Students can refer to Banking ICSE Class 10 notes and exam questions provided for ICSE students. This is an important chapter in ICSE commercial studies class 9. We have provided here questions and answers which are expected to come in the upcoming ICSE exams for class 10th. Prepared based on the latest examination pattern and guidelines issued by ICSE. You can also refer to ICSE Books in pdf available for the latest academic session.
ICSE Class 10 Commercial Studies Banking Important Questions
Students should learn the important questions and answers given below for Chapter Definitions From Topo Maps in Commercial Studies for ICSE Class 10. These board questions are expected to come in the upcoming exams. Students of ICSE Class 10th should go through the Important questions and answers ICSE Class 10 Commercial Studies which will help them to get more marks in exams.
Board Exam Questions Banking ICSE Class 10 Commercial Studies
Question: Name the central bank of our country.
Ans. The Reserve Bank of India is the central bank of our country.
Question: What are the two main functions of a commercial bank?
Ans: The two main functions of a commercial bank : Receive deposit & provide loan, Overdraft, cash credit
Question: Give two major functions of the central bank of our country.
Ans. Receiving deposit and Providing loans are the two major functions of the central bank of our country.
Question: What is meant by an overdraft facility given by a commercial bank ?
Ans. A customer who has a current account with the bank can withdraw more than the amount standing to his credit upto a specified limit. This is a temporary arrangement on which interest is charged by the bank. It may be allowed on the security of assets or on personal guarantee.
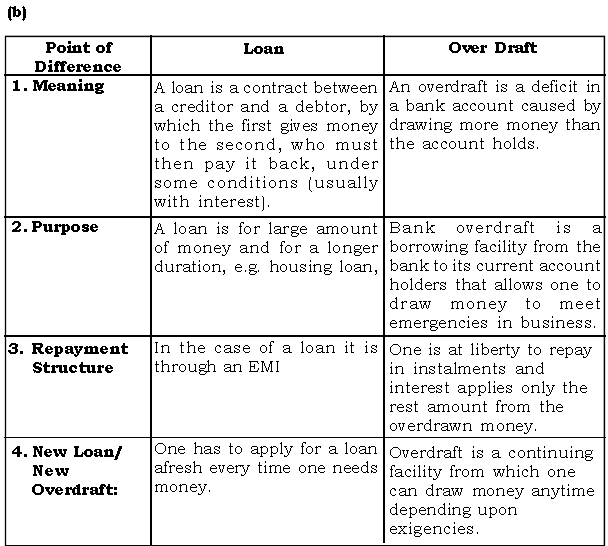
Question: Distinguish between :
(a) Postal Order and Money Oorder.
(b) Loan and Over Draft.
(c) Credit Transfer and Direct Debit
Ans. (a)


Question: “A central bank is a bankers’ bank”. Explain.
Ans. The central bank acts as a banker to all the commercial banks in the country. As a banker’s bank, the central bank provides short-term loans and bill discounting facilities to commercial banks. It also advises the commercial banks on various matters relating to their business. Commercial banks are required to keep a certain proportion of their deposits in the form of cash reserves with the central bank. These reserves enable the central bank to exercise control over credit by commercial bank.
Question: State two agency functions performed by commercial banks.
Ans. Commercial bank serves as an agent for its customers in the following ways :
(a) Collects cheques, bills, dividends, interest, rent, etc., on behalf of customers.
(b) Pays cheques, bills, rent, taxes, interest, insurance, premium, fees, subscriptions, etc., on behalf of customers.
Question: What is meant by clearing house function of the RBI?
Ans. It settles the claims of commercial banks through a process of book entries. The daily balances between the commercial banks can easily be adjusted by means of debit and credit entries in their respective accounts with the central bank.
Question: Name the largest Commercial Bank of India.
Ans. State Bank of India is the largest Commercial Bank of India.
Question: What is Pass Book?
Ans. A Pass Book is a book issued by the bank to its customer. As the book passes from banker to customer, it is known as pass book. A pass book is issued when a bank account is opened. It contains entries relating to the deposits and withdrawals made by the customer from his bank account. The pass book contains a true copy of the customer’s account as it appears in the bank’s ledger. Whenever the customer deposits cash/ cheques or earns some interest, a credit entry is made in the pass book. A debit entry is made whenever the customer withdraws money from his account. At regular intervals the customer sends the pass book to the banker and entries are recorded. The balance to the customer’s account is shown on specified dates.
