Students of ICSE Class 10 should refer to Organic Chemistry ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Questions below which have come in past board exams. You should always go through questions that have come in previous years. This will help you to understand the pattern of questions in ICSE Class 10 Chemistry and prepare accordingly. This will help you to get better marks in ICSE Class 10 Board Exams
ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Important Questions Organic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry is an important chapter in ICSE Class 10 Chemistry. Our faculty has prepared the following ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Questions and answers based on the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Please refer to the solved questions below and also see links provided for other chapters.
Organic Chemistry ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Questions
Organic Chemistry ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Questions
Introduction
Originally the word ‘organic’ means ‘pertaining to life’. It involves the study of substances of plant & animal origin. German chemist Friedrich Wohler prepared urea in the laboratory by heating ammonium cyanate. All organic

compounds contain carbon, & most of them contain hydrogen & may contain oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, halogen etc.
A. Organic Chemistry – Hydrocarbons
1. Define ‘Organic Chemistry’.
Ans. It is the chemistry of organic compounds which are derived from natural sources like plants, animals, coal & petroleum. Eg : Carbohydrates, Proteins, Dyes, Petrol etc.
2. What are organic compounds?
Ans. These are the compounds mainly built up of carbon and hydrogen along with O, N, S, P, halogens etc. Majority of them are covalent with low boiling and melting points. They are non-conductors of electricity, insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents.
3. ‘Carbon atoms show unique nature’. Explain.
Ans. Large number of organic compounds are formed due to unique nature of carbon atoms. Following are the characteristic nature of carbon atoms :
i) Tetravalency : 12 C / 6 Electronic Configuration K L / 2 4
Carbon atom shows the valency of 4 because of the presence of 4 valence electrons. To attain stability it forms covalent bonds by mutual sharing of electrons.
ii) Catenation : It is the tendency of an element to form chains of identical atoms. Carbon atom easily combines with other carbon atoms to form chains which may be linear, branched & closed.

iii) Formation of single & multiple bonds : Due to its small size carbon atom can form multiple bonds (i.e. double & triple bonds) with not only carbon but with atoms of other elements like Oxygen, Nitrogen etc.
4. Differentiate between Organic & Inorganic Compounds.
Ans.

5. What are hydrocarbons?
Ans. They are the simplest organic compounds composed of carbon & hydrogen
only. Eg : methane (CH4), ethane(C2H6), ethyne (C2H2).
6. State how organic compounds are classified. State which of the following are ‘Aliphatic organic compounds :-
Methane, benzene, ethene, ethyne, ethyl alcohol, Lead acetate, Pyridine, acetic acid.
Ans. Organic compounds are classified into
(i) Aliphatic – open chain compounds.
(ii) Cyclic – closed chain compounds.
Aliphatic organic compounds are methane, acetic acid, ethene, ethyne, ethyl alcohol, lead acetate.
7. What are acyclic, aliphatic carbon compounds?
Ans. Carbon compounds which are formed by carbon atom linked in open chain are acyclic, aliphatic compounds. For eg : Hydrocarbons like alkanes, alkenes & alkynes.
CH4 , C2H4 , C2H2 , CH3OH etc.
8. What are closed chain cyclic compounds?
Ans. When carbon atoms are linked in closed chains, they form cyclic compounds.
They could be homocyclic (consisting of only carbon atoms).

9. What is a homologous series ?
Ans. Series of organic compounds in which all members share a same general formula & successive members follow a regular structural pattern. Each
member in the series differs by – CH2 group.
Eg : Alkanes General formula – CnH2n+2
10. State three characteristics of the membres of the Homologous series which are same or similar & two characteristics which increase down the series with reasons.
Ans. The three charactersitcs of the members of Homologous series which are same/similar are:
(i) Composition (ii) General formula (iii) chemical properties The two characteristics of the members of Homologous series which increase down the series are :
(i) Molecular weight : Increase in molecular weight is due to increase in – CH2 group down the series.
(ii) Physical properties : Increase in phyical properties is due to gradual gradation with increase in molecular weight.
11. What is the difference in the molecular formula of any two adjacent homologues:
(i) in terms of molecular mass
(ii) in terms of number and kind of atoms per molecule?
Ans. (i) Each member of the series differs from the preceding one by molecular mass of 14 a.m.u.
(ii) Each member of the series differs from the preceding one by the addition of CH2 group.
13. State three main groups of hydrocarbons. And give the structural and electron dot formula of one example.
Ans.

× : electron of Carbon
º : electron of Hydrogen
13. What are hydrocarbons? What are the two main groups of hydrocarbons?
Organic compounds containing carbon & hydrogen only. They have molecular formula CxHy where x & y are whole numbers.
They are divided into 2 main groups :-
(a) Saturated : containing C atoms joined by single covalent bonds.
Eg : alkane (general formula CnH2n+2 ) C2H6 (ethane)
(b) Unsaturated : containing carbon atoms joined by double or triple covalent bonds.
Alkenes : (CnH2n : general formula) Eg : ethene
H2C = CH2
Alkynes : (General formula : CnH2n – 2) Eg : ethyne
HC = CH
14. Differentiate between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Ans.

