Students should refer to Transpiration ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions provided below with solutions. These will help the students to understand the type of questions which have been asked in previous year examinations and the type of solutions which the student should give to get good marks. You should also refer to ICSE Class 10 Biology Sample papers for more practice
ICSE Class 10 Biology Transpiration Important Questions
Students should learn the important questions and answers given below for Chapter Transpiration in Biology for ICSE Class 10. These board questions are expected to come in the upcoming exams. Students of ICSE Class 10th should go through the Important questions and answers ICSE Class 10 Biology which will help them to get more marks in exams.
Transpiration ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions
Transpiration ICSE Class 10 Biology
Question: Give biological reasons for the following :
a. In hot summer months most herbaceous plants wilt at noon and recover in the evening.
Ans. During the day when the temperature is high and light intensity is high, the rate of transpiration is high. Thus loss of water from leaves, by transpiration far exceeds the absorption of water by the roots, Hence the plant shows wilting due to loss of turgidity. But in the evening when the rate of transpiration reduces the cells of the plant recover again their lost state, due to lower temperature and partially closed stomata.
b. Transpiration cools the plant
Ans. Evaporation of water vapours reduces the temperature of the leaf surface as the latent heat required to convert water into water vapours is taken from the plant body, there by lowering the temperature.
c. Transpiration is a price plant pays for photosynthesis
Ans. During the day time the stomata open for allowing carbon dioxide to diffuse in for the process of photosynthesis. Transpiration occurs along with photosynthesis and most of the water taken in by the plant is lost in the form of water vapour. Thus transpiration is a price a plant pays for photosynthesis.
d. Leaves are reduced to spines in cactus.
Ans. Leaves are modified to form spines is desert plants like cactus to reduce the leaf lamina to reduce the surface area for loss of water by transpiration and evaporation.
Question: Study the diagram given alongside and answer the question.
a. Label the parts marked by guidelines
Ans. 1. Hair
2. Lower epidermis
3. Cuticle

b. State another such adaptation with an example which serves the same purpose.
Ans. Thick cuticle eg. Banyan.
c. Name the adaptation shown.
Ans. Sunken stomata.
d. How does this adaptation help the plant?
Ans. This adaptation helps the plant to reduce excessive transpiration and hence prevents from wilting.
e. Name the plant in which such an adaptation is seen.
Ans. Oleander (Nerium).
Question: Explain kinds of transpiration
Ans. (Transpiration from the aerial parts of plant occurs by one of the following ways :
(a) Stomatal transpiration : Stomata remain open during the day so that CO2 can diffuse in to enable photosynthesis. Simultaneously water vapours from the cells diffuse out.
(b) Cuticular transpiration : Small amount of water escapes directly from the surfaces of leaves and stem.
(c) Lenticular transpiration : Lenticels are always open and vapours escapes through the loose mass of cells.
Question: Differentiate between the following pairs :


Question: Bleeding occurs in plants also. Explain.
Ans. Bleeding is the exudation of sap from the injured parts of the plants. When a cut or incision is made in the stem of a plant growing in a well watered soil, xylem sap starts oozing out due to root pressure. This is known bleeding in plants.
Question: Disadvantages of transpiration in plant.
Ans. (a) Wilting : Excessive transpiration leads to wilting of plants or the plant may die, this is because the rate of transpiration exceeds the rate of absorption.
(b) Stunted growth : If transpiration is high and water is not sufficient for all the vital growth process the plant may show retarded growth.
Question:: Briefly explain how the rate of transpiration is affected by :-
a. Intensity of light
b. Humidity of the atmosphere
c. Wind velocity
Ans. a. During high intensity of light, the stomata are open wider, thus more water vapours escapes. Thus rate of transpiration is high. In cloudy conditions the stomata are partially closed thus rate of transpiration is decreased.
b. When the humidity is high the rate of transpiration reduces as the surrounding air cannot hold any more water.
c. In the windy conditions the rate of transpiration is high as the water laden air around the plant is moved away and the dry air has ability to take in more water vapours.
Question: How is it different from transpiration?
