Students of ICSE Class 10 should refer to Chemical Bonding ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Questions below which have come in past board exams. You should always go through questions that have come in previous years. This will help you to understand the pattern of questions in ICSE Class 10 Chemistry and prepare accordingly. This will help you to get better marks in ICSE Class 10 Board Exams
ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Important Questions Chemical Bonding
Chemical Bonding is an important chapter in ICSE Class 10 Chemistry. Our faculty has prepared the following ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Questions and answers based on the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Please refer to the solved questions below and also see links provided for other chapters.
Chemical Bonding ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Questions
Chemical Bonding ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Questions
A. Introduction
An Atom : An Atom is the smallest unit of matter taking part in a chemical reaction. It is built up of sub-atomic particles-protons, neutrons and electrons.
Electrons : The negatively charged particles, revolving in fixed orbits, around the nucleus of an atom, are called electrons.
Symbolical representation : e–.
Neutrons : Subatomic particles, with no net charge, present in the nucleus of an atom are called neutrons. The neutron, along with the proton, is a nucleon.
Symbolical representation : n0.
Protons : The positively charged particles, present in the nucleus of an atom, are called protons.
Symbolical representation : P+.
Symbolically an Atom can be represented as follows
AZX
Z – Atomic number
A – Atomic mass number
Example : An atom of Krypton will be represented as 8436Kr , where A=84 and Z= 36.
Note :
➢ The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom of an element.
➢ An atom is electrically neutral, i.e. Atoms have no overall electrical charge.
➢ Since an atom is electrically neutral, the number of protons is always equal to the number of electrons.
➢ The mass number is a count of the number of particles in an atom’s nucleus.
Confusion between Atomic Weight and Atomic Mass Number!
The atomic weight is actually a weighted average of all of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element relative to the mass of carbon-12.
The mass number is total number of particles present in an atom’s nucleus, i.e. the nucleons (sum of protons and neutrons).
In the periodic table, Atomic mass number is not given, Atomic weight is given.
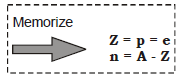
Mass Number (A) = (Number of Protons) + (Number of Neutrons)
In Summary…
For any element :
Number of Protons (p) = Atomic Number (Z)
Number of Electrons (e) = Number of Protons (P)
= Atomic Number (Z)
Number of Neutrons (n) = Mass Number (A) – Atomic Number (Z)
Number of Protons + Number of Neutrons = Nucleons = Mass Number (A)
1. What is an atom?
Ans. It is the smallest part of an element. It may or may not exist in a free state and can take part in a chemical reaction. It is made up of protons, neutrons and electrons.
2. What is a molecule?
Ans. It is the smallest part of an element or compound which can exist in a free state.
3. What do you mean by atomicity?
Ans. Atomicity refers to the number of atoms present in one molecule of that element.
4. Give example of the following :
Ans. a. Monoatomic molecules – He, Ar
b. Diatomic molecules – H2, O2, Cl2
c. Triatomic molecules – O3
d. Polyatomic molecules – P4, S8
5. What are Noble gases / Inert gases?
Ans. These are atoms which have their outermost valence shell complete. They do not lose, accept or share electrons and are therefore unreactive. All of them are gases.
Examples : Helium, Neon, Argon, Krypton, Xenon, Radon
6. Why are the inert gases, inert or inactive?
Ans. Noble gases are inactive because they either have 2 electrons in the first shell (He) OR 8 electrons in the last orbit.
Example :
i. Helium has two electrons i.e duplet configuration in its first and outermost electron shell.
ii. Other inert gases viz. Neon, Argon, Krypton, Xenon and Radon have 8 electrons.
i.e. octet configuration in their outer most electron shell.
Thus the Chemical inertness of inert gases has been regarded on account of completion of their electron shell by duplet (He) or by octet configuration which is considered to be a stable configuration.
7. Why do elements combine or react? Or Give reasons for chemical bonding
Ans. The driving force for atoms to combine is related to the tendency of each atom to attain stable electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas. For an atom to achieve stable electronic configuration it must have-
(i) Two electrons in outermost shell – Duplet rule
(ii) Eight electrons in outermost shell – Octet rule
B. Ions
➢ An atom can gain or lose electrons, becoming what is known as an ion.
➢ An ion is nothing more than an electrically charged atom.
➢ Adding or removing electrons from an atom does not change which element it is, just its net charge.
For example : Removing an electron from an atom of Lithium forms a Lithium ion, which is usually written as Li+. The plus sign means that this is a positively charged ion and one proton is more than the total number of electrons.
Why, on removal of an electron, an atom becomes positively charged? It is positively charged because a negatively charged electron was removed from the atom and so the number of negatively charged electrons is now one less than the number of positively charged protons, i.e. the total number of negative charge around the nucleus of an atom is one less than the total number of positive charge in the nucleus.
Why, on gaining an electron, an atom becomes negatively charged? When an atom accepts an electron, the number of negatively charged electrons is now one more than the number of positively charged protons, i.e. the total number of negative charge around the nucleus of an atom is one more than the total number of positive charge in the nucleus.
Such a negatively charged ion is called as an ANION.
In an atom, the number of protons always remains constant. It is only the increase or decrease in the number of electrons that determines the net negative or positive charge on an atom, respectively & accordingly an atom is called negatively charged ion or positively charged ion (Cation.)
C. Valency
It’s now very simple to understand, what is valency?
Valency is the number of electrons gained (accepted) or lost (donated)or shared by an atom, to become stable, i.e. to acquire a duplet or an octet state.
According to IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry), Valency of an element is also defined as the number of univalent atoms (Hydrogen or Chlorine) that are needed to combine with an atom of the element.
8. What do you mean by Valency?
Ans. Valency is the combining capacity of an element and is defined as the number of electrons an atom gives takes or shares to achieve the stable electronic configuration of the nearest configuration.
Positive Valency : Metal
Metals have 1, 2, 3 electrons in their outermost shells. They GIVE ELECTRONS and become positively charged ions called cations. [Refer Ions diagrammatic representation]

Non Metals have 4, 5, 6, 7 electrons in their outermost shells. They TAKE ELECTRONS and become negatively charged ions called ANIONS.