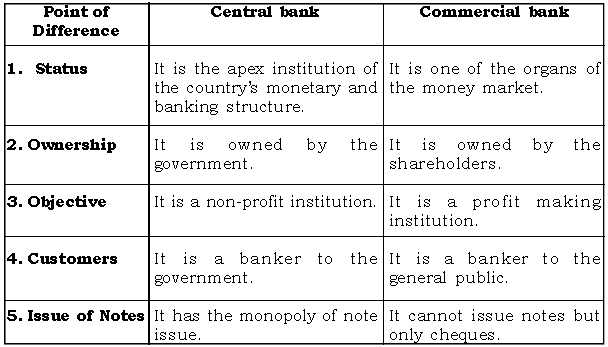
Question: Mention any five differences between a commercial bank and the central bank of a country.
Ans.

Question: What is ATM?
Ans. ATM stands for Automatic Teller Machines.
Question: Give two benefits of payment by cheques.
OR
State two advantages of cheque system.
Ans: Payment through cheques offers the following benefits :
(i) Money can be sent from one place to another easily and at a very nominal cost.
(ii) The need for counting and carrying the money is avoided.
Question: Give one purpose of crossing a cheque?
OR
What is the purpose of crossing a cheque?
Ans. Crossing of cheques offers the following advantages:
(a) It prevents the payment of the cheque to a wrong person.
(b) It assures safe payment of money to the genuine holder.
Question: Distinguish between Cheque and Demand Draft.
Ans.

Question: What is Bank Draft?
Ans: A Bank draft is a type of cheque. It is drawn by a bank either on its own branch or on another bank. Therefore, it is also called “banker’s cheque.” Bank draft is a very convenient, cheap and safe method of remitting money from one place to another. In order to remit money through a bank draft, a person first obtains the bankdraft from the bank.
Question: Name one development bank.
Ans. Industrial Development Bank of India.
Question: What is Banking?
Ans: Banking means the accepting, for the purpose of lending or investment, of deposits of money from the public, repayable on demand or otherwise, and withdrawal by cheque, draft, order or otherwise.
Question: What is the term used for a cheque that can be encashed across the counter of the bank?
Ans. Bearer cheque is the term used for a cheque that can be encashed across the counter of the bank.
Question: What is Traveller’s Cheque? What are its advantages ?
Ans: A travellers’ cheque is a credit instrument issued by a bank. It is made out in the form of circular note on a printed form. Each cheque has a definite sum printed as its value. It bears the signatures of an authorised official of the issuing bank and specimen signatures of the holder. A commission is charged for issuing travellers’ cheques. The holder of a travellers’ cheque can obtain cash from the agents or branches of the bank at different places. The holder will sign the cheque and surrender it and his signatures given on the cheque are verified. The agent or branch will pay cash to the holder. Travellers’ cheques are not technically negotiable instruments. However, they enjoy a very wide acceptance and are often used in the settlement of debts.
Question: Explain five differences between a central bank and commercial bank.
Ans.
Question: What is Cheque?
Ans: A cheque is an unconditional order in writing, drawn and signed by a customer on his bank, requesting the bank to pay on demand the specified amount of money to the person named therein or to his order or to the bearer of the instrument.
Question: Mention two essentials of a cheque.
Ans: The two essential features of a cheque are as follow:
(i) A cheque is a written document.
(ii) It is an unconditional order to pay.
Question: What is the effect of crossing a cheque?
Ans. Crossing means drawing up of two parallel transverse lines on the face of a cheque with or without the words ‘& CO’., ‘Not Negotiable’, ‘A/c Payee only’, etc. The particular bank from where the payment should be made is not mentioned.
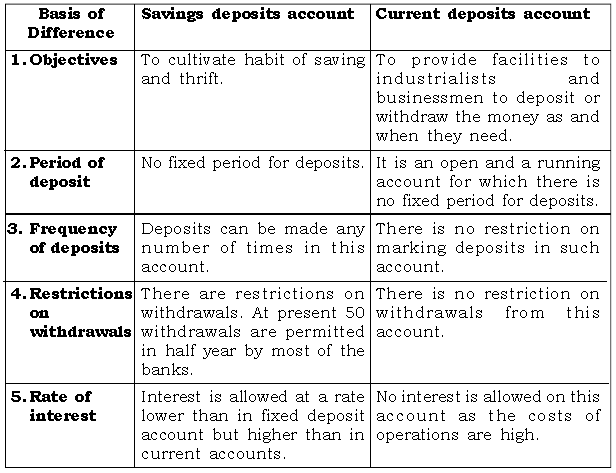
Question: Differentiate between
(i) Savings Deposit and Current Deposit
(ii) Fixed Deposit and Recurring Deposit
Ans. (i) Savings Deposit and Current Deposit
(ii) Fixed Deposit and Recurring Deposit.