Ans.

Question: Mention the advantages of transpiration to plants.
Ans. (a) Ascent of sap : Due to transpiration a suction force is created at the top which helps to draw water from the cells in the lower region.
(b) Distribution of water and minerals : Due to transpiration the transpiration pull that is created helps in distribution of water and minerals through out the plant, body.
(c) Removal of excess of water from the plant.
Question: During a hot summer day sometimes, why do the leaves of a plant remain wilted even if the plant is watered properly?
Ans. When the rate of transpiration exceeds the rate of absorption of water usually during the hot summer days the leaves remain wilted.
Question: Give advantages of transpiration to the surrounding.
Ans. Cools the environment : The moisture released from plants, during transpiration contributes towards lowering the temperature of the surrounding.
Question: The figure along represents an experiment performed to demonstrate certain phenomenon in plants. The set up was kept in sunlight for about two hours.
a. What is the aim of the experiment ?
Ans. To show transpiration
b. What precautions should be taken for proper results in the experiment?
Ans. (i) Bell jar should be air tight to prevent the entry of water vapour from outside
(ii) Do not keep the apparatus in very hot place as the water vapour will not condense.
c. Suggest a suitable control experiment for comparison.
Ans. Take a bell jar set up but without plant as a control
d. What do you observe in the experiment as an evidence of the process stated in
(a) and (b) above.
Ans Droplets of water can be seen on the inner surface of the bell jar.
e. Define the process mentioned in (a) above.
Ans. It is the loss of water in the form of water vapour from the aerial parts of the plant

Question: What is guttation?
Ans. It is process by which water droplets ooze out of special structures called hydathodes along the margin of the leaves, when hydrostatic pressure is high and transpiration is low.
Important terms
(a) Transpiration : It is a process during which water in the form of water vapour is lost through the aerial parts of the plant. (Stomata, lenticles, cuticle)
(b) Wilting : The drooping down of the plant due to water deficit is called wilting.
(c) Bleeding : It is the exudation of the cell sap from the injured parts of plant.
(d) Stomata : Stomata are tiny pore present in the epidermis of the leaf and young stem through which diffusion of gases occur.
(e) Lenticels : They are small pores on the stems that allows passage of gases to and fro from the internal tissues.
(f) Cuticle : Cuticle is the waxy covering present generally on the dorsal surface of the leaf which checks the loss of water due to evaporation.
(g) Anti-transpirants : These are chemical substance which minimizes the rate of transpiration. Some anti-transpirants are silicon emulsions, phenylmercuric acetate etc.
Question: What are the external factors that affect the rate of transpiration?
Ans. (a) Intensity of light : More is the light intensity during day high is the rate of transpiration as the stomata are open wide.
(b) Temperature : Increase in temperature allows more water to evaporate. At optimum temperature the rate of transpiration is high.
(c) Humidity : The rate of transpiration is reduced when the air outside is saturated with moisture. i.e. higher the humidity-lesser is the rate of transpiration.
(d) Wind velocity : The wind takes away the water vapour, higher the wind velocity more will be the rate of transpiration.
(e) Carbon dioxide concentration : When the CO2 concentration in the atmosphere increases above optimum level it leads to closure of stomata partially thus reducing the rate
Question: Write the mechanism of stomatal transpiration.
Ans.

Question: Given adjacent is the diagram of an experiment set up to study the process of transpiration in plants. Study the same and then answer the question that follow.

a. Define the term ‘transpiration’.
Ans. Transpiration is the process by which water as water vapours is lost through internal tissue from the aerial parts of the plant especially the leaves.
b. Why are the glass slides placed over the dry cobalt chloride papers?
Ans. In order to prevent atmospheric moisture from coming in contact with the cobalt chloride paper.
c. Is the experimental leaf monocot or dicot? Give a reason to support your answer.
Ans. Dicot. It has reticulate / network venation.
d. After about half an hour what change if any, would you expect to find in the cobalt chloride paper?