14. State the molecular formula and draw the condensed structural formula and branched structural formula of Alkanes – Methane, ethane; Alkenes – Ethene, propene & Alkynes- ethyne, propyne.
Ans. (i) Alkanes : a. Methane b. Ethane
Molecular formula : CH4 C2H6
Structural formula :
Condensed : CH4 H3C – CH

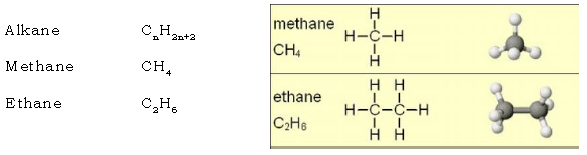
15. (a) What are alkanes?
(b) Give structures of first two alkanes.
Ans.

16. (a) What are alkenes?
(b) Give structures of first two alkenes
Ans.

(a) What are alkynes?
(b) Give structures of first two alkynes
Ans. (a) They are unsaturated organic compounds having carbon to carbon triple

18. Define isomerism.
Ans. It is the phenomenon in which the organic compounds have same molecular formula but differ from each other in structural formula. They have similar chemical properties but different physical properties.
Eg : n – butane & isobutane.
19. State the two main types of isomerism and the reason for its cause.
Ans. The two main types of isomerism are:
(a) Structural isomerism: This is caused due to difference in the mode of linking of atoms.
(b) Stereo isomerism: This is caused due to difference in arrangement of atoms or groups in space.
20. What is-
(a) Chain isomerism
(b) Position isomerism
(c) Geometrical isomerism
Ans. Chain isomerism: It is due to the difference in arrangement of carbon atoms in carbon chain. Eg : isomers of butane, Two isomers of butane are n-butane & iso butane.

Position isomerism : It is due to the difference in position of double bond or any other functional group. Eg – butene.

Geometrical isomerism : It is due to the difference in arrangement of atoms around double bond. Eg : 2 – butene.

21. Explain the term – Isomers.
Ans. Isomers are organic compounds having the same molecular formula but differing in molecular arrangement or in structural formula.
22. Draw the structural formula and give the IUPAC names of 2 chain (structural) isomers of butane.

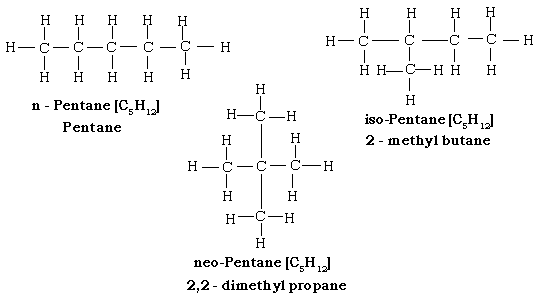
23. Draw the structural formula and give the IUPAC names of 3 chain (structural) isomers of pentane.
Ans.
24. Draw the structural formula and give the IUPAC names of 2 position isomers of butene.
Ans.

25. (a) State what are ‘Alkyl groups’. State the alkyl group to the parent – alkane – methane and ethane.
(b) State what are functional groups. Name the following functional
groups. – OH ; – CHO; – COOH; – F; – Cl; – Br; – I
Ans. (a) Alkyl groups are groups derived from parent alkane by loss of H atom.
Alkyl group of methane is – CH3, (methyl), ethane is – C2H5 (ethyl).
(b) Functional group is an atom, radical or bond – which defines the structure of organic compounds & confers characteristic properties to it.
-OH : Alcohol, -CHO : Aldehyde, -COOH : Carboxylic,
-F, -Cl, -Br, – I : Halide
26. Which part of the organic compound determines (i) physical properties
(ii) chemical properties.
Ans. (i) In an organic compound the alkyl group determines the physical properties
(ii) Chemical properties of an organic compound are determined by the functional group attached.
27. What is IUPAC system of nomenclature.
Ans. Nomenclature is the system of assignment of names to organic compounds.
International Union of Pure & Applied Chemistry [IUPAC] is the most modern system which clearly directs in writing only molecular structure of the compound.
B. ALKANES
28. What are Alkanes? Give the structural formula of methane & ethane.
Ans. Alkanes are saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons containing carbon – carbon single bond.
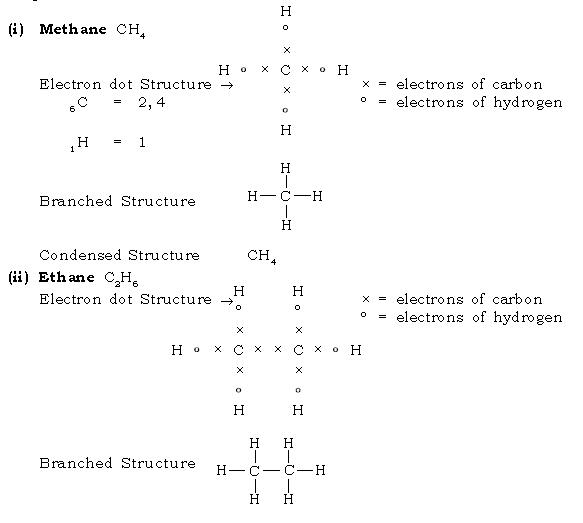
Condensed Structure H3C – CH3
29. Give reason why -(i) alkanes are said to be saturated organic compounds.
(ii) alkanes are known as paraffins.
Ans. (i) Alkanes are said to be saturated organic compounds because all the valencies of carbon are satisfied by single covalent bonds in their molecules.
(ii) Alkanes are known as paraffins because they contain strong carbon to carbon and carbon to hydrogen bonds and hence are relatively chemically inert.
30. Give balanced chemical equations for lab preparation of methane & ethane.
Ans.