D. Chemical Bond
9. What is a Chemical bond?
Ans. The linkage or force which acts between two or more atoms to hold them together as a stable molecule is called chemical bond.
10. Which are the types of bonding?
Ans. Bonds are of three types :-
i. Ionic / electrovalent bon
ii. Covalent / molecular bond.
iii. Co – ordinate / Dative bond.
11. Define – Electrovalent bond. Discuss the periodic properties affecting electrovalent bond formation.
Ans. The chemical bond formed between two atoms by transfer of one or more electrons from the atom of a metallic electropositive element to an atom of a non-metallic electronegative element.
Periodic properties which affect chemical bond formation:
Ionisation potential – Lower value of Ionisation potential of a metallic atom. Electronaffinity – Higher value of electron affinity of a non-metallic atom.
Electronegativity difference – Larger the electronegativity difference between combining atoms, electron transfer takes place easily.
12. What is electrovalency?
Ans. The number of electrons donated or accepted by the valence shell of an atom of an element so as to achieve stable electronic configuration is called – electrovalency.
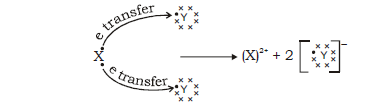
13. Give the formation of electrovalent compoun
Ans. Formation of electrovalent compound involves transfer of valence electrons from one atom generally metallic to another atom generally non-metallic. Metallic atom – Loses electrons to attain stable electronic configuration and becomes a cation
Metallic atom X. X – 1e– → X1+[Cation]
Non-metallic atom – gains electrons to attain stable electronic configuration and becomes an anion
Non-metallic atom Y. Y + 1e– → Y1- [Anion]
Cation and anions are oppositely charged particles, which attract one another with strong electrostatic force to form an electrovalent bond leading to formation of an electrovalent compound.
X1+ Y1- → XY
14. What type of compounds are usually formed between metals and non- metals and why ?
Ans. Electrovalent compounds are usually formed between metals and non- metals. An atom of a metallic elements readily loses electrons to form positively charged ions or cations whereas an atom of non-metallic elements readily gain electrons to form negatively charged ions or anions. The cation and anion attract each other by electrostatic force of attraction, hence the bond is called electrovalent bond.
15. Give the Characteristic of electrovalent or ionic compoun
Ans. The characteristics of electrovalent or ionic compounds are as stated below :
a. They are generally hard crystalline solids. They are made up of ions which are held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction.
b. The compounds are non – volatile.
c. They undergo chemical reactions at a fast rate. Therefore, the speed of the reactions are fast.
d. These compounds have a high boiling point and melting point as large amount of energy is required to break the strong force of attraction.
e . They are soluble in water and not in organic solvents.
f. They are good conductors of electricity when the hard solid is heated or dissolved in water, the bond breaks up and the ions formed move to their respective electrodes.
16. Give the formation of the following electrovalent compounds :
a. Sodium chloride molecule.
b. Calcium oxide molecule.
c. Magnesium chloride molecule.
Ans. a. Sodium chloride molecule.
In formation of sodium chloride the transfer of electron is from sodium to chlorine as follows :
Na (11) = (2, 8, 1) Nearest noble gas Ne (2, 8)
Cl (17) = (2, 8, 7) Nearest Noble gas Ar (2, 8, 8 )
Electron dot structural diagram :
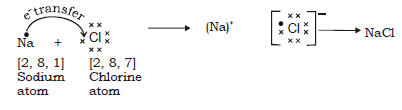
Ionic equation :
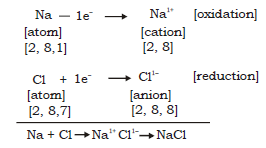
Thus sodium donates 1 electron to chlorine to become Na+ and chlorine accepts an electron to become Cl–. Strong electrostatic forces of attraction develop between the two oppositely charged ions and this leads to formation of sodium chloride molecule.

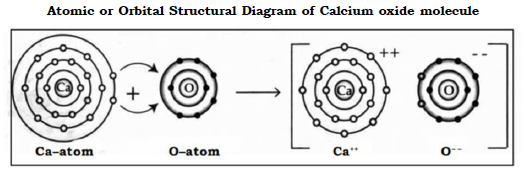
b. Calcium oxide molecule
In formation of Calcium oxide molecule the transfer of electron is from Calcium to oxygen as follows
Ca (20) = 2, 8, 8, 2 Nearest noble gas Ar (2, 8, 8)
O (8) = 2, 6 Nearest Noble gas Ne (2, 8)
Electron dot structural diagram :