Ans. Paper on dorsal side remains blue in colour, dicot leaves have no stomata on the dorsal side. Paper on ventral side turns pink in colour, stomata are present on the ventral side in dicot leaves.
e. What is the colour of the dry cobalt chloride paper?
Ans. Blue.
Question: Given along is an apparatus used to study a particular process in plants. Study the same and answer the questions that follow.
g. What happens to the movement of the air bubble if the apparatus is kept in?
a. Dark b. Sunlight c. Front of the fan
Ans. a. Dark : It will move, i.e., very slowly as transpiration will not occur due to closure of stomata and the rate of cuticular transpiration is very slow.
b. Sunlight : The bubble will move faster due to rapid transpiration because of open stomata.
c. Front of the fan : Bubble will move faster as transpiration increases with the velocity of wind due to replacement by unsaturated air.
b. Name the apparatus.
Ans. Ganong’s Potometer
c. What is the role of capillary tube?
Ans. Capillary tube gives readings for the volume of water lost in a given time.
d. Which phenomenon is being studied with the help of this apparatus?
Ans. The rate of water intake by a plant, is almost equal to the water lost through transpiration.
e. What is the role of air bubble in the experiment?
Ans. The bubble moveing along in the capillary tube shows the pull of water. The time taken for the bubble to move between two fixed points marked on the horizontal tube should be recorded
f. Mention one limitation of this apparatus?
Ans. Any changes in the outside air or temperature may effect the position of the air bubble in the capillary tube.
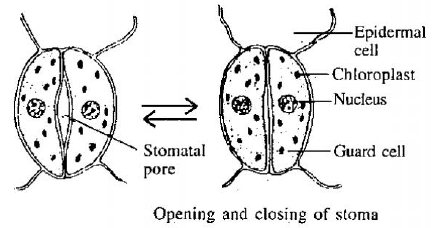
Question: Give the mechanism of opening and closing of stomata.
Ans.
Question: Given along is an apparatus used to study a particular process in plants. Study the same and answer the questions that follow.
g. What happens to the movement of the air bubble if the apparatus is kept in?
a. Dark b. Sunlight c. Front of the fan
Ans. a. Dark : It will move, i.e., very slowly as transpiration will not occur due to closure of stomata and the rate of cuticular transpiration is very slow.
b. Sunlight : The bubble will move faster due to rapid transpiration because of open stomata.
c. Front of the fan : Bubble will move faster as transpiration increases with the velocity of wind due to replacement by unsaturated air.
b. Name the apparatus.
Ans. Ganong’s Potometer
c. What is the role of capillary tube?
Ans. Capillary tube gives readings for the volume of water lost in a given time.
d. Which phenomenon is being studied with the help of this apparatus?
Ans. The rate of water intake by a plant, is almost equal to the water lost through transpiration.
e. What is the role of air bubble in the experiment?
Ans. The bubble moveing along in the capillary tube shows the pull of water. The time taken for the bubble to move between two fixed points marked on the horizontal tube should be recorded
g. Mention one limitation of this apparatus?
Ans. Any changes in the outside air or temperature may effect the position of the air bubble in the capillary tube.

Question: Write one main function of the following :
a. Stomata b. Hydathodes c. Leaf spines d. Cuticle e. Lenticels f. Xylem
Ans. a. Stomata : Stomata help in diffusion of gases in the leaves.
b. Hydathodes : Hydathodes allow escapes of water droplets by guttation when inside the tissue the hydrostatic pressure builds up.
c. Leaf spines : Spines reduce the surface area so that the loss of water due to transpiration is reduced.
d. Cuticle : Cuticle prevents loss of water from the leaves due to evaporation.
e. Lenticels : Lenticels are pores on the woody stem which allow for exchange of respiratory gases.
f. Xylem : Xylem vessels help in transportation of water from the root to other parts of the plant. It helps in ascent of sap.
Question: An experiment is set up as shown alongside. The leafy shoot was cut under water and then fixed to the glass tube with the rubber tubing. Both long tubes were filled with water and then inverted into a trough containing mercury. Study the set up and answer.

a. State 3 advantages of this process to the plant.
Ans. 1. It helps in absorption of water by roots.
