Please refer to Physical Education Class 10 ICSE Handball notes provided below. These revision notes have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination pattern for ICSE Class 10 Physical Education issued for the current academic year. Students should always revise these revision notes prior to their exams to properly prepare and understand all topics. After reading these notes also refer to Sample Papers for Class 10 ICSE Physical Education
ICSE Class 10 Physical Education Handball Revision Notes
Students can refer to the quick revision notes prepared for Chapter Handball in Class 10 ICSE. These notes will be really helpful for the students giving the Physical Education exam in ICSE Class 10. Our teachers have prepared these concept notes based on the latest ICSE syllabus and ICSE books issued for the current academic year. Please refer to Chapter wise notes for ICSE Class 10 Physical Education provided on our website.
Physical Education Class 10 ICSE Handball Notes
➢ Introduction :
Handball also known as team handball is a team sport in which two teams of seven players each (six outfield players and a goalkeeper) pass a ball to throw it into the goal of the other team. A standard match consists of two periods of 30 minutes, and the team that scores more goals wins.
➢World History
The game was originated at the end of the 19th century in Germany by German gymnast Konrad Koch. The first international games were played under these rules for men in 1925 and for women in 1930. Men’s handball was first played at the 1936 Summer Olympics in Berlin as outdoors, and the next time at the 1972 Summer Olympics in Munich as indoors, and has been an Olympics sport since. Women’s team handball was added at the 1976 Summer Olympics.
➢ Indian History
In the history of Handball, it is presumed that the game of Handball was brought to India by Shri J.S. Chauhan of Haryana in 1970. He conducted two all India seminars on Handball at Rohtak in Haryana before the formation of Federation in year 1971-72. Amateur Handball Federation of India (AHFI) was formed in 1972 and got provisional affiliation with International Handball Federation.
➢ Governing Bodies
International Handball Federation (IHF) : IHF is the administrative and controlling body for international teams of handball.