Thus Calcium donates 2 electrons to oxygen to become Ca2+ and Oxygen accepts 2 electrons to become O2–. Strong electrostatic forces of attraction develop between the two oppositely charged ions and this leads to formation of Calcium oxide molecule.
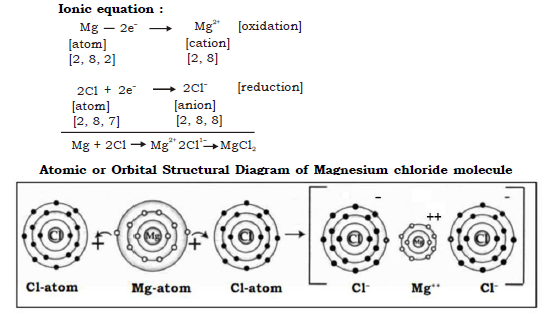
c. Magnesium chloride molecule
In formation of Magnesium chloride the transfer of electron is from magnesium to chlorine as follows :
Mg (12) = 2, 8, 2 Nearest noble gas Ne (2, 8)
Cl (17) = 2, 8, 7 Nearest Noble gas Ar (2, 8, 8 )
Thus Magnesium donates 1 electron each to two chlorine atoms to become Mg2+ and each chlorine accepts an electron to become Cl–. Strong electrostatic force of attraction develops between the two oppositely charged ions and this leads to formation of magnesium chloride molecule.
Electron dot structural diagram :
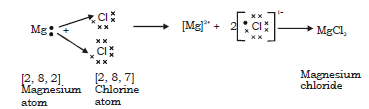
17. Define Covalent bon What is shared pair of electrons?
Ans. A bond which is formed due to mutual sharing of electrons between bonded atoms is known as a covalent bond. A pair of electrons present in covalent bonding which belongs to both the atoms.
18. What are the Factors favoring formation of covalent bonds?
Ans. There are two main factors :
i. Non – metal : A covalent bond is favorably formed between two non- metallic element The ionisation potential and the electron affinity of the element is high.
ii. Electronegativity : Electronegativity difference should be negligible between the two combining atom
19. What is covalency?
Ans. The number of electron pairs which an atom shares with one or more ato ms of the same o r different kind to achieve a stable e lectro nic configuration is termed as covalency.
20. Give the formation of covalent compoun
Ans. Formation of Covalent Compounds :
a. Elements that have 4, 5, 6 and 7 valence electrons (non metals) complete their octet by sharing of electrons with other atoms to form bonds between them.
b. This bond formation does not involve transfer of electrons therefore ions or charged particles are not formed and hence covalent compound are composed of molecules on are composed of molecules only.
c. As covalent compounds have molecules therefore covalent bond is also known as molecular bond.
d. Sharing of electrons takes place between atoms of non – metallic elements.
The number of electrons contributed for sharing by an element is known as its covalency.
e . Each contributing atom contributes equal number of electrons for formation of bond.
f. A covalent bond is formed by the two electrons (1 pair).
g. There exits a single bond (1 pair of electrons) or double bond (2 pairs of electrons) or triple bond (3 pairs of electrons).
21. Give the Characteristic of covalent compounds.
Ans. The characteristics of covalent compounds are as stated below :
a. The molecules have weak Vander Waals forces of attraction between them thus the compounds are soft solids, or liquids or gases.
b. They are volatile in nature.
c. They have a low M.P and B.P as less energy is required to break the Vander Waals forces of attraction.
e . They are not good conductors of electricity since there are no free ions. f. Polar compounds like NH3 and HCl ionises into ions when dissolved in a polar compound water.
g. They are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvent like benzene, toluene.
h. Molecular reactions are slow as the bonds are first broken and then new bonds are slowly establishe
22. Which are the two types of covalent bonds?
Ans. The two types of bonds are :
a. Polar covalent bond
b. Non – polar covalent bond
23. Explain in brief the concept of polar and non polar covalent bond.
Ans. a) Covalent compounds are formed by sharing of the electron pair between the combining atoms.
b) When these atoms differ in their electronegativities then there is a tendency for the electron pair to be attracted towards the more electronegative atom.
c) Thus the more electronegative atom develops a partial negative character ( δ–) and the other develops a partial positive character ( δ+).
d) Such compounds are called as polar covalent compounds and the bond formed between them is called polar covalent bond.
Example : Water, Hydrogen chloride molecule.
e ) Non polar compounds have atoms which have the same electronegativities and thus the pair of electrons is shared equally between the combining atoms. Thus no charge develops within the molecules.
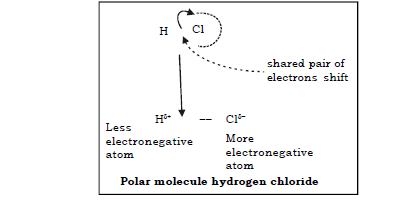
24. Define Polar covalent bond.
Ans. A polar covalent bond is defined as a bond in which the shared pair of electrons are unequally distributed between the two atoms resulting in the charge separation due to the drifting of shared pair of electrons towards more electronegative atom.
25. Give examples of polar covalent compounds.
Ans. Water and ammonia.
26. Give the formation of water molecule.
Ans. Water consists of 2 H atoms and 1 oxygen atom. Thus when a molecule of water is to be formed, the two hydrogen atoms each share an electron with oxygen atom, thereby forming two single covalent bonds between oxygen and hydrogen as follows:
Electron dot structure :
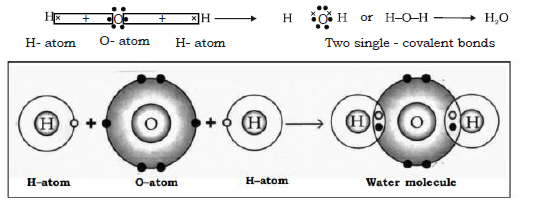
27. Give the formation of ammonia molecule.
Ans. A molecule of ammonia contains 1 nitrogen atom and 3 hydrogen atoms. When a molecule of ammonia is to be formed the three hydrogen atoms each share an electron with three electrons of nitrogen, thus forming three single covalent bonds between hydrogen and nitrogen.
Electron dot structure :
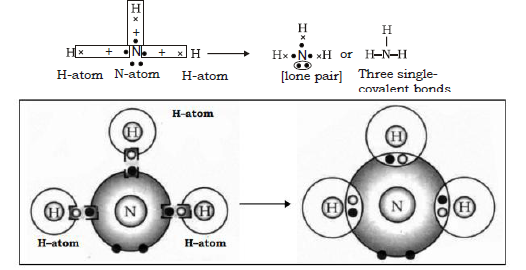
28. Define Non Polar covalent bond.
Ans. A non polar covalent bond is defined as a bond in which the shared pair of electrons are equally distributed between the two atoms resulting in no charge separation due to the drifting of shared pair of electrons and thus the molecule is symmetrical and electrically neutral.
29. Give examples of non polar covalent compounds.
Ans. Carbon tetrachloride, methane, hydrogen molecule, oxygen molecule etc.
30. Draw the formation of the following non polar covalent molecules :
a) Methane b) Carbon tetrachloride
c) Hydrogen molecule d) Chlorine molecule
e) Oxygen molecule f) Nitrogen molecule
a) METHANE
Atomic number : C = 6, H = 1
Carbon (2,4) requires 4 electrons to complete its octet, like the nearest noble gas – neon. Hydrogen (1) requires 1 electron to complete its duplet, like the nearest noble gas – helium.
Therefore 4 H atoms share 4 electrons of Carbon atom resulting in the formation of four C – H single covalent bonds.

