Students can refer to Sources of Finance ICSE Class 10 notes and exam questions provided for ICSE students. This is an important chapter in ICSE commercial studies class 9. We have provided here questions and answers which are expected to come in the upcoming ICSE exams for class 10th. Prepared based on the latest examination pattern and guidelines issued by ICSE. You can also refer to ICSE Books in pdf available for the latest academic session.
ICSE Class 10 Commercial Studies Sources of Finance Important Questions
Students should learn the important questions and answers given below for Chapter Definitions From Topo Maps in Commercial Studies for ICSE Class 10. These board questions are expected to come in the upcoming exams. Students of ICSE Class 10th should go through the Important questions and answers ICSE Class 10 Commercial Studies which will help them to get more marks in exams.
Board Exam Questions Sources of Finance ICSE Class 10 Commercial Studies
Question: Define business finance.
Ans. Business finance may be defined as the activity concerned with planning, raising, controlling and administering of the funds used in business
Question: What are the sources of long term finance for a business enterprise ? Explain
Ans.

(i) Equity shares : Equity shares are those shares which do not carry any special or preferential rights in the payment of annual dividend or repayment of capital. The rate of dividend on such shares are not fixed. Dividend on equity shares is paid out of the residual profits left after paying interest on debentures and dividend on preference shares.
(ii) Preference shares : Preference shares are those shares which carry certain preferential or priority rights. Dividend at a fixed rate is payable on these shares before any dividend is paid on equity shares. At the time of winding up the company, capital is repaid to preference shareholders prior to the return of equity capital. Preference shares do not carry voting rights.
(iii) Retained Earnings : Retained profits refer to the profits which have not been distributed as dividends but have been kept for use in business. Profits are usually retained in the form of general reserves and reused in business. A part of the profits is transferred to the reserves every year. After a few years, it becomes a large amount which is then employed for modernisation, expansion etc. of business. Therefore retained profits are also known as ploughing back of profits, self-financing.
(iv) Debentures : Debentures constitute the borrowed funds of a company. They are known as creditorship securities because debentureholders are the creditors of a company. Debenture capital may, therefore. be called debt capital.
(v) Financial Institutions : Institutional finance means finance raised from financial institutions other than commercial bank. These financial institutions act as a intermediary or link between savers and investors. They provide finance and financial service in areas which are outside the purview of traditional commercial banking.
Question: Describe the different types of preference shares.
Ans. Types of Preference shares are :
(i) Cumulative Preference Shares : When dividends go on accumulating if they are not paid due to some reason, preference shares are said to be cumulative and will be carried forward to the next year.
(ii) Non-cumulative Preference Shares : In this type of preference shares, if dividends are unpaid because the company is unable to pay dividend in a particular year, the shareholders right to dividend in respect of that year is lost for ever.
(iii) Participating Preference Shares : These shares carry a right to share in the surplus profits left after a fixed dividend is paid on both equity and preference shares. In addition to a fixed rate of dividend, the holders of such shares get a part of residual profits.
(iv) Non-participating Preference Shares : Such preference shares carry a right of only a fixed rate of dividend and do not give their holders a right to share in the residual profits of the company.
(v) Redeemable Preference Shares : These preference shares can be refunded either on the expiry of the specified period or at the option of the company. The Companies Act had laid down that preference shares must be repayable within 20 years from the date of issue.
(vi) Irredeemable Preference Shares : Such shares are refunded only at the time of winding up of the company. They are not paid up during the lifetime of the company.
(vii) Convertible Preference Shares : Holders of these shares are given the option to convert their shares into equity shares after a fixed period.
(viii)Non-convertibale Preference Shares : Such shares cannot be converted into equity shares.
Question: What are Public Deposits?
Ans. Public deposits refer to the unsecured deposits invited by companies from the public mainly to finance working capital needs. A company can invite public deposits for a period of six months to three years. Therefore, public deposits are primarily a source of short term finance. The rate of interest on public deposits depends on the period of deposit and reputation of the company.
Question: Distinguish between cumulative and non-cumulative preference shares.
Ans.

Question: Discuss the importance of equity shares and preference shares as sources of long-term finance.