31. How will you prepare methane from iodomethane? Give Equation.
Ans.

32. Give equation for the conversion of Bromoethane to ethane.
Ans.

33. Give the substitution reaction of methane & ethane showing chlorination.
Ans. Substitution reaction [Chlorination] of Methane


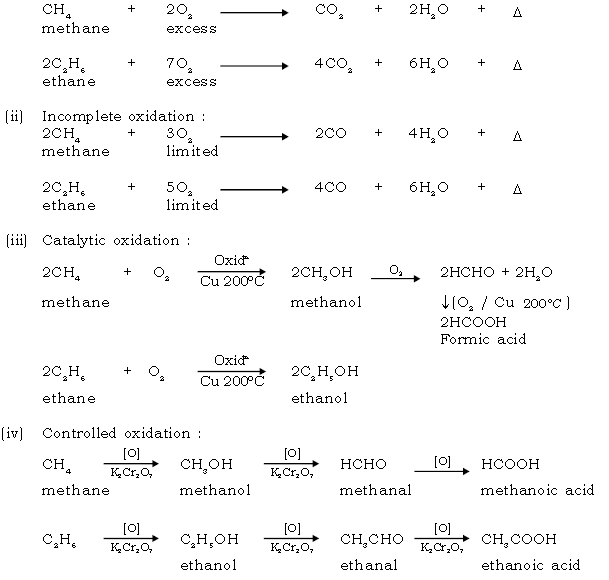
34. Give equation for complete oxidation of methane & ethane.
Ans. CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O + ↑
methane excess
2C2H6 + 7O2 4CO2 + 6H2O + →
ethane excess
35. Give the reaction for oxidation of ethane using acidified potassium dichromate.
Ans.

36. What is pyrolysis of alkanes?
Ans. Thermal or catalytic decomposition of alkanes in absence of air at high temperatures is called pyrolysis.

37. Give important uses of methane and ethane.
Ans. 1. It is used as domestic fuels in the form of natural gas or gobar gas.
2. In the manufacture of chemicals like Chloroform, Carbon black, Formaldehyde, methanol, ethanol etc.
38. Give a test to distinguish between ethane and ethene.
Ans.

C. ALKENES
39. What are alkenes? Give the (a) Molecular formula (b) electron dot formula and (c) structural formula of ethene (ethylene)
Ans. Alkenes are unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons containing a carbon – carbon double bond in their molecule.
Ethene C2H4
Electronic Configuration
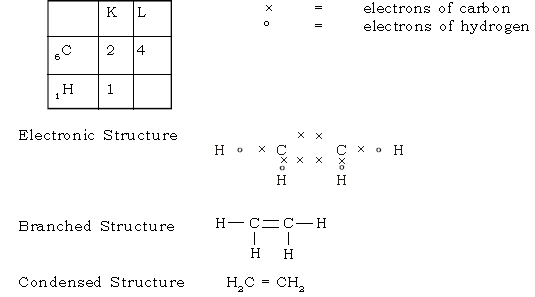
Two carbon atoms are linked by double covalent bond formed by sharing of 2 pairs of electrons between them.
40. Give the laboratory preparation of ethene.
Ans. From ethanol

It is a dehydration reaction involving the removal of water molecule from ethanol.
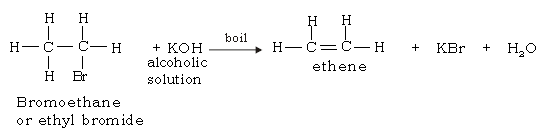
41. What is dehydrohalogenation of ethyl bromide?
Ans. Dehydrohalogenation involves the elimination of hydrogen & halogen (in the presence of hot concentrated alcoholic KOH solution
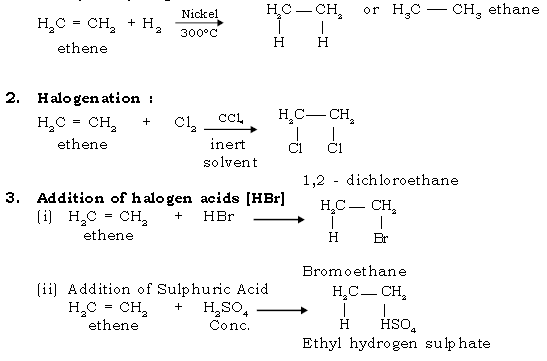
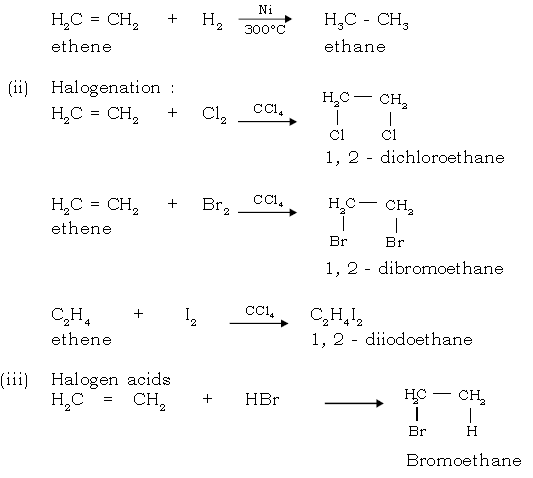
42. Give the addition reaction of ethene.
Ans. 1. Catalytic Hydrogenation :
43. Give oxidation reaction of ethene with cold dil. KMnO4 (alkaline). [Baeyer’s reagent]

