Students of ICSE Class 10 should refer to Study of Compounds Hydrogen Chloride ICSE Class 10 Chemistry board year questions and solutions. below which have come in past board exams. You should always go through questions that have come in previous years. This will help you to understand the pattern of questions in ICSE Class 10 Chemistry and prepare accordingly. This will help you to get better marks in ICSE Class 10 Board Exams
ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Study of Compounds Hydrogen Chloride Board Exam Questions
Students should learn the important questions and answers given below for Chapter Study of Compounds Hydrogen Chloride in Chemistry for ICSE Class 10. These board questions are expected to come in the upcoming exams. Students of ICSE Class 10th should go through the below board exams questions and answers which will help them to get more marks in exams.
Board Exam Questions Study of Compounds Hydrogen Chloride ICSE Class 10 Chemistry
Multiple Choice Questions
Question. An aqueous solution of HCl gas is named.
(a) Aqua fortis
(b) Aqua regia
(c) Oil of vitriol
(d) Muriatic acid
Answer
D
Question. An acid which is not a monobasic acid.
(a) HNO3
(b) HCOOH
(c) H2SO4
(d) HCl
Answer
C
Question. An acid which is not an oxidising agent.
(a) H2SO4
(b) HCl
(c) HNO3
(d) CH3COOH
Answer
B
Question. Hydrogen chloride gas being highly soluble in water is dried by :
(a) Anhydrous calcium chloride
(b) Phosphorous penta oxide
(c) Quick lime
(d) Concentrated sulphuric acid
Answer
D
Question. A substance which reacts with conc. HCl to liberate chlorine :
(a) PbO
(b) PbCl2
(c) PbO2
(d) Pb3O4
Answer
C
Question. A metal which reacts with dil HCl to liberate hydrogen.
(a) Zn
(b) Cu
(c) Ag
(d) Pb
Answer
A
Question. Gas liberated when dil. HCl gas is added to iron (II) sulphide.
(a) Hydrogen gas
(b) Chlorine gas
(c) Hydrogen sulphide gas
(d) Carbon dioxide gas
Answer
C
Question. Gas liberated when hydrochloric acid reacts with galena.
(a) Sulphur dioxide
(b) Carbon dioxide
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Hydrogen sulphide
Answer
D
Question. The gases which react chemically to form a solid :
(a) H2(g) and Cl2(g)
(b) NH3(g) and HCl(g)
(c) CO2(g) and SO2(g)
(d) NO2(g) and CO2(g)
Answer
B
Question. Constant boiling mixtures are known as :
(a) Constant compounds
(b) Woulfe’s compound
(c) Distillators
(d) Azeotropes
Answer
D
Question. Aqua regia is a mixture of :
(a) Dilute hydrochloric acid and concentrated nitric acid
(b) Concentrated hydrochloric acid and dilute nitric acid
(c) Concentrated hydrochloric acid [1 part] and concentrated nitric acid [3 parts]
(d) Concentrated hydrochloric acid [3 parts] and concentrated nitric acid [1 part]
Answer
D
Question. The aim of the fountain experiment is to prove that :
(a) HCl turns blue litmus red
(b) HCl is denser than air
(c) HCl is highly soluble in water
(d) HCl fumes in moist air
Answer
C
Give One Word/Chemical Term
Question. The gas obtained when rock salt reacts with conc. sulphuric acid.
Answer
Hydrogen chloride gas
Question. Give the name of a chemical, which on being added to sodium chloride, will produce hydrogen chloride gas.
Answer
Conc. sulphuric acid
Question. Name the experiment use for the density of hydrogen chloride.
Answer
Fountain experiment
Question. Drying agent for hydrogen chloride gas.
Answer
Concentrated sulphuric acid
Question. Compound which cannot be used to dry hydrogen chloride gas.
Answer
Quick lime, CaO
Question. A polar covalent compound which on dissolving in water produces ions.
Answer
Hydrogen chloride gas
Question. The experiment which demonstrates extreme solubility of hydrogen chloride gas.
Answer
Fountain experiment
Question. A compound formed when iron reacts with hydrogen chloride.
Answer
Iron (II) chloride
Question. Name one lead compound that can be used to oxidise HCl to chlorine.
Answer
Lead dioxide or Red lead
Question. The gas evolved when Mangnese (IV) oxide and concentrated hydrochloric acid are heated.
Answer
Chlorine (Cl2).
Question. Two colourless gases, when mixed, form white dense fumes. Name the two gases and white dense fumes.
