Question 1. Name the following:
(i) Gland secreting growth hormone
(ii) Growth hormone
(iii) Hormone regulating metamorphosis
(iv) Gland secreting insulin
(v) The largest endocrine gland
(vi) Gland secreting adrenaline
(vii) Anterior lobe of pituitary
(viii) Posterior lobe of pituitary
(ix) The hormone that controls the basal metabolic rate
Solution 1:
1. Pituitary gland
2. Somatotrophin
3. Thyroxine
4. Pancreas
5. Liver
6. Adrenal gland
7. Adenohypophysis
8. Neurohypophysis
9. Thyroxine
Question 2. Give the special function of the following:
(i) Somatotrophic hormone
(ii) Thyroid stimulating hormone
(iii) Adrenocorticotrophic hormone
(iv) Gonadotrophic hormone
(v) Insulin hormone
(vi) Corpus luteum
(vii) Glucagon hormone
Solution 2:
1. Somatotrophic Hormone – responsible for growth, increased utilisation of fat by cell so the level of fat is degrees but protein and carbohydrate is increased, increase length of bone, increase synthesis in DNA and RNA and proteins in cell.
2. Thyroid stimulating hormone – It is responsible for the growth as well as activity of the thyroid gland.
3. Adrenocorticotrophic hormone – It is responsible for the activities of adrenal cortex.
4. Gonadotrophic hormone– It’s stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles and females and the growth of spams in male.
5. Insulin hormone – It maintain the blood glucose level
6. Corpus luteum – It helps in the secretion of progesterone.
7. Glucagon hormone – It increase the blood glucose level.
Question 3. Select the odd one out of the following:
(i) TSH, ACTH, Insulin
(ii) FSH, LH, STH
(iii) Adenohypophysis, Neurohypophysis, Islets of Langerhans
(iv) Insulin, Glucagon, STH
(v) Adrenaline, Noradrenaline, Insulin
Solution 3:
1. Insulin
2. STH
3. Islets ofLangerhans
4. STH
5. Insulin
Question 4. Expand the following biological abbreviations:
(i) FSH
(ii) LTH
Solution 4:
1. The full form of FSH is Follicle stimulating hormone.
2. The full form of LTH is Luteotropic hormone.
Question 5. Label the following diagram:

Solution 5:

Question 6. Match the term of column I with those of column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Adenohypophysis | (a) Thyroxine |
| (ii) Neurohypophysis | (b) STH |
| (iii) Thyroid | (c) Oxytocin |
| (iv) Adrenaline | (d) Insulin |
| (v) Islets of Langerhans | (e) Noradrenaline |
Solution 6:
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Adenohypophysis | (b) STH |
| (ii) Neurohypophysis | (c) Oxytocin |
| (iii) Thyroid | (a) Thyroxine |
| (iv) Adrenaline | (e) Noradrenaline |
| (v) Islets of Langerhans | (d) Insulin |
Question 7. Which one of the following statements is true/ false?
(i) Diabetes is caused due to insulin deficiency.
Solution :
True
(ii) Insulin is secreted by thyroid.
Solution :
False
(iii) Islets of Langerhans are found in the brain.
Solution :
False
(iv) Adrenaline is secreted by pituitary.
Solution :
False
(v) The pituitary gland is both exocrine and endocrine in function.
Solution :
False
Question 8. Define the following:
(i) Hormone
(ii) Endocrine gland
(iii) Exocrine gland
(iv) Hypothyroidism
(v) Hyperglycemia
(vi) Hypersecretion
Solution 8:
1. Hormone:- They are non-nutrient chemical which act as intracellular messengers and are produced in trace amount.
2. Endocrinegland:– The gland which secretes hormone and do not having duct is known as endocrine gland.
3. Exocrinegland: – The gland which secretes hormones and having ducts are known as exocrine gland.
4. Hypothyroidism:– Decreased secretion of thyroid hormone.
5. Hyperglycemia:– Hormone that increase the blood glucose level.
6. Hyper secretion:– The over secretion of any gland leads to hyper secretion.
Question 9. Name the hormone produced by the following glands giving one function of each:
(i) Thyroid
(ii) Pancreas
(iii) Adrenal medulla
Solution 9:
| Name of Gland | Hormone | Function |
| (i) Thyroid | Thyroxine | It regulates the body’s glucose absorption. |
| (ii) Pancreas | Insulin | It helps to release energy by lowering blood glucose levels. |
| (iii) Adrenal medulla | Adrenaline | It triggers quick physiological reactions in situations when there is a threat of terror. |
Question 10. Define the following:
(i) Diabetes mellitus
(ii) Beta cells
(iii) Exophthalmic goiter
(iv) Releasing hormones
Solution 10:
1. Diabetes mellitus:– Prolonged hyperglycemia leads to a complex disorder called diabetes mellitus. This is characterized by loss of excess glucose through urine and also the formation of complex harmful compound known as ketone bodies.