b) CARBON TETRACHLORIDE
Atomic Number : C = 6, Cl = 17
Carbon (2,4) requires 4 electrons to complete its octet, like the nearest noble gas – neon. Chlorine (2,8,7) requires 1 electron to complete its octet, like to the nearest noble gas – argon.
Therefore one atom of carbon shares four electron pairs one with each of the four atoms of carbon.


c) Molecule of Hydrogen (H = 1)
Hydrogen (1) has only one electron in its outermost orbit and to attain a stable duplet structure of helium, it requires one electron.
Thus when 2 hydrogen atoms come together each contributes one electron to form one shared pair of electrons between them thereby both of the atoms attain a stable duplet structure.
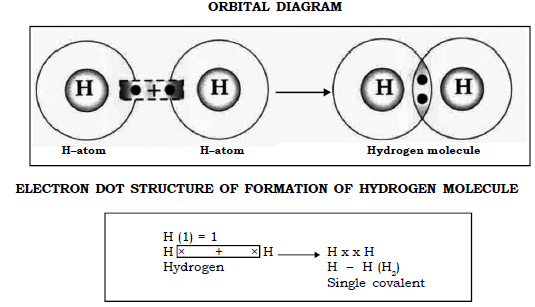
d) Molecule of Chlorine (Cl = 17)
Chlorine (2,8,7) has seven electrons in its outermost orbit and to attain a stable octet structure of argon it requires one electron.
Thus when 2 Chlorine atoms come together each contributes one electron to form one shared pair of electrons between them thereby both of the atoms attain a stable octet structure.
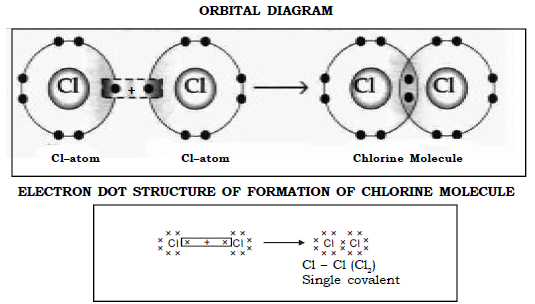
e) Molecule of Oxygen (O = 8)
Oxygen (2,6) has only 8 electrons in its outermost orbit and to attain a stable octet structure of neon it requires 2 electrons.
Thus when 2 Oxygen atoms come together each contributes 2 electrons to form two shared pair of electrons between them thereby both of the atoms attain a stable octet structure.