44. What is polymerization of ethene?
Ans. It is a process by which simple molecules of ethene join to form large molecules at high temperature and pressure in the prescence of a catalyst HF, H2SO4 or organic peroxide

45. Give uses of ethene.
Ans. 1) Production of oxy-ethylene torch for welding and cutting metals.
2) For ripening of green fruits.
3) For catalytic hydrogenation used in hardening of oils.
4) For manufacture of chemicals like PVC, Polyethylene, ethylene glycol (antifreeze), mustard gas etc.
D. ALKYNE
46. What are alkynes? Give the general formula. Give the structural formula of ethyne.
Ans. Alkynes are unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons containing a carboncarbon
triple bond [– C → –]. General formula = CnH2n – 2
Ethyne C2H2
Electronic Configuration : Carbon : 2,4
Hydrogen :1
× = electrons of carbon
º = electrons of hydrogen

Two carbon atoms are linked by triple covalent bond formed by sharing of 3 pairs of electrons.
47. Give the lab preparation of ethyne [acetylene].
Ans. (a) From Calcium Carbide :
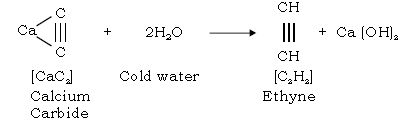
(b) From 1,2 dibromoethane : [Dehydrohalogenation reaction]

48. Give the preparation of ethyne from general method.
Ans. From natural or marsh gas (methane)

49. Give the addition reaction of ethyne.
Ans. 1. Hydrogenation : [Addition of hydrogen in the presence of
[catalytic] catalyst (Ni/Pd/Pt) at high temperature

5. With ammoniacal silver nitrate :
H – C = C – H + 2AgNO3 + 2NH4OH → Ag – C ↑ C – Ag + 2NH4NO3 + 2H2O
ethyne Silver acetylide (White precipitate)
This serves as a test for ethyne.
50. Give the important uses of acetylene.
Ans. 1. Ethyne is used for the production of oxy-acetylene torch for welding & cutting metals (flame temp 3500º C)
2C2H2 + 5O2 → 4CO2 + 2H2O + △[exothermic reaction]
2. For ripening of green fruits.
3. Manufacture of organic compou△nds like acetic acid (vinegar), acetaldehyde, ethyl alcohol (alcoholic beverages, drugs, antiseptic), oxalic acid (for removing ink stains)
4. Manufacture of synthetic products like polymers (polyvinylacetate), synthetic rubber and fibres.
51. Give a test to distinguish between ethene and ethyne.
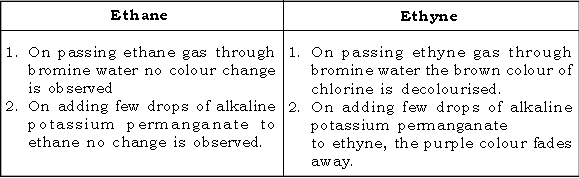
52. Give a test to distinguish between ethene and ethyne.
Ans.
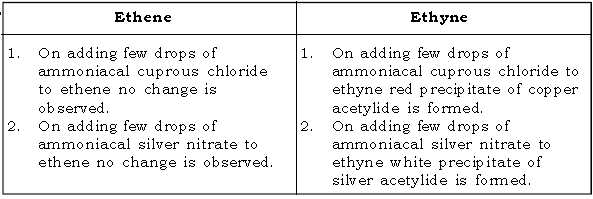
E. ALCOHOLS
53. What are alcohols?
Ans. Alcohols are the hydroxy derivatives of alkanes obtained by replacement of 1, 2 or 3 hydrogen atoms of alkanes by hydroxyl [-OH] groups.
For eg : Methane (alkane) → corresponding alcohol → methanol (CH3OH] → CH4 (methane) → CH3OH (methanol)
54. Give the structural formula and IUPAC names of methyl and ethyl alcohol.
Ans. Alcohol → General formula CnH2n+1OH
CH3OH Methanol (methyl alcohol)
CH3-CH2OH Ethanol (ethyl alcohol)
Structural formula