Answer
Two gases : hydrogen chloride and ammonia. White dense fumes : ammonium chloride
Question. A gas evolved when HCl is added to red lead.
Answer
Chlorine
Question. Two compounds of lead which combine with conc. HCl to liberate chlorine.
Answer
Lead dioxide and red lead (Pb3O4)
Question. A substance which reacts with conc. HCl to liberate chlorine.
Answer
PbO2
Question. The colour of a gas evolved when conc. hydrochloric acid is heated with manganese dioxide.
Answer
Greenish yellow
Question. A gas evolved when metal carbonates reacts with hydrogen chloride.
Answer
Carbon dioxide, CO2
Question. An acid which is not an oxidising agent.
Answer
Hydrogen chloride, HCl
Question. A mixture of three parts of conc. HCl and one part of conc. nitric acid.
Answer
Aqua regia
Question. Name chemical in which gold can be dissolved.
Answer
Aqua regia
State the Observation
Question Hydrogen chloride gas is passed through silver nitrate solution.
Answer
A white precipitate is formed which is soluble in excess of ammonium hydroxide.
Question Hydrogen chloride gas comes in contact with ammonia solution.
Answer
Dense white fumes are observed.
Question. Hydrogen chloride gas is passed through lead nitrate solution and the product thus formed is heated.
Answer
A white precipitate is formed which gets dissolved on heating.
Question. A few drops of dilute hydrochloric acid are added to silver nitrate solution followed by addition of ammonium hydroxide solution.
Answer
- A white precipitate of silver chloride (AgCl2) is formed which dissolves in excess of
NH4OH.
QuestionDilute hydrogen chloride is added to lead nitrate solution.
Answer
- A white precipitate of lead chloride (PbCl2) is obtained. It is insoluble in cold water but
soluble in hot water.
Question Copper sulphide is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Answer
Rotten egg smell of hydrogen sulphide (H2S) gas will be given out.
Question Manganese dioxide is treated with concentrated hydrochloric acid.
Answer
- Black coloured manganese dioxide on reacting with conc. hydrochloric acid gives light
brown coloured solution with the evolution of greenish yellow coloured gas.
Question Copper oxide is treated with conc. hydrochloric acid.
Answer
- Black coloured copper oxide on reacting with conc. hydrochloric acid gives blue coloured
solution with the evolution of greenish yellow coloured gas which turns moist starch
iodide paper blue black, turns moist blue litmus to red and finally bleaches it to white.
Question Magnesium strip is dropped in dil. hydrochloric acid.
Answer
- Magnesium metal slowly dissolves with the evolution of a colourless and odourless gas
which burns off with a popping sound.
Question When platinum is added to a solution of aqua regia.
Answer
Platinum dissolves in the solution of aqua regia.
Question. Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to copper carbonate.
Answer
When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to copper carbonate, a brisk effervescence is seen due to the evolution of CO2, with the formation of copper chloride.
CuCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) ⎯→ CuCl2(aq) + H2CO3(aq)
⎯→ CuCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
Question Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to sodium thiosulphate.
Answer
Sodium thiosulphate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce sodium chloride, gas of sulphur dioxide, water and sulphur in a yellow solid form.
Na2S2O3 + 2HCl ⎯→ 2NaCl + S + H2O + SO2
Balancing/Writing the Chemical Equations
(a) Write balanced equations for the reaction of dilute hydrochloric acid with each of the following :
1. Iron
Answer
Fe + 2HCl ⎯⎯→ FeCl2 + H2
(Dil.)
2. Sodium hydrogen carbonate
Answer
NaHCO3 + HCl ⎯⎯→ NaCl + H2O + CO2
(Dil.)
3. Iron(II) sulphide
Answer
FeS + 2HCl ⎯⎯→ FeCl2 + H2S
(Dil.)
4. Sodium sulphite
Answer
Na2SO3 + 2HCl ⎯⎯→ 2NaCl + SO2 + H2O
(Dil.)
5. Sodium thiosulphate solution
Answer
Na2S2O3 + 2HCl ⎯⎯→ 2NaCl + H2O + SO2 + S↓
(Dil.)