2. It helps in absorption of minerals from soil water.
3. It helps in movement of water in the plants.
b. What is observed after a few hours?
Ans. The level of mercury in the glass tubing (A and B) has risen.
c. Name the process taking place in B that accounts for the change observed.
Ans. No change in the level of mercury as there is no loss of water.
d. What would you abserve if the leafy shoot was replaced by a leafless shoot? Explain.
Ans. There will be no or very less transpiration due to the absence of stomata of leaves as stomatal transpiration is always maximum.
e. Name the process taking place in A that accounts for the change observed.
Ans. Transpiration.
f. Which conducting tissue of the plant does the glass tube represent?
Ans. Xylem
g. What is the aim of the experiment?
Ans. To show that transpiration occurs from aerial parts of the plant.
Question: What is transpiration stream?
Ans. Transpiration stream is the uninterrupted movement of mineral sap through the vessels and tracheids of xylem tissue, due to transpiration.
Morphological adaptation. Since maximum water loss takes place through the leaf surface, the leaf area is considerably reduced. This is achieved in various ways.
(a) Leaves may be modified into spines as in desert plants like the cactus, or into needles as in pine.
(b) Leaves may be folded or rolled up.
(c) Leaves may be shed off as in deciduous trees.
Question: Given belolw is a diagrammatic sketch of the stomatal apparatus as seen in surface view.
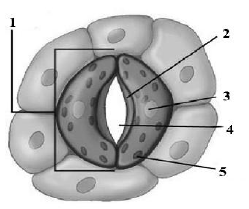
a. Is this state seen during daytime or night?
Ans. More transpiration occurs during daytime.
b. What is the function of guard cells?
Ans. Guard cells help in opening and closing of stomata.
c. What is the function of the structure shown?
Ans. Stomata helps in transpiration.
d. Label the parts marked 1 to 5.
Ans. 1. Guard cell
2. Inner thick layer of guard cell
3. Nucleus
4. Stoma
5. Chloroplast
Question: Four leaves of equal size were cut from the same plant. They were weighed and then vaseline was applied in the following waybefore leaving the set up for few days
Leaf A : Applied vaseline on both surfaces
Leaf B : Applied vaseline on lower surface
Leaf C : Applied vaseline on upper surface
Leaf D : No vaseline was applied.
Study the results of the above and answer :
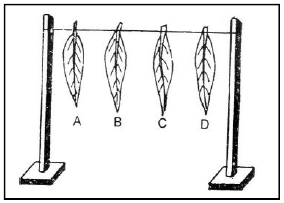
a. What is the aim of the experiment?
Ans. To find out which surface transpires more water in a dorsiventral leaf.
b. Which leaf weighs the most?
Ans. Leaf A.
c. Which leaf is least shrivelled and why?
Ans. Leaf A has vaseline smeared on both the surfaces, do not allow any transpiration and shows very little change.
d. Which leaf weighs the least?
Ans. Leaf D.
Question: Give various adaptations how plants reduce transpiration by a plant.
Ans. (a) Sunken stomata : Many plants show sunken stomata into pits which may be covered by multicellular hair in order to reduce the amount of water lost during transpirations, e.g., Nerium.
(b) Thick cuticle : Thicker the waxy covering lesser is the rate of transpiration. (Thick waxy cuticle minimizes the amount of water lost.) e.g., Banyan.
(c) Rolled leaves : On hot days the leaves get folded or rolled up to reduce exposure or surface area. e.g., young leaves of ferns.
(d) Narrow leaves : Narrower the leaves lesser is the surface area exposed so less transpiration e.g., pine.
(e) Spines : Leaves are modified to form spines (desert plants)e.g., Opuntia.
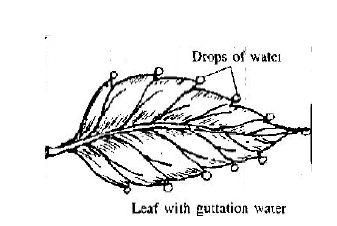
Question: Study the diagram and answer the question.
a. Name the anatomical structure involved in the process.