55. Give the laboratory preparation of ethanol.
Ans. By hydrolysis of alkyl halides
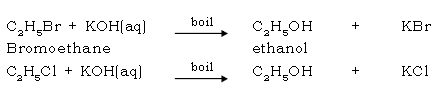
56. Give the industrial preparation of ethanol.
Ans. Ethanol : (From ethene)
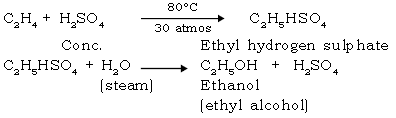
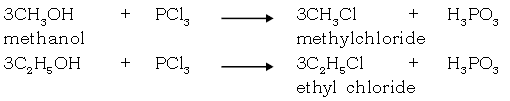
57. Give the reaction of methanol & ethanol with
(i) Sodium, (ii) Phosphorous halide (iii) Conc. H2SO4 acid (iv) Acetic acid.
Ans. Reaction of methanol & ethanol.
(i) With Sodium
2CH3OH + 2Na → 2CH3ONa + H2
methanol sodium → sodium methoxide
2C2H5OH + 2Na → 2C2H5ONa + H2
ethanol → sodium ethoxide
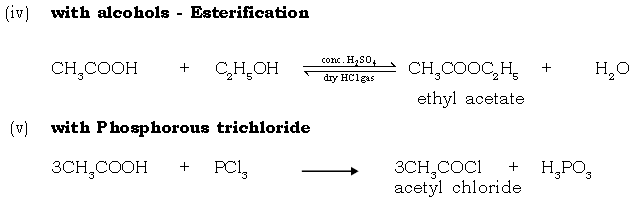
(ii) With Phosphorous → halide
3CH3OH + PCl3 → 3CH3Cl + H3PO3
methanol → Phosphorus methyl
trichloride → chloride
3C2H5OH + PCl3 → 3C2H5Cl + H3PO3
Ethanol → Ethyl Chloride
(iii) With conc. H2SO4 acid (Dehydration)

58. Give the oxidation reaction of methyl & ethyl alcohol.
Ans. Oxidation [with acidified K2Cr2O7 or aq KMnO4]
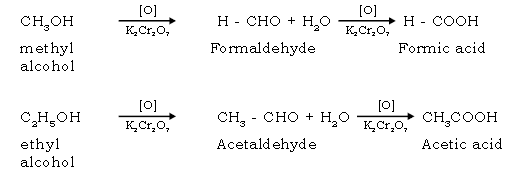
59. Give uses of ethyl alcohol.
Ans. Uses of ethyl alcohol :
(i) As a solvent for gums & resins.
(ii) In thermometers & spirit levels.
(iii) In the manufacture of chemicals like acetaldehyde (dyes), acetic acid (vinegar), chloroform (antiseptic), diethyl ether (anaesthetic).
60. What is – (a) spurious alcohol. (b) methylated spirit (c) denatured alcohol
(d) absolute alcohol.
Ans. (a) Spurious alcohol : It is illicit liquor made by improper distillation. It contains large proportions of methanol in a mixture of alcohols. It is fatal for human consumption but can be used as a solvent for paints and varnishes.
(b) Methylated spirit or alcohol : Ethyl alcohol containing about 5% methyl alcohol is termed as methylated spirit.
(c) Denaturated alcohol : Ethyl alcohol containing pyridine or copper sulphate is termed as denaturated alcohol.
(d) Absolute alcohol : Is anhydrous alcohol obtained by distilling moist alcohol (95% pure alcohol) with benzene.
F. ALDEHYDES
61. What are aldehydes?
Ans. Aldehydes are carbonyl compounds containing a carbon-oxygen double bond
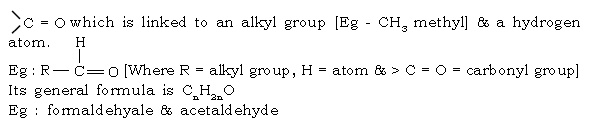
62. Give the IUPAC & common names of following compounds.
Ans. Compounds Common names I UPAC names
H – CHO Formaldehyde Methanal
CH3 – CHO Acteldehyde Ethanal
CH3– CH2 – CHO Propionaldehyde Propanal
CH3– CH2 – CH2– CHO Butyraldehyde Butanal
(CH3)2– CH – CHO Isobutyraldehyde 2 – methyl propanal
G. CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
63. What are carboxylic acids?
Ans.
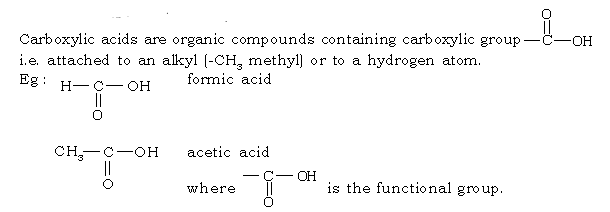
64. Give the common & IUPAC names of following carboxylic acids.
Ans. Compounds Common names IUPAC names
H – COOH Formic acid Methanoic acid
CH3 – COOH Acetic acid Ethanoic acid
CH3 – CH2 – COOH Propionic acid Propanoic acid
CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – COOH Butyric acid Butanoic acid
CH3 – CH – COOH Iso butyric acid 2-Methyl propanoic acid
|
CH3
65. Give the equation for the preparation of acetic acid.
Ans. (i) By oxidation of ethyl alcohol.

66. What is glacial acetic acid?
Ans. Pure anhydrous acetic acid forms an ice like crystal on cooling below 16.5 0C. This pure form of acetic acid is called glacial acetic acid.
67. Give the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of acetic acid with the following subst ances:
(a) Sodium bicarbonate (b) potassium carbonate
(c) Sodium (d) zinc
(e) sodium hydroxide (f) calcium hydroxide
(g) ammonium hydroxide (h) phosphorous trichloride
Ans. With Sodium carbonate / bicarbonate