6. Calcium bicarbonate
Answer
Ca(HCO3)2 + 2HCl ⎯⎯→ CaCl2 + 2H2O + 2CO2↑
(Dil.) Calcium
chloride
7. Calcium carbonate
Answer
CaCO3 + 2HCl ⎯⎯→ CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
8. Sodium hydroxide
Answer
NaOH + HCl ⎯⎯→ NaCl + H2O
9. Zinc metal
Answer
Zn + 2HCl ⎯⎯→ ZnCl2 + H2
10. Potassium permanganate
Answer
2KMnO4 + 16 HCl ⎯⎯→ 2KCl + 2NaCl2 + 8H2O + 5Cl2(g)
11. Red lead heated
Answer
Pb3O4 + 8HCl ⎯⎯→ 3PbCl2 + 4H2O + Cl2(g)
(Conc.)
12. Magnesium metal
Answer
Mg + 2HCl (g) ⎯⎯→ MgCl2 + H2(g)
13. Ammonium hydroxide.
Answer
NH4OH + HCl ⎯⎯→ NH4Cl + H2O
Ammonium
hydroxide
14. Magnesium sulphite.
Answer
MgSO3 + 2HCl ⎯⎯→ MgCl2 + SO2 + H2O
Magnesium
sulphite
15. Sodium hydrogen sulphide.
Answer
NaHS + HCl ⎯⎯→ NaCl + H2S (g)
Sod. hydrogen
sulphide
16. Manganese dioxide.
Answer

Chemical Tests
1. Manganese dioxide and copper(II) oxide.
Answer
When conc. hydrogen chloride is added to manganese dioxide, greenish yellow gas (Cl2) is liberated.
MnO2 + 4HCl ⎯→ MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2 ↑
(Conc.) Greenish
yellow gas
When conc. hydrogen chloride is added to copper(II) oxide, no gas is liberated but the solution turns bluish because of the formation of copper chloride.
CuO + HCl ⎯Δ→ CuCl2 + H2O
(Conc.) Greenish
blue solution
2. Hydrogen chloride gas and carbon dioxide gas.
Answer
When hydrogen chloride gas is passed into silver nitrate solution, it forms a curdy white precipitate of silver chloride.
HCl + AgNO3 ⎯→ AgCl ↓ + HNO3
Curdy
white ppt.
When carbon dioxide gas is passed into lime water, it forms a milky white precipitate of calcium carbonate.
CO2 + Ca(OH)2 ⎯→ CaCO3 + H2O
Milky white
ppt.
3. Give three tests for HCl gas.
Answer
(i) When a glass rod dipped in ammonia, solution is held near the vapours of the acid, it form a dense white fumes of ammonium chloride.
(ii) When hydrochloric acid is treated with silver nitrate solution, it forms curdy white precipitate which is soluble in excess of ammonium hydroxide solution.
(iii) When hydrochloric acid is boiled with manganese dioxide, greenish yellow chlorine gas is evolved.
Reasoning Based Questions
Q. 1. Mixture of sodium chloride and concentrated sulphuric acid does not heated above the temperature of 170°C while preparing hydrogen chloride. Why ?
Answer
The mixture of sodium chloride and concentrated sulphuric acid is not heated above 170°C in preparing hydrogen chloride gas because at a higher temperature sodium sulphate is formed which is a hard substance and difficult to remove from the reaction flask.
2NaCl + H2SO4 ⎯→ Na2SO4 + 2HCl
Q. 2. Hydrogen chloride gas cannot be dried over quick lime. Why ?
Answer
Hydrogen chloride gas cannot be dried over quick lime because quick lime is basic in nature and combines with moist hydrogen chloride gas forming calcium chloride.
Q. 3. Quick lime and phosphorus pentaoxide cannot be used for drying hydrochloric acid gas. Why ?
Answer
Quick lime and phosphorus pentaoxide cannot be used for drying HCl gas, because both reacts with HCl.
CaO + 2HCl ⎯→ CaCl2 + H2O
2P2O5 + 3HCl ⎯→ 3HPO3 + POCl3
Q. 4. Hydrogen chloride is not collected over water. Why ?
Answer
Hydrogen chloride is not collected over water because it is highly soluble in water.
Q. 5. When the stopper of a bottle full of hydrogen chloride gas is opened there are fumes in the air ?
Answer
When the stopper of a bottle full of hydrogen chloride gas is opened there are fumes in the air because hydrogen chloride gas has an affinity for water, hence, when the stopper is opened it immediately reacts with water vapour present in the atmosphere which leads to the formation of fumes.
Q. 6. Dilute hydrochloric acid cannot be concentrated by distilling (boiling) the dilute acid. Why ?
Answer
When dilute hydrochloric acid is distilled, a constant boiling mixture containing 20 – 24% of hydrochloric acid distills over unchanged at 760 mm Hg pressure. This constant boiling mixture cannot be separated into its constituents by simply distilling.