2. Betacells:– the beta cell produce a peptide hormone called insulin which regulates the glucose homeostasis.
3. Exophthalmic goiter:–The enlarged thyroid is overactive and secretes excessive amount of thyroid hormone. So the goitre is associated with symptoms of thyroid over activity such as high metabolic rate, rapid heart rate, rise in body temperature, emaciation, nervousness, irritability, temor and restlessness..
4. Releasing hormones:– Hypothalamic Hormone which stimulates the pituitary gland to synthesize and release the hormone.
Question 11. Which glands are responsible for the following disease?
(i) Goitre
(ii) Diabetes mellitus
(iii) Gigantism
(iv) Diabetes insipidus
(v) Cretinism
(vi) Exophthalmic goiter
Solution 11:
(i) Disease:- Goitre
Name of Gland:- Thyroid
(ii) Disease:- Diabetes mellitus
Name of Gland:- Pancreas
(iii) Disease:- Gigantism
Name of Gland:- Pituitary gland
(iv) Disease:- Diabetes insipidus
Name of Gland:- Pancreas
(v) Disease:- Cretinism
Name of Gland:- Thyroid
(vi) Disease:- Exophthalmic goitre
Name of Gland:- Thyroid
Question 12. Name the hormone which controls (reduces) the level of glucose in blood, and the gland which secretes it?
Solution 12:
Insulin secreted by pancreas controls the level of glucose in blood.
Question 13. Explain briefly, why adrenaline is called the emergency hormone?
Solution 13:
Alrenaline is called an emergency hormone as these hormones are released during stress of any kind or emergency situation and are therefore called as emergency hormone and adrenal gland is called emergency gland. These hormones also prepare the body during the flight, fright and fight hence are also called as 3F or fight, flight and fright hormone.
Q14. Name the hormones secreted by the following glands:
(i) Anterior pituitary
(ii) Testes
(iii) Ovary
(iv) Adrenal cortex
(v) Pancreas
Solution 14:
(i) Name of the Galnd:- Anterior Pituitary
Hormones:- a.) Growth hormone/Somatotrophin
b.) Adrenocorticotrophic hormone
c.) Thyroid stimulating hormone
d.) Gonadotrophic hormone
e.) Luteotrophic hormone
(ii) Name of the Galnd:- Testes
Hormones:- Testosterone
(iii) Name of the Galnd:- Ovary
Hormones:- a.) Oestrogen
b.) Progesterone
(iv) Name of the Galnd:- Adrenal cortex
Hormones:- a.) Adrenaline
b.) Noradrenaline
(v) Name of the Galnd:- Pancreas
Hormones:- a.) Insulin
b.) Glucagon
Question 15. Make a table indicating the glands, hormones produced, their main functions and diseases caused due to their hypo and hypersecretions.
Solution 15:
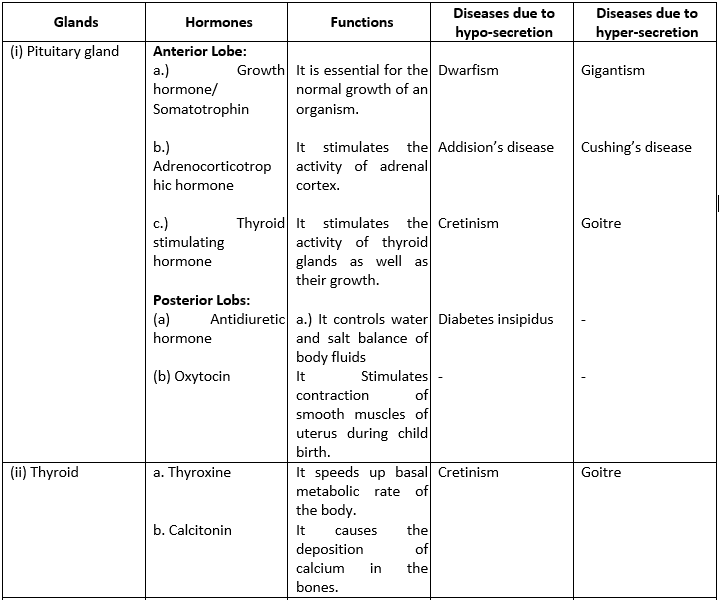


Question 16. Write briefly about
(i) Exophthalmic goitre (symptoms and cause).
