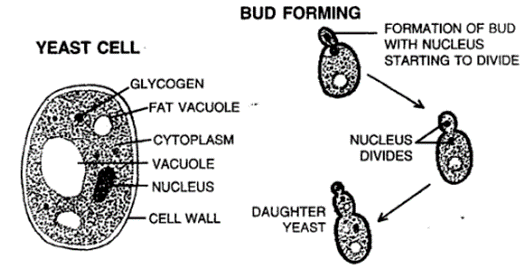
(b) Budding in yeast cell:- In a yeast cell, budding is the most typical process. A bud is an extension from the parent cell. The bud develops and finally separates from the parent body to live on its own.
ADDITIONAL Questions:
REPRODUCTION — INTRODUCTION AND ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS
I. Multiple choice Questions.
Tick (✓) the correct choice:
1. The common method of reproduction in bacteria is
a. budding
b. fragmentation
c. binary fission
d. all the above
Solution: (c) binary fission
2. Budding is commonly seen in
a. yeast
b. grasses
c. Amoeba
d. Spirogyra
Solution: (a) yeast
3. Reproduction or propagation by stem is common in
a. begonia
b. potato
c. sweet potato
d. Bryophyllum
Solution: (b) potato
II. Fill in the blanks:
1. Budding is a kind of __________ reproduction.
2. The amount of cytoplasm in the parent cell is __________ than the amount in the bud.
3. Yeast cells reproduce by __________
4. Amoeba reproduces by __________.
5. Binary fission produces cells of __________ size.
6. Budding produces cells of __________ size.
7. Fungi, ferns and mosses reproduce by __________.
Solution:
1. Budding is a kind of asexual reproduction.
2. The amount of cytoplasm in the parent cell is more than the amount in the bud.
3. Yeast cells reproduce by budding .
4. Amoeba reproduces by binary fission .
5. Binary fission produces cells of equal size.
6. Budding produces cells of different size.
7. Fungi, ferns and mosses reproduce by spore formation .
III. State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F):
1. Asexual reproduction is more common than the sexual reproduction.
2. Producing life is called respiration.
3. Dogs and cats reproduce from two parents.
4. Bacteria and yeast reproduce by sexual reproduction.
5. Reproduction by spores is a method of asexual reproduction.
6. A potato tuber is really an underground stem.
7. A whole new plant can grow from the eye of a tuber.
8. Cutting and grafting are natural means of reproduction.
9. Most organisms have the capacity of regeneration in some or the other way.
Solution:
1. Asexual reproduction is more common than the sexual reproduction. (False)
2. Producing life is called respiration. (False)
3. Dogs and cats reproduce from two parents. (True)
4. Bacteria and yeast reproduce by sexual reproduction. (False)
5. Reproduction by spores is a method of asexual reproduction. (True)
6. A potato tuber is really an underground stem. (True)
7. A whole new plant can grow from the eye of a tuber. (True)
8. Cutting and grafting are natural means of reproduction. (False)
9. Most organisms have the capacity of regeneration in some or the other way. (True)
IV. Find the odd-one out, giving reasons.
Question 1. Gamete, budding, fragmentation, regeneration.
Solution:
Gamete is the odd-one out as it is responsible for sexual reproduction while rests three are methods of asexual reproduction.
Question 2. Cutting, grafting, layering, binary fission.
Solution:
Binary fission is the odd-one out as it a method of asexual reproduction while the rest
three are artificial methods of vegetative propagation.
V. Differentiate between the following:
Question 1. Binary fission and budding?
Solution:
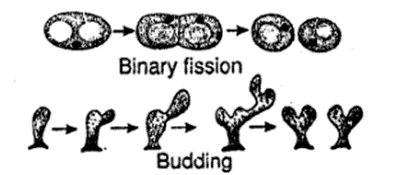
Binary fission:
Asexual reproduction known as binary fission:-
1) Occurs when a parent cell divides into two identically sized offspring.
2) Many single-celled species, such as bacteria, exhibit binary fission.
3) The parent cell and freshly created cells are of similar size.
4) Equal division of the parent cell’s cytoplasm.
5) It can’t be artificially achieved because it is a natural process.
Budding:-
It is the type of asexual reproduction when a parent cell develops an outgrowth as:-
1) However, a bud detaches from this to create a new multicellular individual.
2) Multicellular organisms like yeast use budding for reproduction.
3) Parent cell dimensions exceed those of the developing bud.
4) Parent cell has more cytoplasm than bud. Cytoplasm splits unfairly.
Question 2. Cutting and grafting?
Solution:
Cutting:-
1. It is a technique for vegetative propagation when a piece of a plant’s stem, root, or leaf is utilised to create a new plant.