Q. 7. Anhydrous HCl is a poor conductor while aqueous HCl is an excellent conductor. Why ?
Answer
Anhydrous HCl is a poor conductor while aqueous HCl is an excellent conductor because anhydrous HCl does not contain any free ions. But when HCl is dissolved in water, it
dissociates into hydronium ion (H3O+) and chloride ion (Cl–). Due to the presence of free ions, aqueous solution of HCl conducts electricity.
Q. 8. Sodium is not used to prepare hydrogen from hydrochloric acid (or any other acid). Why ?
Answer
Sodium is not used to prepare hydrogen from acids because sodium metal is highly reactive.
So, the reaction with acids is much exothermic and there are more chances of explosion. It is also very dangerous to handle sodium metal.
Q. 9. Silver nitrate crystals are dissolved in distilled water and not in tap water in order to prepare a solution of silver nitrate as a laboratory reagent. Why ?
Answer
Tap water always contains some amount of dissolved sodium chloride. Thus when the solution of silver nitrate is prepared in tap water, it reacts to form curdy white precipitate of silver chloride.
AgNO3 + NaCl ⎯→ AgCl + NaNO3
Q. 10. Water for drinking purpose and in swimming pools, is treated with chlorine. Give reason.
Answer
Water for drinking purpose and in swimming pools is treated with chlorine because it sterilises the water. Due to its strong oxidizing action, it destroys bacteria, fungus and other microorganisms.
Short Answer
Q. 1. (i) State one condition under which chlorine and hydrogen react to form hydrogen chloride gas.
(ii) Give balanced chemical equation for the above reaction.
(iii) Name the gas which is a covalent compound but becomes electrovalent when dissolved in water ?
(iv) For which gas, ammonia fountain experiment can be used ?
Answer
(i) Presence of diffused sunlight.
(ii) H2 + Cl2 ⎯→ 2HCl
(iii) Hydrogen chloride (HCl) gas.
(iv) Hydrogen chloride gas.
Q. 2. A colourless gas G fumes strongly in the air. The gas gives dense white fumes when a glass rod dipped in ammonia solution is held near the gas.
Answer the following questions :
(i) Name the gas G.
(ii) Name two chemicals used in the preparation of the gas G.
(iii) Write the chemical equations for the reaction of the chemicals named in (ii) when :
(a) The reaction mixture is not heated.
(b) The reaction mixture is heated above 100°C.
(iv) Why does the gas G fume strongly in air ?
(v) Why does the gas G form dense white fumes with ammonium hydroxide ?
Answer
(i) The gas G is hydrogen chlorine gas.
(ii) The chemicals are (i) sodium chloride, (ii) concentrate sulphuric acid.
(iii) (a) NaCl + H2SO4 (conc.) ⎯⎯→ NaHSO4 + HCl (g)
(b) NaCl + NaHSO4 Heat⎯→ Na2SO4 + HCl (g)
(iv) It is because the HCl gas is extremely soluble in water. Thus, the gas dissolves in water vapour present in the air to form tiny droplets of hydrochloric acid, which appear in the form of fumes.
(v) The HCl gas reacts with vapours of ammonium hydroxide to form very fine solid particles of ammonium hydroxide which are white in colour. These white particles of solid ammonium hydroxide appear in the form of white fumes.
Q. 3. (i) How will you dry HCl acid gas.
(ii) Give three tests of hydrogen chloride.
(iii) Which two colourless gases combine to form a white solid.
Answer
(i) HCl gas can be dried by passing it over conc. H2SO4, which acts as a powerful dehydrating agent.
(ii) Tests for hydrogen chloride.
(1) It gives dense white fumes with a rod dipped in NH4OH solution.
(2) It produces white ppt. with AgNO3 solution.
AgNO3 + HCl ⎯→ AgCl ↓ + HNO3
White ppt.
(3) It turns moist blue litmus red.
(iii) NH3 and HCl gases combine to form a white solid NH4Cl
NH3 + HCl ⎯→ NH4Cl
Gas Gas Solid
Q. 4. (i) (a) What must be added to sodium chloride to obtain hydrogen chloride ?
(b) Write the equation for the reaction which takes place in (a) (i) above.
(c) What would you see when hydrogen chloride is mixed with ammonia ?
(ii) Hydrogen chloride dissolve in water forming an acidic solution :
(a) Name the experiment which demonstrates that hydrogen chloride is very soluble in water.