f) Molecule of Nitrogen (N = 7)
Nitrogen (2,5) has five electrons in its outermost orbit and to attain a stable octet state like neon it requires 3 electrons.
Thus when 2 Nitrogen atoms come together each contributes 3 electrons to form 3 shared pair of electrons between them thereby both of the atoms attain a stable octet structure.
This is an example of triple bond. Two atoms of nitrogen share three pairs of electrons to form one molecule of Nitrogen.
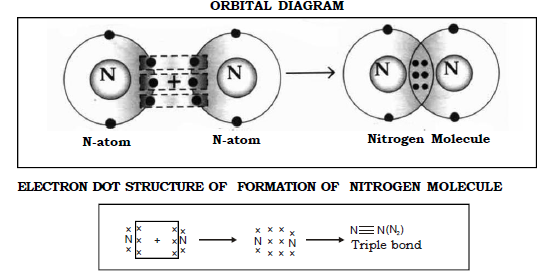
31. Define Co-ordinate bond. What is lone pair of electrons?
Ans. A chemical bond which is formed by a shared pair of electrons with both electrons coming from the same atom.
Lone pair of electron are a pair of electron not shared with any other atom.
CO-ORDINATE BOND FEATURES
a. The atom, which provides a lone pair of electrons, is known as donor atom and the other one is known as a gainer / acceptor atom.
b. Transfer of lone pair of electrons is indicated by an arrow, which is directed towards the gainer.
c. The formation of a co-ordinate bond due to the transfer of electrons is also known as the Lone pair effect.
d. Co-ordinate bond is also known as dative bond.
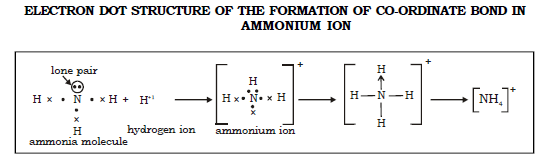
32. Give the formation of co-ordinate bond in :
a) Hydronium Ion
b) Ammonium Ion
Ans. a) Hydronium ion
The Hydronium ion is a hydrogen ion in association with a molecule of water. The water molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms covalently bonded with the oxygen atom.
The oxygen atom has two pairs of unshared electrons called the lone pair of electrons, in its outermost shell. The hydrogen ion does not have any electron in its valence shell. Therefore it shares a pair of electrons from the oxygen atom by means of co-ordinate co-valency to form a (H3O+) ion.

b) The ammonium ion is a hydrogen ion in association with a molecule of ammonia. The ammonia molecule consists of 3 hydrogen atoms covalently bonded with the nitrogen atom.
The nitrogen atom has one pair of unshared electrons called the lone pair of electrons, in its outermost shell. The hydrogen ion does not have any electron in its valence shell. Therefore it shares a pair of electrons from the nitrogen atom by means of co-ordinate co-valency to form an ammonium ion. (NH4)+
E. Oxidation and Reduction
33. Define:
a) Oxidation
b) Reduction
Ans. From the electron point of view oxidation is defined as
“Oxidation is the loss of electrons from an atom.”
“Reduction is the gain of electrons from an atom.”
34. Explain the concept of Oxidation.
When an atom loses an electron it is said to be oxidised.
Na – le– → Na+
i. Metals lose electron to form cations
Ca – 2e– → Ca2+
Al – 3e– → Al3+
ii. Anions lose electrons and get converted to neutral atoms.
Cl– – le– → Cl
iii. In electrolysis oxidation takes place at anode.
35. Explain the concept of Reduction.
Ans. When an atom gains an electron it is said to be reduced.
Cl + le– → Cl–
i. Non metals generally gain electrons to form anions.
O + 2e– → O2–
N + 3e– → N3–
ii. In cases of metals, cations with higher valency will gain electron and form cations of lower valency.
Fe3+ + le– → Fe2+
Ferric Ferrous
iii. In electrolysis reduction takes place at the cathode.
Na+ + le– → Na
Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu
36. What is redox reaction?
Ans. When oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously then the reaction is called as a redox reaction.
It means that an atom loses its electrons if there is an atom to simultaneously gain electrons. Thus the electrons transfer from one atom to another only if both the atom are present in the reaction. Thus they occur simultaneously, that is if one gets oxidized, then the other gets reduced.

F. Properties of Electrovalent and Covalent Compounds
37. Compare the properties of electrovalent compounds and covalent compounds.

ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS
I. Name the following :
1. Force which holds two or more atoms together in a stable molecule.
Ans. Chemical Bond.
2. An atom that has a charge.
Ans. Ion.
3. Type of reaction which results in loss of electrons.
Ans. Oxidation.
4. Conversion of Fe3+ to Fe2+.
Ans. Reduction.
5. Bonding between two atoms due to the transfer of electron
Ans. Electrovalent bond.
6. Pair of electrons not shared with any other atom.
Ans. Lone pair.
7. Electrons that form co – ordinate bond.
Ans. Lone pair of electrons.
8. Examples of polar covalent compound.
Ans. Water, Ammonia, Hydrogen chloride.
9. Example of a non – polar covalent compound.
Ans. Methane, Carbon tetra chloride.
10. Type of bonding between a metal and a non – metal.
Ans. Electrovalent bond.
11. Polar covalent compound which, on dissolving in water, produces ions.
Ans. Hydrogen chloride gas and ammonia gas.
12. The type of bonding present in metallic Chlorides.
Ans. Ionic or electrovalent bonding
13. The types of bonding present in non-metallic Chlorides.
Ans. Covalent bonding
14. The bond formed by the mutual sharing of electrons.
Ans. Covalent bond
15. The bond formed by the transfer of electrons.
Ans. Ionic bond
16. An ion formed by the loss of electron from the neutral atom.
Ans. Cation
17. An ion formed by the gain of electron by the neutral atom.
Ans. Anion
18. Outermost shell of an atom.
Ans. Valence shell
19. The electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom.
Ans. Valence electrons
20. Elements having eight electrons in the outermost shell.
Ans. Inert gases or noble gases
22. The charged particles which attract one another to form electrovalent compounds
Ans. Ions
23. One bivalent anion
Ans. Oxide ion (O2-)
24. One electrovalent compound containing chlorine
Ans. Sodium chloride (NaCl)
25. One compound which contains both ionic and covalent bonds
Ans. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
26. One cation having same electronic configuration to neon
Ans. Sodium ion (Na+)
27. One covalent compound containing chlorine.
Ans. Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)
28. A bond formed by a shared pair of electrons with both electrons coming from same atom.
Ans. Coordinate or dative bond
II. Fill in the Blanks :
1. NaCl is an electrovalent compound formed as a result of _________________ of electrons.
Answer
transfer
2. The reaction in which metals lose electrons is called ______________________.
Answer
oxidation
3. The bond between two halogens is likely to be ______________________.
Answer
covalent
4. In the reaction Cl2 + 2KI 2KCl +2I2 conversion of KI to I2 is ________________.
Answer
oxidation
5. Molecule with three single covalent bonds is ______________________.
Answer
Ammonia or NH3
6. When a molecule of water combines with a hydrogen ion _____________________ is formed.
Answer
hydronium ion
7. Water is an example of ______________________ covalent bond.
Answer
polar
8. There are ______________________ bonds in 1 molecule of oxygen.
Answer
two
9. Nitrogen has ______________________ bond in its molecule.
Answer
triple covalent
10. In a molecule of sodium chloride sodium and chlorine are held together by ____________ force of attraction.
Answer
Electrostatic
11. __________ forces of attraction are present between atoms forming a covalent bond.
Answer
Vander waals
III. Complete the following sentence choosing the correct word from those given in brackets.
a) ……………….is a process by which electrons are removed from an atom or an ion. (Oxidation/Reduction)
Answer
Oxidation
b) The ability of an atom to attract shared electrons is called its…………… (electropositivity/electronegativity)
Answer
Electronegativity
c) Methane is a …………….. compound. (covalent/ionic)
Answer
covalent
d) In forming O2 molecule, …………. electrons are shared by each atom of oxygen. (two/three)
Answer
two
e) An oxidizing agent is …………… of electrons. (an acceptor/a donor)
Answer
an acceptor
f) The ions in …………… compounds are held together by electrostatic forces of attraction. (Covalent, electrovalent)
Answer
Electrovalent
g) In the formation of magnesium chloride magnesium is getting …………… (oxidized / reduced)
Answer
oxidised
h) An element present in group IV A will form a …………… bond with an element present in group VII A (electrovalent, covalent)
Answer
Covalent
IV. Answer the following :
1. What is meant by the term ‘electrovalency’. State why Na [at. no. 11] has a electropositive valency of + 1 and Cl [at. on. 17] an electronegative valency of -1.
Ans. Electrovalency is defined as the number of electrons donated or accepted by the valence shell of an atom of an element to achieve stable electronic configuration. Chlorine [at. no. 17] (2,8,7) has 7 electrons in its valence shell and requires 1 electron to form a stable ion with octet structure. Hence chlorine has electronegative valency of – 1.
Sodium [at. on. 11] (2, 8, 1) has 1 electron in its outermost electronic shell which it loses to form a (octet structure) stable ion. Hence sodium has electropositive valency of + 1.
2. State three differences between ‘X’ and ‘X1+’ i.e. an atom and an ion.
Ans.

3. Give reasons for the following :
(i) Electrovalent compounds are soluble in water.
(ii) Electrovalent compounds are insoluble in organic solvents.
(iii) Electrovalent compounds are good conductors of electricity in molten or aq. solution state.
(iv) Solid Sodium Chloride does not conduct electricity.
(v) Molten Sodium Chloride conducts electricity.
(vi) Sugar solution does not conduct electricity. [2005]
(vii) Ionic compounds have high melting point and boiling point.
(viii)Bond formed in Hydrogen molecule is non-polar covalent bond.
(ix) The rate of reaction of covalent compounds is less compared to electrovalent compounds.
Ans. (i) Water is a polar compound, in which the molecules have the ability to break the bond between atoms of the electrovalent compound. Hence electrovalent compounds are soluble in water.
(ii) Organic solvents are non-polar solvents, in which molecules have no ability to break bonds between atoms of electrovalent compounds. Hence Electrovalent compounds are not soluble in water.
(iii) Electrovalent compounds in molten or aqueous solution have free ions which can carry electric current. Hence electrovalent compounds are good conductors of electricity in molten/aqueous solutions.
(iv) Solid Sodium chloride does not conduct electricity because the oppositely charged ions in Sodium chloride are held by strong electrostatic force of attraction and hence, they are not free to carry electric current.
(v) Molten Sodium chloride conducts electricity because the electrostatic forces of attraction are overcome by the heat energy. Therefore, the ions become free to carry electric current.
(vi) Sugar being a covalent compound does not dissociate into ions in an aqueous solution. Molecules do not conduct electricity. Hence sugar solution does not conduct electricity.
(vii) The constituents of ionic compounds, i.e. oppositely charged particles are held by strong electrostatic forces of attraction therefore large amount of heat is to be supplied to separate the constituents from their lattice. So to melt, it requires high amount of energy.
(viii)The combining elements in hydrogen are identical, i.e. they have no difference in their electronegativity. Hence, the shared pair of electrons lie exactly in the centre of two combining atoms. Therefore, the bond formed is non-polar bond.
(ix) In covalent molecules, bonds have to be broken and new bonds are formed as against electrovalent compounds where free ions are easily formed in different solutions which reunite. Thus, rate of reaction in covalent to electrovalent compounds is slow as compared to electrovalent compounds.
4. Complete the table :

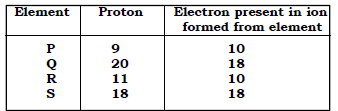
5. Elements A, B, and C have atomic number 8, 10, 13 respectively.
i. Which forms cation?
Ans. C
ii. Which forms anion?
Ans. A
iii. Which one would be inert?
Ans. B
6. An element ‘Q’ has electronic configuration 2, 8, 8, 2.
i. Write the symbol for the ion of (Q).
Ans. Q2+.
ii. Will Q have oxidising or reducing properties? Give reasons.
Ans. Q. would tend to donate its electrons which would be accepted by another element. As gain of electrons is reduction. Q will act as reducing agent (or would have reducing properties)
7. Identify the following equations as oxidation or reduction.

