Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Question 1: Transpiration pull will be maximum under which set of the following conditions?
(a) Open stomach, dry atmosphere and moist soil.
(b) Open stomata, high humid atmosphere and well irrigated soil.
(c) Open stomata, high humid atmosphere and dry soil.
(d) closed stomata, dry atmosphere and dry soil.
Solution :
Open stomata, dry atmosphere and moist soil
Question 2: With decrease in atmospheric pressure, the rate of transpiration will
(a) increase
(b) decrease rapidly
(c) decrease slowly
(d) remain the same
Solution :
increase
Question 3: The rate of transpiration is more when
(a) atmosphere is dry
(b) temperature is high
(c) humidity is high
(d) atmosphere is dry and temperature is high
Solution :
temperature is high
Question 4: One of the internal factors which affect the rate of transpiration is
(a) big size of the leaf
(b) colour of the leaf
(c) sunken stomata
(d) sunny day
Solution :
Sunken stomata
Question 5: Guttation takes place through
(a) stomata
(b) lenticels
(c) lower epidermis of leaves
(d) hydathodes
Solution :
hydathodes
Question 6: The loss of water as water vapour from the acrial parts of a plant is known as
(a) evaporation
(b) perspiration
(c) guttation
(d) transpiration
Solution :
transpiration
Question 7: Transpiration will be fastest when the day is
(a) cool, humid and windy
(b) hot, humid and still
(c) hot, humid and windy
(d) hot, dry and windy
Solution :
hot, dry and windy
Question 8: Most of the transpiration in tall trees occurs through
(a) stomata
(b) Lenticels
(c) cuticle
(d) Bark
Solution :
Lenticels
Question 9: Transpiration is best defined as
(a) loss of water by the plant
(b) evaporation of water from the surfaces of a plant
(c) loss of water, as water vapour, by a plant
(d) release of water by a plant into the atmosphere
Solution :
evaporation of water from the surfaces of a plant
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1: Name the following:
(a) openings on the stem through which transpiration occurs
(b) The process by which the intact plant loses water in the form of droplets.
(c) An instrument used to find the rate of transpiration
(d) A plant in which the stomata are sunken
(e) The apparatus to record the rate of transpiration in a cut shoot.
(f) Any two parts of a leaf which allows transpiration.
(g) The structure in a leaf that allows guttation.
(h) Loss of water as droplets from the margins of certain leaves.
Solution 1:
(a) Lenticels
(b) Guttation
(c) Potometer
(d) Nerium
(e) Ganong’s photometer
(f) Stomata and cuticle
(g) Hydathodes
(h) Guttation
Fill in the blanks:
(a) Transpiration is the loss of water as water …………… from the parts of the plant.
Solution :
vapour, aerial
(b) Closing of …………… and shedding of leaves reduce …………..
Solution :
stomata, transpiration
(c) Transpiration helps in creating ………………. Force and in eliminating excess………….
Solution :
Suction, water (heat)
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1: Given below is an example of a certain structure and its special functional activity:
Chloroplasts and Photosynthesis.
In a similar way, write the functional activity against each of the following:
(a) Hydathodes and ……………………….
(b) Leaf spines and …………………………
(c) Lenticels and ……………………………
(d) Thick cuticle and ………………………..
Solution 1:
(a) guttation
(b) protection and reduced transpiration
(c) transpiration
(d) reduced transpiration
Question 2: a) State whether the following statements are True (T) Or False (F)?
(i) Most transpiration occurs at midnight.
(ii) Transpiration creates a pull for upward movement of the sap.
(iii) Wind velocity has an effect on transpiration.
(iv) Voltmeter is an instrument used for measuring the rate of transpiration in green plants.
(b) Rewrite the false statements, in (a) above, in the correct form by changing either the first or the last word only.
Solution 2:
a)
(i) False
(ii) True
(iii) True
(iv) False
b)
(i) Most transpiration occurs at mid-day.
(iv) Potometer is an instrument used for measuring the rate of transpiration in green plants.
Question 3: Give suitable explanation for the following:
a) A higher rate of transpiration is recorded on a windy day rather than on a calm day.
b) Excessive transpiration results in the wilting of the leaves.
c) Water transpired is the water absorbed.
d) More transpiration occurs from the lower surface of a dorsiventral leaf.
e) Cork and bark of trees help in preventing loss of water.
f) Perspiration and transpiration help to cool the body temperature of the organism.
g) On a bright sunny day, the leaves of certain plants roll up.