Ans. As a source of finance, Equity shares offer the following benefits :
(i) Permanent Capital : Equity shareholders provide the permanent funds of a company. There is no obligation to return the money except at the time of winding up the company.
(ii) No Obligation as to Dividend : Equity shares do not impose an obligation to pay a fixed dividend. Dividends are payable only if the company has adequate profits. Equity shareholdrs stand by the company through thick and thin.
(iii) No Chanrge on Assets : For issuing equity shares, the company is not required to mortgage or pledge its assets.
(iv) Source of Prestige : A company with substantial equity capital has a high credit standing. Creditors readily lend money to it because they regard equity capital as a safety sheild.
Advantages of Preference Shares :
(i) Appeal to Cautious Investors : Preference shares can be easily sold to investors who prefer reasonable safety of their capital and want a regular and fixed return on it. These shares carry a preferential right of repayment in the event of liquidation of the company.
(ii) No Obligation for Dividends : A company is not bound to pay dividend on preference shares if its profits in a paritcular year are insufficient. It can postpone the dividend in case of cumulative preference shares also. No fixed burden is created on its finances.
(iii) No Interference : Generally, preference shares do not carry voting rights. Therefore, a company can raise capital without dilution of control. Equity shareholders retain exclusive control over the company.
(iv) Trading on Equity : The rate of dividend on preference shares is fixed. Therefore with the rise in its earnings, the company can provide the benefits of trading on equity to the equity shareholders.
(v) No charge on Assets : Prefernce shares do not create any mortgage or charge on the assets of the company. The company can keep its fixed assets free for raising loans in future
Question: What is ADR?
Ans. An ADR is a negotiable instrument issued by an American Depository Bank certifying that shares of a non-US issuing company are hold by the depository’s custodian bank. An American Depository Receipt (ADR) is an American dollar-denominated instrument representing equity ownership in any non-American company. It represents the shares of any non-US company held on deposit by a custodian bank outside USA.
Question: Distinguish between Shares and Debentures.
Ans.

Question: Describe advantages and limitations of loans from financial institutions.
Ans. The main advantages of Institutional finance are as follows :
(i) Both risk as well as loan capital are available. Public financial institutions provide underwriting facilities also.
(ii) New companies which may find it difficult to raise finance from the public can get it from these institutions. Assistance is available when recourse to normal sources is unprofitable.
(iii) As these institutions carry out a thorough investigation before granting assistance to a concern, relationship with them helps to increase the credit-worthiness of a company.
(iv) The rate of interest and repayment procedures are convenient and economical. Facilities for repayment in easy instalments are made available to the deserving concerns.
Institutional financing involves the following limitations :
(i) The concern requiring finance from public financial institutions has to submit itself to a through investigation that involves a number of formalities and documents.
(ii) Many deserving concerns may fail to get assistance for want of security and other conditions laid down by these institutions.
(iii) These institutions place restrictions on the autonomy of management. They lay down a convertibility clause in loan agreements. In some cases, they insist on the appointment of their nominees to the Board of Directors of the borrowing company.
Question: Distinguish between convertible and non-convertible debentures.
Ans.

Question: What is IDR?
Ans. An IDR is a rupee denominated instrument that represent the share of foreign company. It is issued by a foreign company to Indian investors for raising funds from the Indian market.
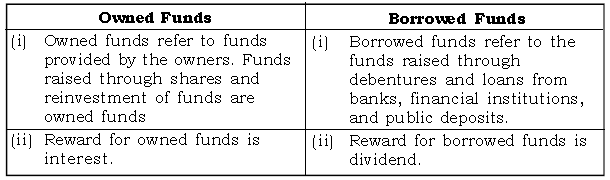
Question: Distinguish between Owned Funds and Borrowed Funds.
Ans.
Question: Discuss the importance of debentures and public deposits as sources of medium and short-term finance.
Ans. The main advantages of debentures are as follows :
(i) Appeal to Cautious Investors : Large amount of finance can be raised by issue of debentures from cautious and orthodox investors who prefer safety of investment and a fixed return. In tight money conditions, debentures are best source of finance.