Ans.

Question: What is a post-dated cheque?
Ans. It is a cheque bearing some future date. The payment of such a cheque cannot be obtained before the date mentioned in it.
Question: Order cheques are the safer mode of payment then bearer cheques. Justify.
Ans. Order cheques are a safer mode of payment because unlike bearer cheques they cannot be encashed directly on the bank counter. Order cheques require endorsement in favour of the payee.
Question: What is a RTGS ?
Ans. Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) is an electronic system of inter bank transfer of funds involving Rs. 2 lac and above.
Question: What is a negotiable instrument drawn by a person and requiring acceptance of another person called?
Ans. A negotiable instrument drawn by a person and requiring acceptance of another person is called cheque.
Question: Give two credit facilities provided by banks to the traders.
Ans. (i) Loans and Advances : A specified amount is granted for a specified time period. The borrower may withdraw the entire amount in lumpsum or in installments.
(ii) Cash Credit : Under this arrangement, the bank allows the borrower to borrow up to a specified limit. The amount is credited to the account of the customer.
Question: Define the term Banking. What is a Bank Draft ?
Ans. According to the Banking Regulations Act, 1949, “banking means the accepting, for the purpose of lending or investment, of deposits of money from the public, repayable on demand or otherwise, and withdrawal by cheque, draft, order or otherwise.” A bank draft is a type of cheque. It is drawn by a bank either on its own branch or on another bank. Therefore, it is also called “banker’s cheque.”
Question: Distinguish between NEFT & RTGS
Ans.

Question: What is a promissory note?
Ans. A promissory note is an unconditional undertaking in writing signed by the maker to pay a certain sum of money only to or to the order of a certain person.
Question: State any two features of a bearer cheque.
Ans. Two features of a bearer cheque are as follows :
(i) Whoever gets a bearer cheque can encash it without having a bank account.
(ii) A bearer cheque can be transferred without any endorsement.
Question: What is meant by a stale cheque?
Ans. It is cheque which has not been encashed within six moths of the date mentioned in it. Banks do not make payment on such a cheque.
Question: What are Indigenous banks ?
Ans. These are moneylenders in villages and small towns. They accept deposits from and grant loans to farmers, artisans and local traders. They also deal in hundies. They generally charge high rates of interest. They may carry on commercial activities along with banking business.
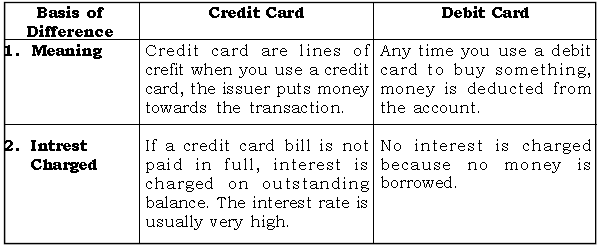
Question: Distinguish between Debit card and a Credit card.
Ans.
Question: State any two general utility functions of commercial banks.
Ans. Two general utility functions of commercial banks are as follows :
(i) Providing lockers for safe custody of valuables.
(ii) Issuing traveller’s cheques, bank drafts, etc.
Question: What is the bank account called, in which the depositers can deposit and withdraw amount at will ?
Ans. ‘Current account’ is the bank account, in which the depositers can deposit and withdraw amount at will.
Question: What is a mobile Wallet ?
Ans. Mobile wallet or E-wallet is a type of electronic card which is used for transactions made online through a computer or a smartphone, a credit or debit card. An E-wallet needs to be lined with the individual’s bank account
o make payment.
Question: What is meant by E-banking ?
Ans. EFT stands for Electronic Funds Transfer System. Electronic banking means banking transactions carried out with the help of computer systems. Any user having a PC and a browser can access the bank website and avail of banking services. Electronic banking is banking over the Internet. It is a part of virtual banking.
Question: Distinguish between a saving account and a current account.
Ans.