Officials
(a) Referees–2 (b) Timekeeper–1 (c) Scorekeeper–1

➢ Handball Court Marking
(i) Short lines : The shorter ones are called goal lines (between the goalposts) or outer goal lines (on either side of the goal).
(ii) Centre line : The centre line connects the midpoints of the two sidelines.
(iii) Free throw line (9 metre line) : It is a broken line, drawn 3m outside the goal area line. This line should be parallel to the goal line.
(iv) 7- metre line or penalty line : It is a 1m long line directly in front of the goal. It is parallel to the goal line and 7m away from it (measured from the rear edge of the goal line to the front edge of the 7m line).
(v) Goalkeeper ’s restraining line (4- Metre line) : It means that beyond this area only the goal keeper can go. It is a 15cm long line directly in front of the goal. It is parallel to the goal line and 4m away from it (measured from the rear edge of the goal line to the front edge of the 4m line).
(vi) Substitution line : The substitution line is the place from where the player is substitution takes place and the line for each team extends from the centre line to a point at a distance of 45m from the centre line.
➢ Basic Rules of the Game
(i) The game begins by giving the pass to another player from the centre line.
(ii) A player may be changed at any time during the game.
(iii) Each team has the right to receive a single 1-minute team time-out in each half of the regular playing time, but not in overtime.
(iv) In the case of an injury to a player, the game may be stopped at any time on the instructions of the referee and the injured player may be replaced by the other player.
(v) In the game, running while holding the ball is not allowed.
(vi) If ball goes out of court during the game, the opposing team shall be given a throw from the same place.
(vii) A goal keeper shall not go out through the outer “D”.
(viii)The team that scores maximum goals shall be considered the winner.
(ix) A referee may turn a player out of the game for two minutes after giving two warnings.
(x) No other person except the goal keeper shall enter the goal area.
(xi) A goal scored from inside the “D” (i.e. 6m line) shall not be considered.
➢ Throws Used In The Game
(i) Throw-off : A throw-off is used to start play at the beginning of each half or after a goal has been scored.
(ii) Throw-in : A throw-in is awarded when ball goes out of bounds on the sideline or when the ball is last touched by a defensive player (excluding the goal line) and goes out of bounds over the endline. The throw- in is taken from the spot where the ball crossed the sideline, or if it crossed the endline, from the nearest corner. The thrower must place one foot on the sideline to execute the throw. All opposing players must stay 3m away from the ball.
(iii) Free-throw : For a minor foul or violation, a free-throw is awarded to the opponent at the exact spot it took place. If the foul or violation occurs between the goal area line and the 9m line, the throw is taken from the nearest post outside the 9m line. The thrower must keep one foot in contact with the floor, then pass or shoot.
(iv) Goalkeeper-throw : The goalkeeper throws the ball back in bounds after he or an opposing player has knocked the ball over the backline.
(v) 7-metre throw / penalty throw : A penalty throw is a throw awarded when there is an infringement in any part of the court and spoils a clear chance of scoring.
(vi) Referee throw : A referee throw is awarded when the ball touches anything above the court after a simultaneous infringement of the rules or after simultaneous possession of the ball.
(vii) Corner throw : A corner throw is awarded when a defender, other than the goalkeeper, has knocked the ball over the backline. The team on offense throws the ball back in bounds from a corner closest to where the ball went out of bounds.
➢ Punishments
Fouls such as reaching around, holding, pushing, hitting, tripping and jumping into an opponent are to be punished progressively.
(i) Warnings (yellow card) : The referee gives only one warning to a player for rule violations and a total of three to a team. Exceeding these limits results in 2-minute suspensions thereafter.
(ii) Disqualification and exclusion (red card) : A disqualification is the equivalent of three 2-minute suspensions.
A disqualified player must leave court and bench, but the team can replace player after the 2-minute suspension expires.
➢ Fundamentals Skills of Handball
(i) Holding and catching the ball
(ii) Throw the ball
(iii) Pass the ball
(a) Bounce pass
(b) Hook pass
(c) Chest pass
(d) Overhead pass
(e) Jump pass
(f) Shoulder pass
(g) Side arm pass
(iv) Dodge
(v) Dribble
(a) Low dribble and
(b) High dribble
(vi) Shot
(a) High jump shot and long jump shot.
(b) Dive shot
(c) Underhand shot
(d) Reverse shot
The brief explanation of some of the fundamental skills is given below :
➢ Shot
(i) Jump shot : A shot attempted while leaping.
(ii) Dive shot : The player stretches the body out and directs the momentum towards the goal. The ball should be released at the last possible moment by taking a dive.
➢ Pass the Ball
(i) Hook pass : It is used when a player is in the air for a jump shot. The ball is simply released, while at the top of the jump, to his/her teammate, who is expected to penetrate towards the goal.
(ii) Chest pass : The chest pass is used frequently in handball. It is a short distance pass. This pass is the most accurate pass. Generally, it is given by both hands.
(iii) Bounce pass : In bounce pass, the ball should be thrown in such a way that it should bounce towards the teammate. It should bounce approximately three feet in front of the receiver.
➢ Dribble
To move the ball by bouncing it on the floor.
➢ Terminology Related To Handball
(i) Fast- Break : When the defence gains possession of the ball because of blocked shot, interception or rule violations, the team is at that moment in a position to begin a fast break.
(ii) Double-dribble : A player may run three steps, dribble any number of times, pick the ball up and run three more steps. If the player dribbles again after the last sequence of steps, it is called double dribble.
(iii) Screen : It means the players of the serving team must not prevent their opponents from seeing the ball.
(iv) Line cut : When the ball crosses the goal line, opponent team player throws the ball inside the field without touching the goal line. If he touches the line then it is called a line cut.
(v) Court Player/Field Player : Any player on the court except the goalkeeper.
(vi) Free Kick : When the ball strikes the hand or arm of a player and the referee deems that a player has deliberately handled the ball, a direct free-kick will be awarded to the opposing team.
(vii) Running : If a player moves more than three steps while holding the ball in his hand, he is called for running.
(viii)Passive play : It is illegal to keep the ball in a team’s possession without making a recognizable attempt to attack and to try to score. In other words, a team cannot stall (free-throw awarded to the other team).
(ix) Fault : A fault is illegally served ball.
➢ Important Tournaments and Venues
International Tournaments
(i) World championship
(ii) World games
(iii) Men’s youth world
(iv) Olympic Games
(v) Super Globe
(vi) Asian Games
(vii) SAP Games
➢ National Tournaments
(i) Federation Cup
(ii) Inter-university handball championship
(iii) School national
(iv) National championship
➢ Sports Awards

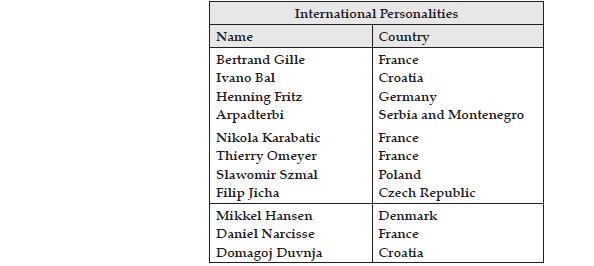
➢ Sports Personalities