Ans. Hydathodes.
b. Name the process.
Ans. Guttation.
c. Name a plant where such a phenomenon is commonly seen.
Ans. Banana, strawberry
d. Explain how these drops are seen early in the morning on a humid day.
Ans. A humid environment hampers transpiration while the roots continue to absorb water from soil. This builds a big hydrostatic pressure, within the plant which leads to loss of water in the form of droplets through hydathodes. This happens in the early morning because the climate is warm and humid during the day.
Question: The apparatus shown in the following diagram is Garreau’s potometer designed to demonstrate unequal transpiration from the two surfaces of a dorsiventral leaf. Before keeping the leaf in between the cups, anhydrous calcium chloride (CaCl2) contained in two small vials were weighed and placed in both the cups. The ends of the cups were closed with corks through which two mercury manometers were connected. After few hours, CaC12, vials were taken out and weighed again.
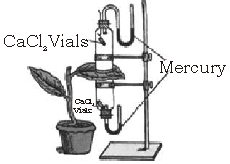
(a) What is the purpose of keeping CaCl2 vials inside the cup?
(b) After few hours CaC12 vials were taken out and weighed again. Will you expect any difference in weight? If so, give reason.
(c) What was the purpose of using a manometer?
(d) What do you mean by transpiration?
Ans. (a) Purpose of keeping CaCl2 vial is to detect the amout of water vapor released.
(b) The vial below the leaf will be heavier than the one above. This is because the lower surface shows more stomatal transpiration.
(c) Manometer is used to measure the pressure exerted by the fluid.
(d) Transpiration is the evaporative loss of water from the aerial parts (leaves and stem) of the plant.
Question: Name the following:
1. Loss of water through special pores at the tips of veins along the margin of a leaf. _________
Ans.
Guttation
2. Structure through which most of the transpiration takes place. _______
Ans.
Stomata
3. Special pores at the tips of veins through which guttation occurs. _________
Ans.
Hydathodes
4. Openings on woody stems for diffusion of gases. ___________
Ans.
Lenticels
5. A plant with sunken stomata. ___________
Ans.
Nerium
6. Instrument to measure the rate of transpiration. __________
Ans.
Potometer
7. Loss of water vapours from the aerial parts. _________
Ans.
Transpiration
8. Leaf modification in cacti to check transpiration. __________
Ans.
Spine
9. A plant with no stomata. ____________
Ans.
Hydrilla
10. The tissue that conducts water. _________
Ans.
Xylem
11. Kidney shaped cells that surround the stoma. ___________
Ans.
Guard cells
12. Exudation of sap from injured parts. ___________
Ans.
Bleeding
13. A waxy layer on the dorsal surface to check evaporation. __________
Ans.
Cuticle
14. A paper used to check transpiration. __________
Ans.
Cobalt chloride paper
15. Chemical substances used to reduce the rate of transpiration. ___________
Ans.
Dimethyl silicon
Question: Complete the following statements by choosing the correct alternative out of the choices given:
1. Special anatomical structure through which guttation occurs _________
a. Hydathode
b. Stomata
c. Lenticel
Ans.
Hydathode
2. Most transpiration in a herbaceous plant occurs through _________
a. Stomata
b. Lenticels
c. Cuticle
Ans.
Stomata
3. Which of the following is an anti-transpirant?
a. Auxin
b. Dimethyl silicon
c. Gibberellins
Ans.
Dimethyl silicon
4. Transpiration pull will be maximum under which condition?
a. Open stomata, dry atmosphere and moist soil
b. Open stomata, dry atmosphere and dry soil
c. Open stomata, high humidity and moist soil.
Ans.
Open stomata, dry atmosphere and moist soil
5. Transpiration is highest during ___________
a. Rainy season
b. Winter
c. Summer
Ans.
Summer
6. Lenticels are present on __________
a. Green stem
b. Woody stem
c. Leaves
Ans.
Woody stem
7. The rate of transpiration is more when _________
a. Atmosphere is dry
b. Temperature is high
c. Atmosphere is dry and temperature is high
Ans.