(ii) Diabetes mellitus (symptoms and cause).
Solution 16:
1. Exophthalmic goiter:– The enlarged thyroid is overactive and secretes excessive amount of thyroid hormone. So the goitre is associated with symptoms of thyroid over activity such as high metabolic rate, rapid heart rate, rise in body temperature, emaciation, nervousness, irritability, tremor and restlessness.
2. Diabetes mellitus:- prolonged hyperglycemia leads to a complex disorder called diabetes mellitus. This is characterized by loss of excess glucose through urine and also the formation of complex harmful compound known as ketone bodies.
Question 17. Write brief statement explaining the following: People living in hilly region usually suffer from simple goitre.
Solution 17:
In hilly regions, amount of iodine is less in water for the production of thyroxin. So due to the deficiency of thyroxin, people in hilly areas suffer from goiter.
Question 18. Insulin is injected into the body of a highly diabetic patient and not given orally. Comment
Solution 18:
Insulin is a protein hormone, if it is taken orally it would be digested upon
Question 19. (i) Name the endocrine cells present in the pancreas.
(ii) Name two hormones secreted by the above mentioned cells.
(iii) Mention one main function of each hormone named above.
Solution 19:
(i) The endocrine cells present in pancreas are:- Alpha cells, Beta cells, Delta cells
(ii) Insulin and glucagon.
(iii) Insulin – Lower blood glucose level.
Glucagon – raises blood glucose level.
Question 20. Name the hormone responsible for the following functions:
(i) Increase in heartbeat
(ii) Maintains glucose level in the blood
(iii) Converting glycogen to glucose
(iv) Regulates basal metabolism
(v) Ossification of bones
(vi) Prepares the body during emergency
(vii) Responsible for normal growth of the whole body
(viii) Regulates the functioning of the male and female reproductive organs
(ix) Increased reabsorption of water in the kidneys
(x) Increased blood supply to muscles.
Solution 20:
| (i) Increase in heartbeat | 1. Adrenaline |
| (ii) Maintains glucose level in the blood | 2. Insulin |
| (iii) Converting glycogen to glucose | 3. Glucagon |
| (iv) Regulates basal metabolism | 4. Thyroxine |
| (v) Ossification of bones | 5. Calcitonin |
| (vi) Prepares the body during emergency | 6. Adrenaline |
| (vii) Responsible for normal growth of the whole body | 7. Growth stimulating hormone |
| (viii) Regulates the functioning of the male and female reproductive organs | 8. Sex corticoids |
| (ix) Increased reabsorption of water in the kidneys | 9. Antidiuretic hormone |
| (x) Increased blood supply to muscles. | 10. Non adrenaline |
Question 21. Choose the correct answer:
(i) Which one of the following is a hormone deficiency disease?
(a) Scurvy
(b) Diabetes
(c) Cancer
(d) Malaria
Solution :
Diabetes
(ii) Adrenaline is secreted by
(a) thymus
(b) adrenal gland
(c) islets of Langerhans
(d) thyroid
Solution :
Adrenalgland
(iii) A gland having endocrine as well as exocrine function is
(a) pituitary
(b) adrenal
(c) thyroid
(d) pancreas
Solution :
Pancreas
(iv) Excess secretion of growth hormone causes
(a) myxodema
(b) gigantism
(c) pneumonia
(d) goiter
Solution :
Gigantism
(v) Hormone secreted by islets of Langerhans.
(a) Insulin
(b) ACTH
(c) TSH
(d) STH
Solution :
Insulin
(vi) Which one of the following is not an endrocine gland?
(a) Thyroid
(b) Liver
(c) Pancreas
(d) Thymus
Solution :
Liver
(vii) An organ, tissue or cell where a hormone produces its effects is known as
(a) effector
(b) imitator
(c) target
(d) all the above
Solution :
Target
(viii) Diabetes mellitus disease is caused due to
(a) over secretion of insulin
(b) over secretion of glucogen
(c) under secretion of insulin
(d) under secretion of both
Solution :
under secretion of insulin
(ix) Insulin is secreted by
(a) beta cells of pancreas
(b) alpha cells of pancreas
(c) delta cells of pancreas
(d) none of the above
Solution :
beta cells of pancreas
(x) Which hormone produces energy producing effect in the body?
(a) FSH
(b) growth hormone
(c) adrenalin
(d) glucagon
Solution :
glucagon
(xi) Corpus luteum produces
(a) oestradial
(b) testosterone
(c) progesterone
(d) cortisol
Solution :
progesterone