(b) Give three distinct tests (apart from using an indicator) you would carry out with this solution to illustrate the typical properties of an acid.
Answer
(i) (a) Concentrated sulphuric acid.
(b) NaCl + H2SO4
(c) When aqueous solution of ammonia is taken in the jar of hydrogen chloride, it forms dense white fumes of ammonium chloride.
NH3 + HCl ⎯⎯→ NH4Cl
(ii) (a) Fountain experiment.
(b) An acid reacts with :
(1) Metal carbonates and bicarbonates with effervescence to liberate CO2.
(2) Acids react with metal sulphides to liberate H2S gas which has smell of rotten eggs.
(3) Acids react with metal sulphites to liberate SO2 gas.
Q. 5. (i) (a) Name the oxidising agent in the reaction between Manganese dioxide and conc. hydrochloric acid.
(b) State your observation when a rod dipped in ammonium hydroxide solution is brought near a gas jar containing hydrogen chloride gas.
(ii) Manganese (IV) oxide, lead (IV) oxide and red lead (Pb3O4) react with concentrated hydrochloric acid liberating chlorine.
(a) What is the common property being shown by these metal oxides ?
(b) Write the equation for the reaction of concentrated hydrochloric acid with Pb3O4.
(c) What kind of compound can be added to bleaching powder to obtain chlorine ?
Answer
(i) (a) Manganese dioxide acts as an oxidising agent.
(b) Dense white fumes appear in the jar on account of formation of fine particles of ammonium chloride which get suspended in the gas.
(ii) (a) Oxidizing agents
(b) Pb3O4 + 8HCl ⎯→ 3PbCl2 + 4H2O + Cl2
(c) Dilute acid (Hydrochloric acid)
Q. 6. Answer the following questions, stating your answer only to compounds in the following list :
Silver nitrate, hydrochloric acid, chlorine, ammonia, bleaching powder.
(i) What is water sterilizer ?
(ii) Which compound forms curdy white precipitate with hydrogen chloride ?
(iii) Name the gas which produces dense white fumes with ammonia, write the balanced chemical equation.
Answer
(i) Chlorine is water sterilizer.
(ii) Silver nitrate and hydrochloric acid forms white ppt.
AgNO3 + HCl ⎯→ AgCl + HNO3
White ppt.
(iii) Hydrogen chloride (HCl)
NH3 + HCl ⎯→ NH4Cl (Dense white fumes)
Q. 7. (i) When moist chlorine reacts with hydrogen sulphide, two products are formed :
(a) A gas which fumes in moist air
(b) A yellow solid
Name these products.
(ii) What type of reaction is taking place when chlorine acts as a bleaching agent ?
Answer
(i) (a) Hydrogen chloride gas
(b) Sulphur
(ii) Oxidation reaction.
Q. 8. From the gases–ammonia, hydrogen chloride, hydrogen sulphide, sulphur dioxide. Select the following :
(i) The gas which gives a white precipitate when reacted with silver nitrate solution acidified with dilute nitric acid.
(ii) A solution of hydrogen chloride in water is prepared. The following substances are added to separate portions of the solution.
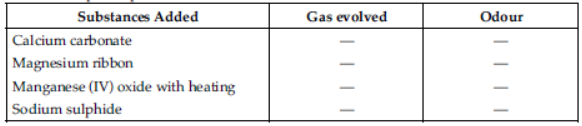
Complete the table by writing the gas evolved in each case and its odour.
Answer
(i) Hydrogen chloride

Q. 9. What is aqua regia ? How does it help in dissolving gold or platinum.
Answer
A mixture of 1 part of conc. nitric acid and 3 parts of conc. hydrochloric acid by weight is called aqua regia.
The conc. HCl and conc. HNO3 reacts to form nascent chlorine which reacts with gold or platinum to form their respective soluble chlorides.
HNO3 + 3HCl ⎯→ 2H2O + NOCl + 2 (Cl)
(Conc.)
Au + 3[Cl] ⎯→ AuCl3
Gold(II) chloride
Pt + 4 [Cl] ⎯→ PtCl4
Platinium(IV) chloride
Q. 10. State three uses of hydrochloric acid.
Answer
(i) It is used in the manufacture of silver chloride, which is used widely in photography.
(ii) It is used in the manufacture of dyes, drugs and paints.
(iii) It is used for cleaning metal surface before painting, electroplating, galvanising, soldering etc.