Question: Name the document which is transferable by delivery or by endorsement and delivery.
Ans. The document which is transferable by delivery or by endorsement and delivery is called ‘Order cheque’.
Question: What is a commercial bank? Explain its main functions.
Ans. These are joint stock banks which receive deposits from the public and business firms. They also provide short-term and medium-term loans to customer. These banks carry on all kinds of banking functions within the framework or the Banking Regulations Act, 1949 in India. Commercial banks are classified into two broad categories-scheduled and non-scheduled banks. Scheduled banks are those included in the second schedule to the Reserve Bank of India Act. Commercial banks not included in this schedule are non-scheduled banks. Commercial banks perform the following functions :
(i) Accepting Deposits : Accepting deposits is the main function of a commercial bank. It attracts deposits for the purpose of making loans and investments. People deposit their money in banks for the sake of safety and for earning interest, A commercial bank receives deposits from individuals, firms and other institutions. Banks offer different types of deposit accounts to suit the needs of various depositors. Public deposits constitute the main resources of a bank
Banks receive the following types of deposits :
(a) Fixed Deposits – A lumpsum is deposited for a fixed time period.
(b) Savings Deposits – This account is opened for the purpose of depositing small saving.
(c) Current Deposits – Such deposits are made by business firms in current accounts.
(d) Recurring Deposits – In these deposits, the deposit holder is required to make deposit of fixed amount every month for a specified period.
(ii) Granting Credit : Commercial banks lend money in the following ways:
(a) Loans and Advances – A specified amount is granted for a specified time period.
(b) Cash Credit – Under this arrangement, the bank allows the borrower to borrow up to a specified limit.
(c) Overdraft – A customer who has a current account with the bank can withdraw more than the amount standing to his credit upto a specified limit.
(d) Discounting of Bills – Banks make payment against the bills before the date of maturity.
(iii) Agency Functions : A commercial bank serves as an agent for its customers in the following ways :
(a) Collects cheques, bills, dividends, interest, rent, etc., on behalf of customers.
(b) Pays cheques, bills, rent, taxes, interest, insurance premium, fees, subscriptions, etc., on behalf of customers.
(c) Purchases and sells securities on behalf of customers as per their instructions.
(d) Acts as trustee, executor, guarantor etc., in financial matters for their customers.
(iv) General Utility Services :
(a) Transfer of funds from one branch to another.
(b) Issuing letter of credit and standing as surety for customers.
(c) Accepting valuables, jewellery and securities for safe custody.
(d) Underwriting capital issues
Question: Marked cheques are more acceptable. Justify.
Ans. Marking a cheque means getting the cheque certified by the bank to the effect that there is sufficient money to the credit of the person to pay that cheque when presented, and that the banker undertakes to pay it at the time of presentation. Marking makes the cheque more acceptable because the payment is guaranteed by the bank on which the cheque has been drawn.
Question: Distinguish between a cheque and Demand Darft.
Ans.
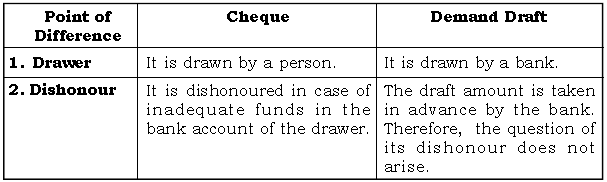
Question: “The central bank is the lender of the last resort.” Explain.
Ans. Whenever a commercial bank needs financial assistance, it may borrow from other commercial banks. But other commercial banks may not be in a position to provide funds to the bank in need. In such a case the central bank provides funds to a commercial bank either by granting loans or by purchasing its securities. In this way the central bank acts as the lender of the last resort.
Question: What is a central bank? What are its important functions ? Which of these functions are more important in a country like India?
OR
Explain any five functions of the central bank of a country.
Ans. Central bank means the bank which regulates the entire banking system in a country and carries out its monetary policy. Central bank is the apex bank, and every country has a central bank. Reserve Bank of India is the central bank of our country.
The Reserve Bank of India performs the following functions :
(i) Monopoly of Note Issue : Government grants the exclusive right to the central bank to issue notes on its behalf. In India, one rupee notes are issued by the Ministry of Finance. All other currency notes are issued by the Reserve Bank of India.
(ii) Government’s Bank : The central bank acts as a banker, fiscal agent and advisor to the Government. It makes and receives payments on behalf of the Government, manages public debts for the Government. As a fiscal agent the central bank advises the Government on matters concerning monetary and banking policies.