(ii) Regular Return : Debentureholders are paid interest at a fixed rate and at periodical intervals irrespective of profits. Therefore, debentureholders are free from risk of fluctuations in the company’s earnings.
(iii) Safety of Investment : Debentures are usually secured by a charge on the company’s assets. Therefore, their repayment is assured.
(iv) Economical Source : A company can raise funds through debentures at a relatively low cost. This is because investors consider debentures a safe investment. Debentures can be sold more easily than shares.
(v) Freedom of Management : Debentures do not carry voting rights. Therefore, a company can raise funds without diluting or weakening the control of the existing members.
The main advantages of Public Deposits are as follows :
(i) Simplicity : Public deposits are a very convenient source of business finance. No legal formalities are involved. The company raising deposits has to simply give an advertisement and issue a receipt to each depositor.
(ii) Economy : Interest paid on public deposits is lower than that paid on debentures and bank loans. Interest paid on public deposits is tax deductible which reduces tax liability. Therefore, public deposits are a cheaper source of finance.
(iii) Flexibility : Public deposits can be raised during the season to buy raw materials in bulk and for other short-term needs. They can be returned when the need is over.
(iv) No Dilution of Control : There is no dilution of shareholer’s control because the depositors have no voting rights
(v) Wide contacts : Public deposits enable a company to build up contacts with a wider public. These contacts prove helpful in the sale of shares and debentures in future.
Question: Distinguish between Equity Shares and Preference Shares.
Ans.

Question: State any three sources of borrwed funds.
Ans. Borrowed funds refer to the funds raised through debentures and loans from banks, financial institutions and public deposits.
Question: What are retained profits ? Discuss their advantages and disavantages as a source of finance.
Ans. Reinvestment of undistributed profits is a very good source of business finance. Retained profits refer to the profits which have not been distributed as dividends but have been kept for use in business. Profits are usually retained in the form of general reserves.
Advantages :
(i) Convenience : Retained profits are the most economical and convenient source of finance. No advertisement of prospectus has to be issued. No floatation expenses or legal formalities are involved.
(ii) No Charge on Assest : No charge or mortgage is created on the company’s assets. The company is free to use its assets for raising loans in future.
(iii) No Obligations : There is no fixed burden of dividend and no obligation of repayment. Retained profits are the company’s own money. These involve no explicit cost in the form of interest or dividend.
(iv) No Interfernce : Retained profit involve no risk of control being diluted as there is no increase in the number of shareholders. Management remains independent as no restrictions are put on the management. There is operational freedom and flexibility of operations.
Disadvantages :
(i) Low Dividends : Ploughing back of profits reduces the current rate of dividends. This may result in dissatisafction among the shareholders as they do not get the expected rate of dividend.
(ii) Misuse and Speculation : Excessive reserves may make the management wasteful and extravagant management may misuse them in unprofitable or undesirable channels
(iii) Unbalanced Growth : Retained profits may interfere in the balanced industrial growth of the country. The profits which might have been invested in other industries are reinvested in the same industry.
(iv) Uncertain : Retained profits are an uncertain source of funds when the profits of the company fluctuate widely.
Question: State any three advantages of debenture issue as a souce of finance.
Ans. (i) Appeal to Cautious Investors : Large amount of finance can be raised by issue of debentures from cautious and orthodox investors who prefer safety of investment and a fixed return. In tight money conditions, debentures are the best source of finance.
(ii) Regular Return : Debenture holders are paid interest at a fixed rate and at periodical intervals, irrespective of profits. Therefore, debentureholders are free from risk of fluctuations in the company’s earnings.
(iii) Safety of Investment : Debentures are usually secured by a charge on the company’s assets. Therefore, their repayment is assured.
Question: A company has to meet its short-term financial needs. It is considering whether it should raise loans from commercial banks or invite public deposits. Discuss the merits and demerits of each form.
Ans. Raising loans from public deposits and commercial banks have the following advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages of raising loans from Public Deposits :
(i) Simplicity : Public deposits are a very convenient source of business finance. No legal formalities are involved. The company raising deposits has to simply give an advertisement and issue a receipt to each depositor.