Ans. (i) Reduction (ii) Oxidation
(iii) Reduction (iv) Oxidation
(v) Reduction (vi) Reduction
(vii) Oxidation (viii) Oxidation
(ix) Oxidation (x) Reduction
8. State which of the following are oxidized or reduced.

Ans. (i) Oxidised (ii) Oxidised
(iii) Oxidised (iv) Reduced
(v) Reduced (vi) Reduced
(vii)Reduced (viii) Oxidised
(ix) Oxidised (x) Oxidised
9. a) In the formation of compound XY2, atom X gives one electron to each Y atom.
i) What is the nature of bond in XY2?
ii) Give two properties of XY2.
b) In the following reaction:
Cu2+ + Zn → Cu → Zn2+
Name the:
i) Oxidizing agent.
ii) Substance oxidized.
iii) Substance gaining electrons.
Ans. a) i) The nature of bonding in XY2 is ionic / electrovalent.
ii) The two properties of XY2 are,
1. It is a good conductor of electricity in molten state.
2. It has high melting and boiling points.
b) i) Cu2+ ion ii) Zn iii) Cu2+ ion
10. Choose the kind of chemical bond formed:
a. Ionic bond
b. Covalent bond
c. Ionic and covalent bond
Ans.
a. MgO Ionic bond
b. NH4NO3 Both ionic and covalent bond
c. H2SO4 Both ionic and covalent bond
d. CO2 Covalent bond
e. ZnSO4 Both ionic and covalent
f. H2O Covalent bond
g. PCl3 Covalent bond
h. CCl4 Covalent bond
i. NH4OH Both ionic and covalent
j. CaO Electrovalent bond
k. CH4 Covalent bond
l. N2 Covalent bond
m. NaCl Ionic bond
n. HCl Covalent bond
o. O2 Covalent bond
p. MgCl2 Ionic bond
11. Identify the type of bond expected to form between the pair of elements with the following atomic number. Identify the element and predict their formula also.
(i) 1, 17 (ii) 11, 9
(iii) 6, 1 (iv) 20, 1
Ans.

12. Complete the following :

Ans.

13. Predict the type of bonding in the following :
(i) Ammonia
(ii) Calcium oxide
(iii) Oxygen
(iv) Chlorine
(v) Methane
Ans. (i) Polar covalent bond
(ii) Ionic bond
(iii) Double covalent bond
(iv) Single covalent bond
(v) Non-polar covalent bond
14. An atom X has three electrons more than the noble gas configuration. What type of ion will it form? Write the formula of its
(i) sulphate
(ii) nitrate
(iii) phosphate
(iv) carbonate
(v) hydroxide.
Ans. X will form a cation (X3+)
(i) X2 (SO4)3
(ii) X (NO3)3
(iii) X PO4
(iv) X2 (CO3)3
(v) X (OH)3
15. State the type of bond present in
(i) Non-metallic chloride (ii) Metallic chloride
(iii) Chlorine molecule (iv) Nitrogen molecule
Ans. (i) Covalent bond (ii) Ionic bond / electrovalent
(iii) Non-polar covalent bond (iv) Non-polar covalent bond
16. How many covalent bonds and coordinate bonds are present in
(i) Hydronium ion (ii) Ammonium ion
Ans.


(a) What type of bond is formed between
(i) A and B (ii) C and D
(iii) B and D (iv) Molecule of D
(v) Molecule of C (vi) Molecule of B
(b) What is the formula of the compound formed between
(i) A and B (ii) C and D (iii) B and D
Ans. (a)
(i) Ionic bond or Electrovalent bond
(ii) (Polar) Covalent bond
(iii) (Polar) Covalent bond
(iv) Single covalent bond
(v) Triple covalent bond
(vi) Single covalent bond
(b) (i) AB (ii) CD3 (iii) DB
18. Given below are five atoms.

(i) Which of the above contains 7 protons?
Ans. A
(ii) Which has an electronic configuration of 2, 8, 8, 2?
Ans. E
(iii) Write down the formula of the bond formed between
a) C and D b) B and E
Ans. a) CD b) EB
(iv) Predict which are
(a) Metals
Ans. C, E
(b) Non – metals
Ans. A, B, D
19.(a) Identify the element which forms (i) Cation (ii) anion
(b) Identify the element with complete octet.
(c) What types of bond is formed between Q and P?
(d) Give the formula of the compound formed between Q and P.
Ans. (a) (i) Q and R (ii) P
(b) S
(c) Ionic bond
(d) QP2
20. Five atoms are labelled A to E as follows:

a) Which one of these atoms:
i) contains 7 protons?
ii) has an electronic configuration 2,7?
b) Write down the formula of the compound formed between C and D.
c) Express these atoms as metals and non-metals.
Ans. a) i) E ii) B
b) C2D
c) A-Metal; B-Non-metal; C-Metal; D-Non-metal; and E- Non-metal
21. The atomic numbers of the elements A, B, C, D and E are 11, 17, 16, 12 and 18 respectively. With reference to the above mentioned elements answer the following questions.
(Note – Do not identify the elements)
(i) Give the electronic configuration of A, B, C, D and E.
(ii) How many valence electrons are present in A, B, C, D and E?
(iii) Name the type of ion (if formed) in A, B, C, D and E.
(iv) Identify the type of element.
Ans.