Solution 3:
a) As the wind speed increases, so does transpiration. The water vapours created during transpiration are eliminated faster when the wind blows faster, and the space surrounding the transpiring leaf is not saturated with water vapour. The wind removes moisture from the atmosphere by drying it out, allowing it to collect more water vapours from the plants.
b) The cells lose their turgidity when the rate of transpiration greatly surpasses the rate of water absorption by roots. As a result, high transpiration causes the leaves to wilt. Exudation is the process by which plants lose water or other fluids, as well as dissolved compounds, in liquid form rather than as water vapour.
c) Plants continuously collect water through their roots, which is subsequently carried upwards to all of the plant’s aerial components, including the leaves. Only a little portion of this water is needed for photosynthesis and other activities, about 0.02 percent. The remaining water evaporates as water vapour. As a result, the water absorbed equals the water transpired.
d) A dorsiventral leaf has more stomatal holes on the lower surface. The rate of transpiration increases as the number of stomata increases. As a result, the lower surface transpires more.
e) Tree bark and cork are the tissues of old wooden stems. The outermost layer of the bark is made up of dead cells, and the cork is hydrophobic in nature. These characteristics make them water-resistant, preventing transpiration.
f) Water is lost from the body of the organism as water vapour in both perspiration and transpiration. This evaporation lowers the temperature of the body surface and causes cooling in the organism’s body.
g) The rate of transpiration is substantially higher on a bright sunny day than on any other day. On a bright sunny day, the leaves of some plants roll up to lower the exposed surface area and consequently the rate of transpiration.
Question 4: Which of the following statements are true and which ones are false? Give reason in support of your answer.
(a) Potometer is an instrument used for Demonstration of transpiration occurring from the lower surface of a leaf.
(b) Forest contribute in bringing rains.
(c) Hydathodes are similar to stomata in plant physiology.
(d) Atmospheric humidity promotes transpiration from a green plant.
(e) Some desert plants have sunked stomata on their leaves.
(f) Most transpiration occurs during midday.
Solution 4:
a) False
Reason: The rate of transpiration in a plant is measured with a potometer. Analyzing the changes in colour of pieces of dry cobalt chloride paper applied (and held in place) to the two surfaces of a leaf is used to demonstrate transpiration occurring from the bottom surface of a leaf.
b) True
Reason: The huge number of trees in a forest performs transpiration. This causes the atmosphere to become more moist, resulting in rain.
c) False
Reason: Hydathodes are unique pores found at the extremities of leaf veins that allow guttation and the release of water droplets. Their apertures are uncontrollable. Stomata, on the other hand, are tiny apertures in the epidermal layer of leaves that allow for gas exchange and transpiration. Water is emitted in the form of water vapour. Guard cells control the opening of the stomata.
d) False
Reason: During periods of high atmospheric humidity, transpiration is reduced. The rate of outward diffusion of internal water vapour across stomata is slowed by high humidity in the air, lowering the rate of transpiration.
e) True
Reason: To live in the hot and dry environment, desert plants must limit transpiration as much as possible. As a result, some of them have sunken stomata as a means of reducing transpiration.
f) True
Reason: During the day, the stomata are open to allow carbon dioxide to diffuse inside for photosynthesis. Because the outside temperature is higher during the middle of the day, there is more evaporation of water from the leaves. As a result, mid-day transpiration is higher.
Question 5: Differentiate between guttation and bleeding in plants.
Solution 5
| Guttation | Bleeding |
| It is the process of removing excess water from plants due to excessive water buildup. | It refers to the withdrawal of water from a plant as a result of an injury. |
| Hydathodes are specialised structures that allow water to escape. | Water flows from the plant’s wounded area in the form of sap. |
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question 1: What is wilting? Some plants show wilting of their leaves at noon even when the soil is well watered, Why is it so?
Solution 1:
Wilting is the loss of cellular turgidity in plants, which causes the leaves or the entire plant to droop due to a lack of water. The rate of transpiration exceeds the rate of water absorption by roots at midday. Leaves lose their turgidity and wilt as a result of excessive transpiration.
Question 2: Why are the stomata in most plants more numerous on the lower surface of a leaf instead of being on the upper surface?
Solution 2:
The leaf’s lower surface is protected from direct sunlight. Excessive transpiration occurs when there are more stomata on the upper surface of a leaf, resulting in rapid wilting of the plant. To control the rate of transpiration, most plants have more stomata on the lower surface of the leaf.
Question 3: Suppose you have a small rose plant growing in a pot. How would you demonstrate transpiration in it?
Solution 3:
Place the little potted rose plant in a transparent polythene bag and cover it. Tie the mouth of the organism to the stem’s base. Allow the plant to stay in direct sunshine for an hour or two.

Due to the saturation of water vapour given out by the leaves, drops of water will soon develop on the inner surface of the bag. In the same way, an empty polythene bag with its mouth tied and stored in the sun will display no water drops. This is the control to demonstrate that plants transpire water as water. The drops will be confirmed as water only if tested with dry cobalt chloride paper.
Question 4: What is a potometer?
Solution 4:

A potometer is a device that measures the rate at which a plant takes in water. This amount of water consumed is nearly equivalent to the amount of water lost through perspiration. Potometers do not measure the amount of water lost by transpiration, but rather the amount of water taken in by the shoot.
Question 5: What is lenticular transpiration? Mention one major difference between lenticular transpiration and stomatal transpiration.
Solution 5:
Lenticular transpiration is the process of breathing through lenticels, which are tiny apertures on the surface of aged stems.
The plant controls stomatal transpiration by changing the size of the stoma, but this does not happen with lenticular transpiration. This is due to the fact that the lenticels never close and are always open.
Stomatal transpiration exceeds lenticular transpiration by a significant margin.