68. What is esterification? Give the balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
Ans. The condensation of alcohol with an acid to give rise to an ester is known as esterification. It is a reversible reaction which is carried out in the presence of a dehydrating agent. It is an important process involved in the
synthesis of vinyl acetate & terylene.
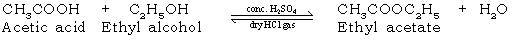
69. Give tests for acetic acid
Ans. (i) On adding acetic acid to carbonates and bicarbonates, a gas is evolved which turns lime water milky.
(ii) When warmed with ethyl alcohol and conc. sulphuric acid, a pleasant fruity smell of ethyl acetate is produced.
(iii) On adding neutral iron (III) chloride, wine red colour is produced.
70. Give important uses of acetic acid.
Ans. 1. In manufacture of important organic compounds like vinyl acetate (used in resins) acetic anhydride (in aspirin), cellulose acetate (in synthetic fibres), perfumes and medicines.
2. In the food industry as vinegar for preserving and flavouring food.
3. As a solvent (for phosphorous, sulphur & iodine)
4. As a laboratory reagent (for preparing acetone, esters etc)
5. As a coagulant for rubber.
V. ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS
I. Name the following:
1. Tendency of an element to form chains of identical atoms.
Ans. Catenation.
2. Organic compounds having same molecular formula but different structural formula.
Ans. Isomers.
3. An example of saturated hydrocarbon.
Ans. Alkane (methane)
4. The type of reactions alkanes undergo.
Ans. Substitution reaction.
5. The type of reactions alkenes undergo.
Ans. Addition reaction.
6. The gas commonly called as marsh gas.
Ans. Methane.
7. General formula of alkanes.
Ans. CnH2n+2
8. The solution which detects the prescence of unsaturation in the given hydrocarbon.
Ans. Bromine solution in Carbon tetrachloride / Alkaline potassium permanganate solution.
9. The process by which ethene is obtained from ethanol.
Ans. Dehydration.
10. The catalyst used during hydrogenation of alkene.
Ans. Nickel / Palladium / Platinum
11. First organic compound synthesized.
Ans. Urea.
12. Mixture of Sodium hydroxide & Calcium oxide.
Ans. Sodalime.
13. The series in which members are arranged in the increasing order of their molecular masses.
Ans. Homologous series.
14. Hydrocarbon used for artificial ripening of fruits.
Ans. Ethene / Ethyne.
15. A reagent which is used to distinguish between ethene & ethyne.
Ans. Ammonical cuprous chloride / Ammonical silver nitrate.
16. General formula of Alkene.
Ans. CnH2n
17. General formula of Alkyne.
Ans. CnH2n-2
18. Decomposition of higher molecular hydrocarbon into a lower molecular with hydrocarbon.
Ans. Pyrolysis.
19. Group derived from alkanes by loss of a hydrogen atom.
Ans. Alkyl group.
20. System of assignment of names to organic compounds.
Ans. Nomenclature.
21. An organic acid which is a chief constituent of vinegar.
Ans. Acetic acid.
22. The compound formed when methane burns in sufficient air
Ans. Carbon dioxide
23. The compound formed when methane burns in insufficient air
Ans. Carbon monoxide
24. The dehydrating agent used to convert ethanol to ethene
Ans. Conc. sulphuric acid or aluminium oxide
25. The type of hydrocarbon known as paraffins
Ans. Alkanes
26. The type of hydrocarbon known as olefin
Ans. Alkenes.
27. The type of hydrocarbon which forms a red precipitate with ammonical cuprous chloride solution.
Ans. Alkyne.
28. The product formed when ethanol reacts with acetic acid.
Ans. Ester.
29. Any one compound which can be oxidised directly, or in stages to produce acetic acid.
Ans. Ethane, Ethanol or Ethanal.
30. The reducing agent used to convert acetic acid into ethanol.
Ans. Lithium aluminium hydride.
31. The substance used to change acetic acid to acetic anhydride.
Ans. Phosphorous pentoxide
32. The addition product formed between ethene and water.
Ans. Ethanol.
II. Fill in the blanks:
1. The conversion of ethanol to ethene is an example of ________ (dehydration, dehydrogenation)
Ans. dehydration
2. Conversion of ethanol to ethene requires the presence of _______ (conc. HNO3, conc HCl, conc. H2SO4)
Ans. conc. H2SO4
3. The conversion of ethene to ethane is an example of _______ (hydration, hydrogenation, hydrohalogenation)
Ans. hydrogenation
4. The catalyst used to convert ethene into ethane is commonly ______ (copper, cobalt, nickel)
Ans. nickel
5. The organic acid present in vinegar is _______ [acetic acid, picric acid, oxalic acid]
Ans. acetic acid
6. The isomer of pentane which has ‘1’ C atom attached to ‘4’ other C atoms [n-, iso-, neo-] pentane.
Ans. neo-
7. The IUPAC name of the product of reaction of ethylene with hydrogen bromide. [ethyl bromide, bromoethane, dibromoethane]
Ans. bromoethane
8. The functional group in ethanoic acid.[aldehydic, carboxyl, hydroxyl]
Ans. carboxyl
9. Propane and ethane are _________ (homologous, isomers, allotropes)
Ans. homologous
10. A saturated hydrocarbon does not participate in a ________ reaction (substitution, addition)
Ans. addition
11. Succeeding members of a homologous, series differ by (CH, CH2, CH3)
Ans. CH2
12. CHO is the functional group of an _________ (alcohol, aldehyde)
Ans. aldehyde
13. But-1-ene and but-2-ene are example of _________ isomerism (chain, position, functional)
Ans. position
III. Choose the correct answer:
1. C5H11 is an
(i) alkane (ii) alkene
(iii) alkyne (iv) alkyl group
2. A hydrocarbon of the general formula CnH2n is
(i) C15H30 (ii) C12H26
(iii) C8H20 (iv) C6H14
3. A hydrocarbon with molecular mass 72 is
(i) an alkane (ii) an alkene
(iii) an alkyne (iv) alkyl group
4. The total number of different carbon chains that four carbon atoms form in alkane is
(i) 5 (ii) 4
(iii) 3 (iv) 2
5. The IUPAC name of the compound is
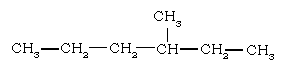
(i) 3-trimethylhexane (ii) 3-methyl hexane
(iii) 4-methyl hexane (iv) 3-methyl heptane
Ans. (1) alkyl group (2) C15H30
(3) an alkane (4) 2
(5) 3 – methyl hexane
IV. Select from the letters A to G the correct answer corresponding to the statements from 1 to 5 :
A : Ammoniacal CuCl2, B : Trichloromethane, C : Trichloroethane, D :
Bromine soln., E : Aqueous KOH, F : Ethene, G : Sodalime, H : Ethanol, I :
Ethyne.
1. The organic compound which forms carbon tetrachloride on reaction with chlorine.
2. The reagent which can distinguish between ethene and ethyne.
3. The substance which reacts with bromoethane to give ethanol.
4. The substance which gives bromoethane on reaction with hydrogen bromide.
5. The substance which reacts with acetic acid to give CH3COOC2H5.
Ans. 1. B. Trichloromethane
2. A. Ammoniacal CuCl.
3. E. Aqueous KOH
4. F. Ethene
5. H. Ethanol
V. Give balanced equations for the following conversation:
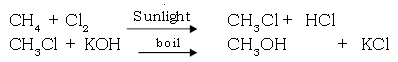
I.a. Methane to Methyl alcohol.
Ans.
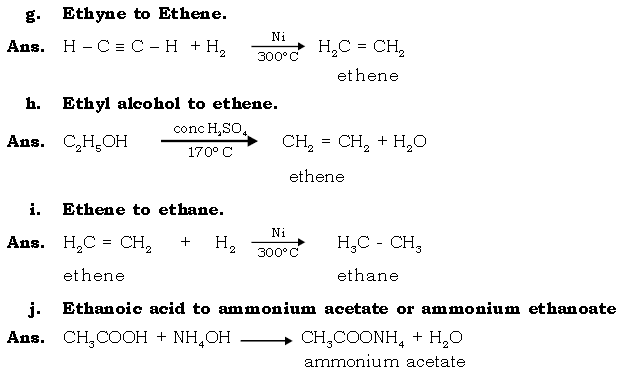
b. Methane to Formaldelyde.
Ans.