Atmosphere is dry and temperature is high
8. Which of the following is not true for transpiration?
a. It cools the plant
b. Water lost has minerals
c. Water is lost as vapours
Ans.
Water lost has minerals
9. Factor that does not affect transpiration is ___________
a. Wind
b. Age of the plant
c. Temperature
Ans.
Age of the plant
10. Colour of cobalt chloride paper when dry is _________
a. White
b. Blue
c. Pink
Ans.
Blue
11. The rate of transpiration increase with _____________
a. Increase in humidity
b. Increase in wind velocity
c. Reduced light intensity
Ans.
Increase in wind velocity
12. Which of the following is not an example of anti-transpirant?
a. Wax
b. Aspirin
c. Salt
Ans.
Salt
13. Potometer is an instrument to measure the rate of ________
a. Photosynthesis
b. Transpiration
c. Respiration.
Ans.
Transpiration
14. Which of the following is not a function of transpirant?
a. Cooling of the plant
b. Uptake of water
c. Excretion of salts.
Ans.
Excretion of salts.
15. Stomata are absent in ________
a. Grasses
b. Hydrilla
c. Balsam
Ans.
Hydrilla
Question Mention if the following statements are True or False, Correct the false statements by changing the underlined word.
1. Most transpiration occurs during midnight .
Ans.
False : Most transpiration occurs during mid-day
2. Bark of a tree helps in preventing loss of water.
Ans.
True
3. High humidity increase the rate of transpiration.
Ans.
False : Low humidity increase the rate of transpiration.
4. Stomata are located at the tips of the veins.
Ans.
False : Hydathodes are located at the tips of the veins
5. Cobalt chloride paper is an indicator of moisture.
Ans.
True
6. The intake of salts is independent of the quantity of water absorbed.
Ans.
True
7. Dry cobalt chloride paper is pink in colour.
Ans.
False : Moist cobalt chloride paper is pink in color.
8. In guttation pure water is lost as droplets.
Ans.
False : In transpiration pure water is lost as droplets.
9. More transpiration occurs from the upper surface of the leaf.
Ans.
False : More transpiration occurs from the lower/ventral surface of the leaf.
10. Low humidity favours guttation.
Ans.
False : High humidity favours guttation.
11. Stomata remain open all the time.
Ans.
False : Lenticels remain open all the time.
12. Excessive transpiration results in wilting of the leaves.
Ans.
True
13. Voltmeter is an instrument used to measure the rate of transpiration.
Ans.
False : Potometer is an instrument used to measure the rate of transpiration.
14. Guttation is the result of root pressure
Ans.
True
15. Stomata are minute openings on the surface of old stems.
Ans.
False : Lenticels are minute openings on the surface of old stems.
Q.IV. Given below is an example of a certain structure and its special functional activity. chloroplast and Photosynthesis.
In a similar way write the functional activity against each of the following:
1. Hydathodes and ________________________________
Ans.
Hydathodes and guttation
2. Leaf spines and ________________________________
Ans.
Leaf spines and prevents transpiration by reducing leaf lamina
3. Thick cuticle and ________________________________
Ans.
Thick cuticle and prevents evaporation of water from leaf surface
4. Stomata and ________________________________
Ans.
Stomata and diffusion of gases
5. Lenticels and ________________________________
Ans.
Lenticels and diffusion of gases on the stem.
Question: Fill in the blanks :
a. Dry cobalt chloride paper is __________ in colour and moist one is ________ in colour
Ans.
blue and pink
b. Transpiration is the loss of water as _________ from ________ parts of the plant.
Ans.
vapours and aerial
c. ________ is a waxy layer secreted by epidermis on the surface of the leaf.
Ans.
Cuticle
d. Nerium has ________ stomata to check transpiration.
Ans.
Sunken
e. Transpiration is __________ if outside air is more humid.
Ans.
Reduced
f. Transpiration helps in creating __________ force for uptake of water.
Ans.
suction
g. _________ occurs through _________ at the tips of veins when a high hydrostatic pressure builds up within the cells.
Ans.
Guttation and hydathodes