Question 6: List any three major factors that accelerate the rate of transpiration.
Solution 6:
The factors that accelerate the rate of transpiration are:
(i) High intensity of sunlight
(ii) High temperature
(iii) Higher wind velocity
(iv) Decrease in atmospheric pressure
Question 7: There is a general belief that forests tend to bring more frequent rains. Can you explain it scientifically?
Solution 7:
Plants, particularly trees, abound in forests. Every day, each plant loses water to the atmosphere in the form of water vapour through transpiration. Each day, a huge apple tree might lose up to 30 litres of water. Forests release a massive amount of water into the sky. This increases the amount of moisture in the atmosphere, resulting in greater rain.
Question 8: List the four advantages of transpiration to the plants.
Solution 8:
The following are some of the benefits of transpiration to plants:
(i) Transpiration cools the plant body by reducing the temperature of the leaf surface due to evaporation of water.
(ii) Transpiration aids sap ascent by creating a suction force that acts from the plant’s top.
(iii) Water and mineral salts are distributed throughout the plant body by transpiration.
(iv) Excess water is removed through transpiration.
Question 9: Mention any three methods by which the plants tend to reduce transpiration.
Solution 9:
(i) If the leaves’ water content drops for any cause, the guard cells become flaccid, blocking the stomatal opening and preventing transpiration.
(ii) To limit transpiration, some plants have sunken stomata, while others have fewer stomata.
(iii) As an adaptation to reduce transpiration, certain plants drop, lose, or convert their leaves into spines.
(iv) The leaves, like those of the Banyan tree, may be wrapped in a thick cuticle to minimize transpiration.
Question 10: Droplets of water may sometimes be seen along the margins of the leaves of a banana plant, growing in wet soil, in the mornings. Are these dew drops? Comment upon your answer.
Solution 10:
They aren’t dew drops, to be sure.
This is the water that the plant body exudes through guttation. The banana plant’s transpiration is impeded since it grows in a humid climate. The roots, on the other hand, continue to absorb water from the earth. This creates a tremendous amount of hydrostatic pressure within the plant, forcing excess water out of the hydathodes, which are holes found at the ends of veins in the leaf. This is most noticeable in the mornings.
Question 11: Briefly explain how the rate of transpiration is affected by
(a) Intensity of light
(b) Humidity of the atmosphere
Solution 11:
a) Light intensity – During the day, the stomata are open to allow carbon dioxide to diffuse inside for photosynthesis. They are closed at night. As a result, there is increased transpiration during the day. The stomata are partially closed and transpiration is reduced during cloudy days.
b) Atmospheric humidity: When the air outside is humid, the rate of transpiration is lowered because internal water vapour diffusion is hampered.
Structured / Application / Skill Type Questions:
Question 1: In an experiment, four freshly plucked leaves (A-D) of a plant, such as those of china – rose, were treated as follows:
(a) Coated with Vaseline on its upper surface.
(b) coated on the lower surface.
(c) coated on both surface
(d) left uncoated.
All the four leaves A, B, C & D were left in a room for about 24 hours.
(i) which leaf would become most limp? Why?
(ii) which leaf would show least limping? Why?
Solution 1:
(i) The leaf D would become extremely saggy. This is because, because leaf D is uncoated, water would be lost through transpiration from both the upper and bottom surfaces.
(ii) Leaf C would have the least limping because its upper and lower surfaces had been treated with vaseline. Because the stomatal holes are sealed by vaseline, no water is lost from the leaf by transpiration.
Question 2: Given below is a diagrammatic sketch (surface view) of a stomatal apparatus from a dicot leaf.

(a) Label the parts numbers 1-3
(b) Is this state, open or closed?
(c) Is this stoma, of a dicot leaf or a monocot leaf?
(d) Redraw a sketch of the stomatal apparatus in the state opposite to the one shown here.
Solution 2:
a)
1- Guard Cell
2- Inner wall of the Guard Cell 3- Stoma/Stomatal Aperture
b) It is an open state.
The structure of the stoma is the same in monocots and dicots. As a result, the stoma in the diagram can be either monocot or dicot.

Question 3:
Given alongside is the diagram of an experimental set-up to demonstrate a certain phenomenon in plants.
(a) Name the phenomenon being demonstrated.
(b) what is the purpose of putting oil the test tube?
(c) Would it make a difference if the experimental set – up is kept in bright sunshine?
(d) what is the purpose of the spring balance in the set-up?
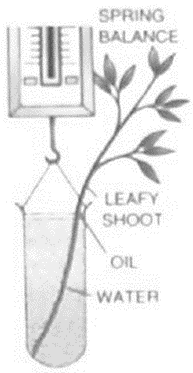
Solution 3:
(a) Transpiration
(b) Oil is sprayed over the surface of water to keep it from evaporating.
(c) The rate of transpiration will increase. Transpiration would happen more quickly. Changes will be visible in a shorter period of time.
(d) The spring balance measures the set-up’s weight change over time. This is because the plant creates a suction force as it transpires, allowing the roots to take more water from the test tube. As a result, the amount of water in the test will be lowered. As a result, the overall weight of the set will be reduced.