VI. Give balanced equations for the following conversions :
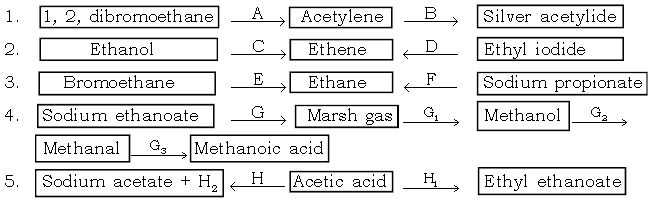
Ans.

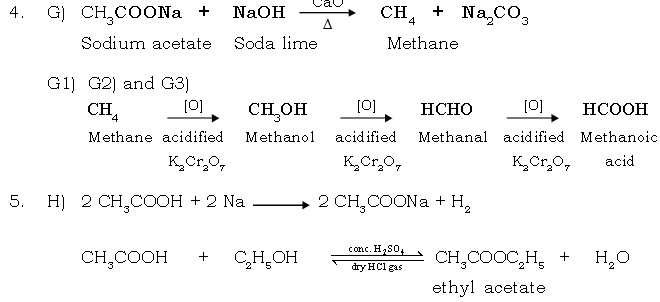
VII. What will you observe when?
1. Ethene is passed through Bromine solution in Carbon tetrachloride.
Ans. Brown colour of Bromine gets discharged.
2. Ethyne is passed through ammonical cuprous chloride solution.
Ans. A red precipitate is formed.
3. Ethyne is passed through ammonical silver nitrate solution.
Ans. A white precipitate is formed.
4. Sodium is dropped in ethanol.
Ans. A gas is evolved which burns with pop sound and a pale blue flame.
5. Ethene is passed through potassium permanganate solution. (Baeyer’s reagent).
Ans. The purple colour of potassium permanganate decolourises.
6. Acetic acid is added to sodium bicarbonate.
Ans. A colourless gas is evolved, which turns lime water milky and has no effect on acidified KMnO4 solution.
7. Acetic acid is added to ethyl alcohol in the presence of sulphuric acid
Ans. A pleasant fruity smelling compound is produced.
8. Acetic acid is added to neutral FeCl3 solution
Ans. Yellow coloured FeCl3 solution turns wine red.
9. Acetic acid is added to litmus solution.
Ans. Purple coloured litmus solution turns red.
10. Ethene / Ethyne is passed through alkaline KMnO4 solution.
Ans. KMnO4 solution turns from pink to colourless.
VIII. Answer the following:
1. Define functional groups and give the structural formula for the following functional groups:
a) Ketone
b) Alcohols
c) Aldehydes
d) Carboxylic acids
Ans. Functional group : An atom, radical or bond which defines the structure of organic compounds and confers characteristic properties to it.