(iii) Controller of Credit : Commercial banks create credit by lending money. They may create too much or too little credit. The level of credit in the country causes fluctuations in the price level. Thus the central baks controls credit in the economy through various quantitative and qualitative methods of credit control.
(iv) Custodian of Foreign Exchange : The central bank is the sole custodian of gold and foreign currency reserves of the country. Foreign exchange reserves are needed for making payments to foreign countries.
(v) Maintaining the Exchange Rate : Exchange rate is the rate at which the home currency can be exchanged for a foreign currency. Whenever there are wide fluctuations in the exchange rate, the central bank, buys and sells foreign currencies to stabilise the exchange rate. The central bank is authorised to fix and change the exchange rate ratio.
Question: Distinguish between a Bearer Cheque and an Order Cheque.
Ans.
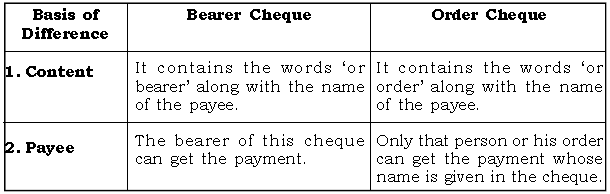
Question: List any four features of NEFT ?
Ans. The main features of NEFT are as follows :
(i) NEFT transactions take place in batches.
(ii) NEFT cannot be used to receive foreign remittances.
(iii) The receiver of funds has to pay no charges.
(iv) An individual, firm or company can make use of NEFT even without having a bank account by depositing cash at a NEFT enabled bank branch.
(v) RTGS is not available at all the bank branches in India. This facility is provided only by CBS enabled bank branches.
(vi) RTGS transactions are processed individually and continuously throughout banking hours rather than in batches.
Question: What is NEFT ?
Ans. National Electronics Funds Transfer (NEFT) is a system of inter bank transfer of funds electronically. The amount involved in this kind of transfer is less than Rs. 2 lac.
Question: Operating a bank account is very useful to businessmen as well as people in general.
Ans. A bank account is very useful to businessmen as well as to people in general. The advantages of opening a bank account are as follows :
(i) A person can keep his savings safe and risk free through a bank account.
(ii) A bank account encourages thrift and habit of saving.
Question: What do you understand by dishonour of a cheque?
Ans. A cheque is dishonoured when the bank on which it is drawn refuses to pay on it. When the payment is refused, the bank states the reason for dishonour and returns the cheque to the payee.
Question: What are the types of deposit account that can be opened in a commercial bank? Briefly explain them.
Ans. (i) Current Deposit Account : A current account is opened generally by businessmen. A person or a firm can open this account with a bank by depositing a certain amount, usually ₹ 5000. The customer can freely deposit more money from time to time and withdraw without notice through the medium of cheques. There is no restrictions on the number of withdrawals. However, a minimum credit balance must be kept as per the rules of the bank. No interest is paid by banks on current accounts. Rather a small charge (called bank charge) is debited for providing bank services. Overdraft facility is available on current accounts.
(ii) Savings Deposit Account : Such a bank account is meant for the general public. The object of a savings bank account is to encourage thrift and foster the habit of savings and to collect the small savings of people. A person can open a savings account by depositing a small amount of money, usually ` 500. Withdrawals are limited and a minimum balance has to be kept by the account holder. A reasonable rate of interest is allowed on the credit balance in the savings account. No overdraft facility is available on savings accounts.
(iii) Recurring Deposit Account : In this type of account, a customer is allowed to deposit a certain amount of money (say `. 10, 50, 100 etc.) every month for a specified period of time. At the end of the period, he is given the total deposit amount along with interest at the prescribed rate. Such an account is also called cumulative time deposit.
(iv) Fixed Deposit Account : Under this account, a person makes a deposit of money in one lumpsum for a specified period of time, say, one year, three years, five years or more. The customer is not allowed to withdraw from the account before the expiry of the specified period but he can borrow against the security of his deposit. The main advantage of fixed deposit is that the depositor is allowed a much higher rate of interest than what is available on other types of deposits
Question: What do you understand by EFT ?
Ans. Under this system, money can be transferred from one account to another account. For example, a bank transfers wages and salaries directly from the company account to the accounts of employees. This service saves both employer and employees from the inconvenience and risk of handling large amounts of cash.