2. There are no differences between the new plant and the parent plant.
3. Stem cutting is used to propagate rose, cactus, and sugarcane, tamarind, lemon, etc. Are propagated by root cutting.
Grafting:-
1. It is a method of vegetative propagation in which the stem of one plant (the branch) is placed on the root of another plant, and the two portions are then grown together to produce a new plant (stock).
2. The new plant differs from its parents in certain ways.
3. Grafting is used to create better types of apple, mango, rose, etc.
VI. Define the following:
1. Grafting
2. Vegetative reproduction
3. Binary fission
4. Tissue culture
5. Budding
6. Regeneration
Solution:
1. Grafting:- Grafting is a type of artificial vegetative propagation in which a desired plant is created from the stock (the root component of one plant) and scion of two different individual plants (stem portion from other plant).
2. Vegetative reproduction: Vegetative reproduction is a type of asexual reproduction in plants that results in the growth of new plants from vegetative parts such as the root, stem, or leaf.
The development of new plants does not include any reproductive organs or seeds.
3. Binary fission: A parent cell divides into two daughter cells of equal size in a process known as binary fission, which is typically used by unicellular organisms like bacteria.
4. Tissue culture: Tissue culture is an artificial vegetative propagation technique in which tissue from the plant tip is cultured in an artificial nutritional solution to generate a callus that can result in the growth of new plants.
5. Budding: Asexual reproduction that involves the separation of an organism’s body’s bud-like extension into a new creature.
6. Regeneration: Regeneration is the ability of living things to repair themselves or grow missing parts.
VII. Mention the common method of reproduction in the following organisms:
1. Bacteria
2. Yeast
3. Spirogyra
4. Micro
5. Mosses
6. Ferns
7. Dahlia
8. Potato
9. Ginger
10. Gladiolus
11. Strawberry
12. Rose
13. Jasmine
14. Mango
15. Bougainvillea
Solution:
1. Bacteria — Binary fission
2. Yeast — Budding
3. Spirogyra — Fragmentation
4. Macro — Spore formation
5. Mosses — Spore formation
6. Ferns — Spore formation
7. Dahlia — Vegetative propagation by roots
8. Potato — Vegetative propagation by stems (tuber)
9. Ginger — Vegetative propagation by stems (rhizome)
10. Gladiolus — Vegetative propagation by stems (corm)
11. Strawberry — Vegetative propagation by stems (runners)
12. Rose — Cutting
13. Jasmine — Layering
14. Mango — Grafting
15. Bougainvillea — Citing and Layering
Answer the following Qs:
Question 1. Why is reproduction necessary for living organisms?
Solution: If living things didn’t reproduce, there wouldn’t be any left over when they died. Thus, the species would disappear. Reproduction is, thus, the means of perpetuation of species.
Question 2. Describe the advantages of vegetative reproduction.
Solution:
Vegetative reproduction has the following benefits:
1) It is a simpler, faster, and less expensive mode of replication.
2) Plants without seeds can be grown.
3) The plants created using this technique are exact copies of the parent plant and have no differences.
4) Unworkable seeds are not produced by plants like banana, rose, and jasmine. This strategy makes it simple to grow these plants.
Question 3. Describe the various methods of vegetative reproduction.
Solution:
In an asexual process known as vegetative reproduction, plant components rather than seeds are used to create new plants. Various methods for vegetative reproduction include:
1. Vegetative propagation by roots: From the enlarged roots that are buried in the earth, new plants grow. Example: Asparagus, dahlias, and sweet potatoes.
2. Leaf-based vegetative propagation: Plants and buds at the leaf margin separate to grow into new plants. For examples: Bryophyllum and begonia.
3. Vegetative propagation by stems: Many plants reproduce vegetative by means of stems or stem-related alterations, such as:
(a) The potato, which is a tuber with eyes that sprouts new plants, is an example of this.
(b) Ginger is an altered rhizome, or enlarged underground stem, which has buds to produce new plants.
(c) Gladiolus and saffron have short swollen underground stem (corm) forming
new plants.
(d) Strawberry has long stems called runners. Buds on them form new plants.
Question 4. Explain the process of
(i) binary fission in bacteria, and
(ii) budding in Hydra

Solution:
(i) In binary fission, a single parent cell in bacteria lengthens and splits into nearly two equal haves. The nucleus splits into two pieces as well. Each of the two parts then \sgrow into full size. Each cell repeats the process.
(ii) Cells divide quickly at a specific location on the parent plant during Hydra’s budding process, forming an outgrowth known as a bud. While still connected to the parent plant, these buds grow into tiny individuals. When this person reaches a specific size, it separates from the parent body and starts to exist on its own.



