ICSE students should refer to Non-Aligned Movement ICSE Class 10 History notes provided below. These revision notes have been prepared based on the latest ICSE Class 10 History Books for the current academic year. Revising notes prior to the exams is really important to get excellent marks in History Class 10 exams. Also, refer to ICSE Class 10 History solutions to understand all chapters properly.
ICSE Class 10 History and Civics Non-Aligned Movement
Students can refer to the quick revision notes prepared for Chapter Non-Aligned Movement in Class 10 ICSE. These notes will be really helpful for the students giving the History and Civics exam in ICSE Class 10. Our teachers have prepared these concept notes based on the latest ICSE syllabus and ICSE books issued for the current academic year.
Non-Aligned Movement ICSE Class 10 History
Flow chart
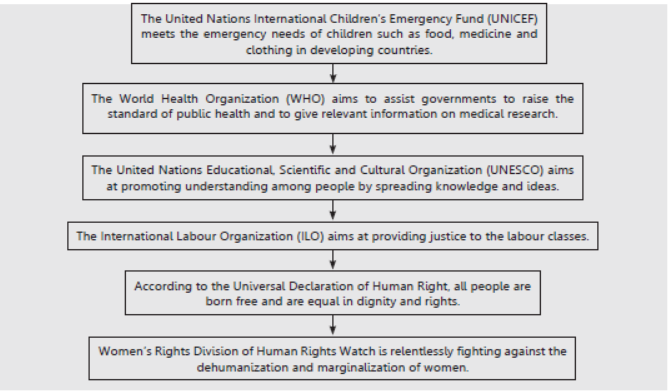
Know the terms
1. Non-Alignment : A strategy of not forming either of the two power blocs.
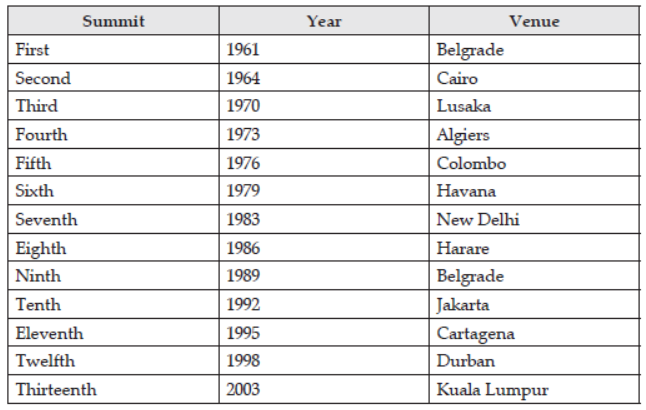
2. Belgrade : The Conference first Summit of NAM was held at Belgrade in Yugoslavia in 1961.
3. Architects of NAM : Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru, Marshall Tito, Colonel Gamal Abdel Nasser.
4. Panchsheel : Five principles of co-existence that allowed good relations between two independent sovereign nations.
5. Bandung Conference : A Conference organized at Bandung in Indonesia. 23 Asian and 6 African nations participated in it. It was the first concrete expression of Afro-Asian unity.
6. Third World : Economically underdeveloped nations.
Know the Dates
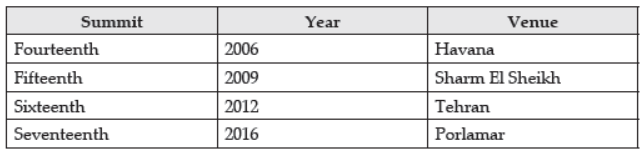
➢ Growth of Non-Aligned Movement :
Know the Personalities
1. V.K. Krishna Menon : He coined the term “Non-Aligned Movement” in 1953.
2. Jawaharlal Nehru : The first Prime Minister of India and the greatest advocate of Non-Alignment Policy.
TOPIC-1
Formation, Meaning and Objectives of NAM
Quick Review
(1) Formation
(i) The countries which had become newly independent were worried that they might lose their complete independence if they joined any power bloc.