22. An atom X has 2, 8, 7 electrons in its shell. It combines with Y having 1 electron in its outermost shell.
(a) What type of bond will be formed between X and Y?
(b) Write the formula of the compound formed. [2006]
Ans. a) Ionic bond
b) YX
23. An element X is a metal with valency 3. Element Y is a non-metal with a valency 2.
(i) Write equations to show how X and Y form ions.
(ii) If Y is a diatomic gas write equation for the direct combination of X and Y to form compound.
Ans. (i) X – 3e– → X3+
Y + 2e– → Y2–
(ii) 4X + 3Y2 → 2X2Y3
24. An element X is a metal with valency 1. Element Y is a non-metal with valency 2.
(i) Write equations to show how X and Y form ions.
(ii) If Y is a diatomic gas write equation for the direct combination of X and Y to form compound
Ans. (i) X – e– → X+1
Y + 2e– → Y–2
(ii) 4X + Y2 → 2X2Y
25. a) An element C has the electronic configuration 2, 8, 18, 8, 1. Without identifying C:
i) Predict the sign and charge on simple ion of C.
ii) State whether you would expect the element C to be a metal or non-metal.
iii) Write the probable formula and appearance of chloride of C.
iv) Write down the probable formula and solubility of hydroxide of C.
b) Elements A,B and C have atomic numbers 9,20 and 10 respectively.
i) State which one is chemically inert
ii) Write down the formula of the compound formed by two of the above elements.
Ans. a) i) Sign is positive, charge is + 1.
ii) C is a metal
iii) CCl. It would be a crystalline solid.
iv) COH. It will be soluble in organic solvents as well as water.
b) i) C is chemically inert.
ii) The formula of the compound formed by A and B is BA2 .
26. The electronic configuration of atoms of three elements A,B, and C are (2,8,1), (2,8,6) and (2,8,18,7) respectively
a) Write down the formula of the molecule of B and its electron dot diagram. Mention the type of bonding.
b) Write down the formula of the compound formed between A and C and type of bonding.
c) Classify the elements A, B and C as metals and non-metals.
d) Which element is likely to be a good conductor of electricity and why?
Ans. a) The formula of the molecule of B is B2
Electron dot diagram is:
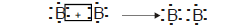
The type of bond in B2 is covalent.
b) AC. The bond involved is ionic.
c) A-Metal; B and C- Non-metals
d) A will be a good conductor of electricity. As it is a metal. it can easily lose its outermost electron.
27. a) Match the atomic numbers 4, 14, 8, 15 and 19 with each of the following:
i) A solid non-metal of valency 3
ii) A gas of valency 2
iii) A metal of valency 1
iv) A non-metal of valency 4.
b) What type of a bond is formed when the non-metallic atoms have high difference of electronegativity?
Ans. a) i) Atomic no. 15 ii) Atomic no. 8
iii) Atomic no. 19 iv) Atomic no. 14
b) Polar covalent bond
28. In the formation of the compound XY2, an atom X gives one electron to each Y atom. What is the nature of bond in XY2? Draw the electron dos structure of this compound.
Ans. Ionic bond is present between XY2
IV] Select appropriate answer from the choices given below :
1. Element M forms a chloride with formula MCl. Which is a solid at room temperature and has high melting point and boiling point. M would be most likely be in the same group as
(i) K (ii) Mg
(iii) Al (iv) C
Answer
(i) K
2. Which of the following have all three types of bonds in its molecule.
(i) Water (ii) Ammonium
(iii) Ammonium chloride (iv) Sodium chloride
Answer
(iii) Ammonium chloride
3. Compound X consists of molecules only in its aqueous solution type of bonding in X will be :
(i) Ionic (ii) electrovalent
(iii) Non-polar covalent (iv) Co-ordinate
Answer
(iii) Non-Polar covalent
4. When a non-metallic atom form its ion
(i) it accepts electrons and is reduced
(ii) it accepts electrons and is oxidized
(iii) it donates electrons and is reduced
(iv) it donates electrons and is oxidized
Answer
(i) it accepts electrons and is reduced
5. Which of the following is not a common characteristic of an electrovalent compound?
(i) High melting point
(ii) Conducts electricity when molten
(iii) Consists of oppositely charged ions
(iv) Ionizes when dissolved in water.
Answer
(iv) Ionizes when dissolved in water
(V) Distinguish between.
(i) Sodium atom and Sodium ion
Ans.

(ii) Chlorine atom and Chloride ion
Ans.
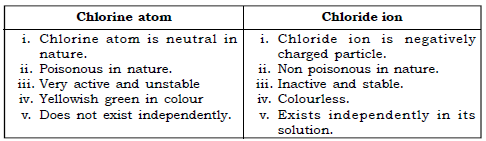
(iii) Ionic Compound and Covalent Compound.
Ans.
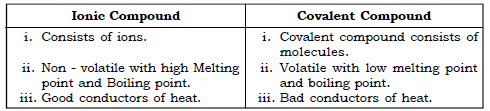
(iv) Non-polar Covalent Compounds and Polar Covalent Compound.
Ans.