Question: What is a cheque? Explain different types of cheques.
OR
What are the various methods of making payment through a cheque ?
Ans. A cheque is an unconditional order in writing, drawn and signed by a customer on his bank requesting the bank to pay on demand the specified amount of money to the person named there in or to his order or to the bearer of the instrument.
Cheques are of the following types :
(i) Bearer Cheque : It is payable to the bearer. Whoever gets such a cheque can encash it on the counter of the bank. It can be transferred by mere delivery and without any endorsement. It is written as pay to “……. or bearer”. Payment through a bearer cheque is risky because the bank is not liable if the payment is made to a wrong person.
(ii) Order Cheque : It is payable to the person named in it or to his order. Such a cheque can be transferred only by endorsement and delivery. To endorse a cheque, the payee has to write on the back of the cheque `the amount may be paid to ‘ (name of the person to whom payment is to be made). He has also to verify the signature of such person.
(iii) Account Payee Cheque : Such a cheque is payable only to the account of the person named in it. No payment on such a cheque can be made on the counter.
(iv) Open Cheque : A cheque which is not crossed and can be presented for payment at the bank counter is called an open cheque. Banks do not accept responsibility for wrong payment on such cheques. Bearer cheques and order cheques are open cheques because payments of such cheques are made at the bank’s counter (v) Crossed Cheque : Two parallel lines with or without some words are drawn on such a cheque. Crossed cheques are considered a safer mode of payment because such cheques cannot be encashed at the bank counter.
Question: What is a IMPS ?
Ans. IMPS stand for Immediate Mobile Payment Service. IMPS is used to make payment through mobile number or Adhaar card number linked to the bank account. In order to use IMPS one must register for mobile banking. Banks levy a transaction charge Rs. 2.5 plus service tax upto a transfer of Rs. 10,000 on IMPS transfers.
Question: Define a cheque. What are the circumstances in which a bank may be compelled to dishonour a cheque ?
Ans. A cheque is an unconditional order in writing, drawn and signed by a customer on his bank requesting the bank to pay on demand the specified amount of money to the person named there in or to his order or to the bearer of the instrument. A bank can dishonour a cheque in the following circumstances :
(i) The amount of the cheque is greater than the balance standing to the credit of the drawer’s account.
(ii) The cheque is not properly drawn, e.g. alterations are not signed, date is not mentioned, etc.
(iii) The amounts in figures and words differ.
(iv) The drawer’s signatures do not tally with the specimen signatures or the drawer has not signed the cheque at all.
(v) The cheque is mutiliated, post-dated or stale. A cheque which is more than six months old is called outdated or stale.
Question: Explain the work of ‘bankers’ clearing house’ and show its importance in modern banking.
Ans. The central bank provides clearing house facility to the commercial banks. In other words, it settles the claims of commercial banks through a process of book entries. The daily balances between the commercial banks can easily be adjusted by means of debit and credit entries in their respective accounts with the central bank. Let us take an example to explain this process. Suppose, the Bank of Baroda has to pay an amount of Rs 20 lakhs to the Punjab National Bank. To settle its due the Bank of Baroda will issue a cheque of Rs 20 lakhs to the Punjab National Bank, The Reserve Bank of India will debit the account of the “Bank of Baroda” by Rs 20 lakhs and credit the account of the Punjab National Bank by the same amount. The clearing house facility offers several advantages. Firstly, settlement between different commercial banks can be made conveniently through book entries. Secondly, the possibilities of cash withdrawals during an economic crisis are reduced. Therefore, it helps to stabilise the banking system in the country. The State Bank of India carries out these settlements where the Reserve Bank of India has no office.
Question: A commercial bank serves as an agent for its customer. Justify.
Ans. A commercial bank serves as an agent for its customers in the following ways :
(i) Collects cheques, bills, dividends, interest, rent, etc., on behalf of customers.
(ii) Pays cheques, bills, rent, taxes, interest, insurance premium, fees, subscriptions, etc., on behalf of customers.
Question: State the advantages of cheque. Explain the points a drawer should keep in mind while drawing a cheque.
Ans. I Advantages of payments through cheques.
(i) Money can be sent from one place to another easily and at a very nominal cost.
(ii) The need for counting and carrying the money is avoided.
(iii) It avoids risks involved in carrying cash from one place to another.
(iv) It increases the credit-worthiness of the business concern.