2. Name the alkyl radical and the functional group of the following organic compounds:
a) CH3OH
b) C2H5OH
c) C3H7CHO
d) C4H9COOH
Ans. a) Alkyl group: Methyl
Functional Group: Alcohol
b) Alkyl group: Ethyl
Functional Group: Alcohol
c) Alkyl group: Propyl
Functional Group: Aldehyde
d) Alkyl group: Butyl
Functional Group: Carboxylic acid
3. Under what conditions does ethane get converted directly to :
a) Ethyl alcohol
b) Acetaldehyde
c) Acetic acid
d) Ethene
Ans. a) In the presence of Cu tube at 200oC
b) In the presence of Molybdenum oxide catalyst at 350 – 500oC
c) In the presence of Platinum catalyst at 300oC
d) In the presence of aluminium oxide at 500oC
4. The molecules of alkene family are represented by CnH2n. Answer the following.
a) What do n and 2n signify?
b) What is the name of the alkene when n = 4?
c) What is the molecular formula of the alkene when n = 4?
d) What is the molecular formula of the alkene when there are 10 H atoms in it?
e) Give the structural formula of the third member of the alkene family
Ans. a) n signifies the number of carbon atoms and 2n signifies the number of hydrogen atoms present in a molecule of the alkene.
b) Butene
c) C4H8
d) C5H10
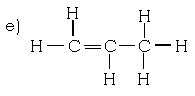
IX. Give reasons.
a. Concentrated sulphuric acid may be added during esterification of acetic acid.
Ans. Concentrated sulphuric acid acts as a strong dehydrating agent, removing chemically combined water molecule to give ester.
b. Isomers belonging to the same homologous series may differ in physical properties but not in chemical properties.
Ans. Isomers belonging to same homologous series have same functional group, since the chemical properties of a compound are determined by the functional group, isomers belonging to same homologous series have same chemical properties.
tional group, isomers belonging to same homologous series have same chemical properties.
X. Give the IUPAC names of following compounds.
Ans. Compounds IUPAC names
1. H3C – CH2 – CH2 – CH3 Butane
2. H3C – CH = CH2 Propene
3. H3C – CH2CH = CH2 1 – butene
4. H3C – CH = CH – CH3 2 – butene
5. H3C – CH2 – C ≡ CH 1 – butyne
6. H3C – C ≡ C – CH3 2 – butyne
7. H3C – CH – CH3 2 – propanol
|
OH
8. H3C – CH2 – CHO Propanal
9. H3C – CH2 – CH2 – COOH Butanoic acid
10. CH3COONa Sodium Ethanoate
11. H2C – CH2 1,2 – dichloroethane
| |
Cl Cl
12. CH3 – CO – CH3 Propanone
13. H2C – CH2 1,2 – ethanediol
| |
OH OH
14. H – C = C – H 1,2 – dichloroethene
| |
Cl Cl
15. Cl Cl 1,1,2,2 – tetrachloroethane
| |
Cl – C – C – Cl
| |
H H
16. H – C = C – H 1,2 – dibromoethene
| |
Br Br

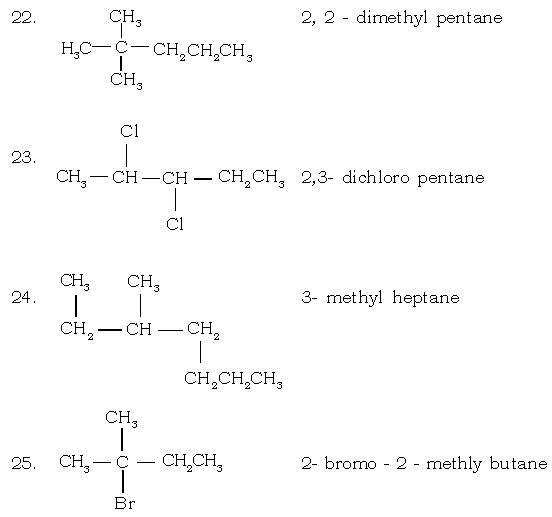

XI. Write the structures of the following compounds :
(a) Prop-1-ene
(b) 2, 3 – dimethylbutane
(c) 2 – methylpropane
(d) 3 – hexyne
(e) Prop – 1 – yne
(f) 2 – methylprop – 1 – ene
(g) Alcohol with molecular formula C4H10O.
(h) 3 – methyl prop – 1 – ene
(i) Pentan – 3 – ol
(j) 2, 2 – dimethyl propan – 1 – ol
Ans.

SUMMARY OF EQUATIONS
ALKANES [Methane & Ethane]
1. Lab Preparation :

2. Substitution Reaction of Methane & Ethane Chlorination :

3. Oxidation :
(i) Complete oxidation :
4. Pyrolysis :

Ethene
1. Lab Preparation :

2. Addition reaction :
(i) Catalytic hydrogenation :

Ethyne
1. Lab preparation :

2. Addition Reaction :
(i) Catalytic Hydrogenation


Reaction of methanol & ethanol
(i) With Sodium

(ii) With Phosphorous halide

Acetic acid
1. Lab preparation :
(i) From ethyl alcohol