(ii) The countries had witnessed so much strife during their national struggles that they wanted to maintain peace.
(iii) Most of these newly independent countries were poor and underdeveloped. They needed help from outside. They could not afford to join any one bloc and thus lost out help from the rival group.
(iv) Jawaharlal Nehru came with the name ‘Non-Aligned’.
a) In an AIR broadcast, he declared that India would keep away from the power groups.
b) In the Asian Relations Conference in New Delhi in 1947, Nehru had stressed cooperation and working together for peace resisting imperialistic forces.
c) The Chinese Premier Chou En-Lai and Nehru declared the Panchsheel which were accepted as basic principles of cooperation during the Bangdung Conference in 1955. The principles were:
• Non-intervention in each other’s internal affairs.
• Equality.
• Non-aggression.
• Mutual acceptance of each others territorial independence or integrity.
• Peaceful cooperation and existence.
d) The Non-Aligned Movement came into existence in 1961 in Belgrade. Tito of Yugoslavia, Nehru of India, Sukarno of Indonesia and Nasser of Egypt were the real founders of the NAM.
(2) Meaning
(v) NAM means not being under the influence of any of the superpower blocs.
➢ NAM stands for peace, cooperation and staying away from the Cold War.
➢ NAM believes in acting according to the merit of the incident, not according to the dictates of any power.
(3) Objectives
(vi) NAM has simple and clear objectives.
➢ Safeguarding the environment, ending of racism, equality, implementing human rights, disarmament, end of imperialism, helping the UN, supporting peace and economic development are the basic objectives of NAM.
(vii) NAM has kept peace with the changing world’s needs.
➢ In the beginning (1960s) its main thrust was to end colonialism and openly called for disarmament.
➢ In the 1970s, it adopted economic progress as its main goal.
➢ In the 1980s, the emphasis was against racial discrimination and even foreign intervention.
➢ Rights through economic progress was also greatly stressed.
➢ 1990s saw the need for even greater economic cooperation, combating terrorism and strengthening the UN.
➢ This ability has to adopt goods and arms to the changing world has been one of the greatest strengths of NAM.
TOPIC-2
Role of India in NAM and Its Importance In Modern Times
Quick Review
(i) Role of India in NAM
➢ Nehru and Indira have played an important role in NAM.
➢ Nehru called for an Asian Relations Conference even before independence where he stressed the need for Asian cooperation.
➢ Along with the Chinese Premier, Chou En-Lai, Nehru enunciated the Panchsheel.
➢ In the First Summit of NAM in 1961 at Belgrade, he was a supporter of the ideals and the aims adopted.
➢ From the very beginning, Nehru opposed supporting any power bloc and insisted on judging every incident according to its merits.
➢India condemned the Eastern Bloc supported North Korean aggression on South Korea in exactly the same way as it condemned the West for action on Egypt on the Suez Canal issue.
➢ Even with Pakistan’s hostility towards India and its forming the SEATO Alliance, India kept its neutrality and did not join any military alliance.
➢ After Nehru, India did not change its stand. Indira Gandhi clearly said that “cooperation between North and South countries will be of mutual benefit”.India was calling for setting up a new International Economic Order.
➢ Later, Rajiv Gandhi came up with the ‘Polluter Pay’s Principle’.
➢ India’s ideas about disarmament have been supported in NAM.
➢ India stand on no third party mediation in bilateral disputes has been supported in NAM.
(ii) Importance of NAM in Modern Times :
➢ With the end of the Cold War, some people felt that there was no need for NAM. But in fact, NAM is still required today.
➢ NAM has adopted itself to the changing world and it lays emphasis on economic development. Earlier, the developing countries could get aid from either or both blocs but now they are increasingly becoming dependent on each other.
➢ NAM has also taken up the task of strengthening the UNO. It is also trying to safeguard the environment. Thus, NAM is still as important today as it was earlier.
➢ NAM plays an important role by stressing on human rights, democracy and peace.