(v) It saves time in payments because the need for counting and checking currency notes is eliminated.
II While writing a cheque, the following precautions should be taken :
(i) The cheque should be clearly and correctly dated.
(ii) It should be written in ink.
(iii) The name of the payee should be written clearly.
(iv) The signature of the drawee should be exactly similar to the specimen signature.
(v) Any alteration should be signed by the drawer.
(vi) The amount in figures and words should be identical.
(vii) The counterfoil must be filled in and kept for future reference.
(viii) The drawer must ensure that sufficient balance is available in his bank account to cover the amount of the cheque as otherwise the cheque would be dishonoured.
Question: What do you understand by agency services of a commercial bank? Explain any four agency services of a commercial bank.
Ans. The service which a commercial bank offers by acting as an agent of customers are known as agency services. Four such agency services Are given below :
(i) Collects cheques, bills, dividends, interest, rent, etc. on behalf are given below :
(ii) Pays cheques, bills, rent, taxes, interest, insurance premium fees, subscriptions, etc. on behalf of customers.
(iii) Purchases and sells securities on behalf of customers as per their instructions.
(iv) Acts as trustee, executor, guarantor etc., in financial matters for their customers.
Question: Compare and contrast the features of RTGS and NEFT ?
Ans. The main features of RTGS are :
(i) RTGS is not available at all the bank branches in India. This facility is provided only by CBS enabled bank branches.
(ii) RTGS transactions are processed individually and continuously throughout banking hours rather than in batches.
(iii) The minimum amount in a RTGS transaction is two lacs. There is no upper ceiling for a RTGS transation.
(iv) The receiving or beneficiary bank must credit the customer’s account within thirty minutes of receiving the fund transfer message.
(v) RTGS has no limit on the number of transfer during the day.
The main features of NEFT are :
(i) A bank branch must be NEFT enabled to become a part of the NEFT funds transfer nertwork.
(ii) In order to receive funds through the NEFT system, an individual, firm or company must have an account with a NEFT enabled bank branch.
(iii) There is no minimum or maximum amount that can be transferred through NEFT when one has a bank account.
(iv) NEFT transactions take place in batches.
(v) NEFT are transferred six tines on a weekday & three times on Saturday.
Question: Explain the meaning of SMS alert.
Ans. Under this service a customer gives his/her mobile number. The bank records the mobile number in its computer system in the customer’s account. Whenever there is a transaction (debit or credit) there is automatically a SMS on the customer’s mobile. The SMS states the nature and amount of transaction, date of the transaction and the balance in the account on that date. Thus, the customer receives all the information about his/ her accounts without visiting the bank.
Question: What are the precautions to be taken while using Credit and Debit Cards?
Ans. (i) Update your contact information with your financial institution. Your bank can’t ask you about a suspicious charge unless it has your current phone number.
(ii) Copy the customer service phone number from the back of each of your debit or credit cards and keep this list in a separate location from your purse or wallet in case a thief steals the latter.
(iii) Let issuers know your travel dates and destination. If your card gets swiped at an unusual location, the card issuer may decline the suspicious transaction.
(iv) Sign up for banking alerts if offered by your financial instititution. These will inform you when particular changes occur, such as irregular card activity.
(v) Stay away from ATMs that appear dirty or in disrepair. At best, such ATMs may not work when used, and at worst, may be fake machines set up to capture card information.
(vi) Do not use ATMs with unusual signage, such as a command to enter your PIN twice to complete a transaction.
(vii) Watch out for ATMs that appear to have been altered. If anything on the front of the machine looks crooked loose or damaged , it could be a sign that someone attached a skimming device.
(viii)Avoid using the ATM if suspicious individuals are standing nearby. Criminals may try to distract you use the machine to steal your cash, or watch as you type your PIN.
(ix) Be aware that if your card gets shake the machine and someone approaches to help, it may be a scam. A criminal may be trying to watch as you enter your PIN code.
(x) If your card gets stuck in the machine, call your financial institution promptly to report the incident.
(xi) AD your Key in your PIN, cover the keypad with your other hand to pluck anyone, or a camera, from viewing the numbers you type.
(xii) Check your balance on a regular basis. In case of loss of your card inform the bank within two days.

We hope you like the above provided Banking ICSE Class 10 notes and questions with solutions. In case you are searching for more study material then you can send us your comments in the box below. Our team of ICSE teachers will work to provide you the ICSE study material for free.

