Students can refer to Capital and Revenue Expenditure Income ICSE Class 10 notes and exam questions provided for ICSE students. This is an important chapter in ICSE commercial studies class 9. We have provided here questions and answers which are expected to come in the upcoming ICSE exams for class 10th. Prepared based on the latest examination pattern and guidelines issued by ICSE. You can also refer to ICSE Books in pdf available for the latest academic session.
ICSE Class 10 Commercial Studies Capital and Revenue Expenditure Income Important Questions
Students should learn the important questions and answers given below for Chapter Definitions From Topo Maps in Commercial Studies for ICSE Class 10. These board questions are expected to come in the upcoming exams. Students of ICSE Class 10th should go through the Important questions and answers ICSE Class 10 Commercial Studies which will help them to get more marks in exams.
Board Exam Questions Capital and Revenue Expenditure Income ICSE Class 10 Commercial Studies
Question: Define capital expenditure and give four examples of such expenditure.
OR
What is meant by the term Captial Expenditure?
Ans. Capital Expenditure means the expenditure the benefits of which are available over a long time period. It is made to acquire fixed assets and is of a non-recurring nature. Purchase of plant and machinery is an example of capital expenditure.
Some examples of captial expenditure are given below:
(a) Purchase of land, building, plant and machinery, equipments, furniture, loose tools, etc.
(b) Cost of addition, extension and improvements to existing fixed assets.
(c) Cost of overhauling second hand machines.
(d) Expenses incurred for putting an asset into a working condition.
Question: Distinguish between Capital Receipts and Revenue Receipts.
Ans.

Question: Give six examples of revenue expenditure becoming capital expenditure.
Ans. The following expenses are revenue in nature. But they are treated as capital expenditure in the following circumstances.
(i) Raw Materials and Stores : When these are used for manufacturing a fixed asset, these expenses are treated as capital expenditure.
(ii) Carriage and Freight : If these expenses are paid on the transportation of newly acquired fixed asset, these are treated as capital expenditure.
(iii) Wages : Wages paid for the construction of a building or for the installation of a machine are treated as capital expenditure and are added to the cost of the asset.
(iv) Repairs : Expenses incurred to repair a second hand machine, purchased by the firm, to make it usable are treated as capital expenditure.
(v) Preliminary Expenses : Expenses incurred on the formation of a company are treated as capital expenses because their benefit will be available over a long period.
(vi) Brokerage : Brokerage paid on the purchase of a fixed asset is treated as capital expenditure
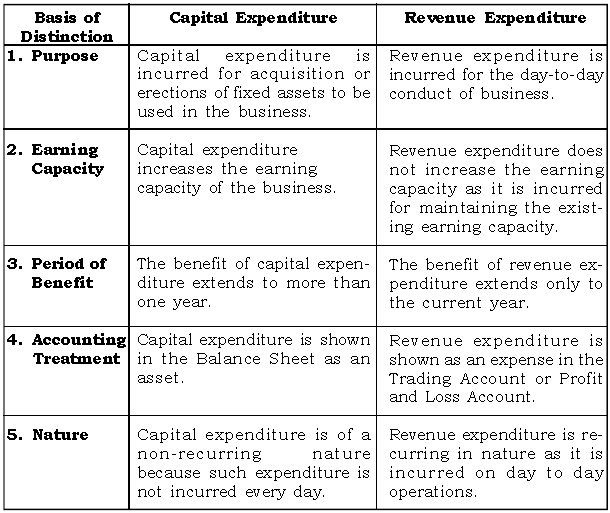
Question: Distinguish clearly between Capital Expenditure and Revenue Expenditure.
Ans:
Question: What is meant by the term ‘Revenue Expenditure’ ?
Ans. Revenue expediture means the expenditure the benefit of which is exhausted within the current year. Such expenditure is of a recurring nature and does not result in the acquisation of permanent assets. The following types of expenses are included in revenue expenditure.
(i) The following types of the day to day running of the business :
These expenses do not yield any benefit beyond the current years and their effect is short-lived, e.g. rent, salaries, wages, power and fuel,etc. These expenses do not to add to the profit earning capacity of the business.
(ii) Expenses incurred for the upkeep of fixed assets : Fixed assets represent Capital expenditure but expenses incurred to keep them in good working condition such as repairs and maintenance, are also revenue expenses.
(iii) Expenses incurred on purchase of stocks of materials and goods :
These include the goods purchased for resale and raw materials purchased for convering them into finished goods. The amount used during the years is revenue expenditure and the remaining amount will be an assets.
(iv) Depreciation on fixed assets : Fixed assets lose part of their value every year due to wear and tear and even with passage of time. Such reduction
Question: Distinguish Between Capital Receipts and Revenue Receipts.
Ans.

Question: Define capital receipts and give two example of such receipts.
Ans. Capital receipts refer to the receipts of a non-recurring nature such as additional capital from owners, loans raised by the firm and money obtained from a sale of fixed assets. Some examples of capital receipts are given below:
(a) Amount received by way of loans.
(b) Capital raised by an issue of shares and debentures.
Question: What is revenue expenditure? Give five examples of such expenditure.
Ans. Revenue expediture means the expenditure the benefit of which is exhausted within the current year. Such expenditure is of a recurring nature and does not result in the acquisation of permanent assets.
The following types of expenses are included in revenue expenditure.
(i) Expenses incurred for the day to-day running of the business
(ii) Expenses incurred for the upkeep of fixed assets
(iii) Expenses incurred on purchase of stocks of materials and goods
(iv) Depreciation of fixed assets
(v) Loss from sale of fixed assets
Question: What are revenue receipts? Give three examples of these receipts.
Ans. Revenue receipts are the receipts obtained during the normal course of business operation and are of a recurring nature. Some examples of revenue receipts are as follows:
(a) Amount received from sale of goods. Total sales during the year are called ‘Turnover’.
(b) Interest and dividend received on investments.
(c) Fees and commission received for services rendered.

We hope you like the above provided Capital and Revenue Expenditure Income ICSE Class 10 notes and questions with solutions. In case you are searching for more study material then you can send us your comments in the box below. Our team of ICSE teachers will work to provide you the ICSE study material for free.