(ii) Economy : Interest paid on public deposits is lower than that paid on debentures and bank loans. Interest paid on public deposits is tax deductible which reduces tax liability. Therefore, public deposits are a cheaper source of finance
(iii) Flexibility : Public deposits can be raised during the season to buy raw materials in bulk and for other short-term needs. They can be returned when the need is over.
(iv) No Dilution of Control : There is no dilution of shareholer’s control because the depositors have no voting rights.
Disadvantages of raising loans from Public Deposits :
(i) Uncertainty : Public deposits are an uncertain and unreliable source of finance. The depositors may not respond when the company needs funds. If a large number of depositors simultaneously withdraw their deposits the company may find it difficult to repay a huge sum at once.
(ii) Limited Funds : A limited amount of funds can be raised through public deposits due to legal restrictions and procedural difficulties.
(iii) Temporary Finance : The maturity period of public deposits is short. The company cannot depend upon public deposits for meeting longterm financial needs.
Advantages of raising loans from commercial banks :
(i) Banks provide funds to business firms as and when needed. Timely financial assistance is available
(ii) Banks keep the information given by the borrowers confidential. Secrecy of business is maintained.
(iii) Banks are an easier source of funds because issue of prospectus, and underwriting formalities are not involved.
(iv) Bank loan is a flexible source of finance as the loan amount can be incerased or repaid as per the needs of business.
Disadvantages of raising loans from commercial banks :
(i) Finance is avaible for short periods Extension or renewal of loan is difflcult and uncertain
(ii) Procedure for raising finance is cumbersome as bank make detailed investigation of the borrower’s business.
(iii) Banks insist on personal guarantee and security of assets.
(iv) Banks many put restrictions on the sale of mortgaged goods causing difficulty in the working of business.
Question: Name two main financial institutions in India.
Ans. Some of the prominent institutions are as follows :
(i) Industrial Finance Corporation of India (now IFCI Ltd.)
(ii) Industrial Credit and Investment Corporaiton of India (now ICICI Bank)
(iii) Industrial Development Bank of India (now IDBI Ltd.)
(iv) State Financial Corporations (SFCs)
Question: What is GDR?
Ans. A GDR is an instrument which a company issues in US dollar in order to collect foreign capital. It is traded on all those foreign stock exchanges where it is listed. These can be purchased and sold only on stock exchange. The term global means the GDRs can be issued in any foreign country. Companies with a good track record issue GDRs.
Question: What are the full forms of IDR and ICD ?
Ans. Indian Depository Receipts (IDRs) and Inter Corporate Deposits (ICD)
Question: Name three sources of owned funds for business.
Ans. Equity shares, preference shares and retained profit are sources of owned funds.
Question: Explain the pros and cons of public deposits as a source of business finance.
Ans. Advantages of Public Deposits :
(i) Simplicity : Public deposits are a very convenient source of business finance. No legal formalities are involved. The company raising deposits has to simply give an advertisement and issue a receipt to each depositor.
(ii) Economy : Interest paid on public deposits is lower than that paid on debentures and bank loans. Interest paid on public deposits is tax deductible which reduces tax liability. Therefore, public deposits are a cheaper source of finance.
(iii) Flexibility : Public deposits can be raised during the season to buy raw materials in bulk and for other short-term needs. They can be returned when the need is over.
(iv) No Dilution of Control : There is no dilution of shareholer’s control because the depositors have no voting rights.
Demerits of Public Deposits :
(i) Uncertainty : Public deposits are an uncertain and unreliable source of finance. The depositors may not respond when the company needs funds. If a large number of depositors simultaneously withdraw their deposits the company may find it difficult to repay a huge sum at once.
(ii) Limited Funds : A limited amount of funds can be raised through public deposits due to legal restrictions and procedural difficulties.
(iii) Temporary Finance : The maturity period of public deposits is short. The company cannot depend upon public deposits for meeting longterm financial needs.
Question: What are the retained earnings ?
Ans. Retained profits refer to the profits which have not been distributed as dividends but have been kept for use in business. Profits are usually retained in the form of general reserves and reused in business.
Question: Describe the characteristics of differnt kinds of shares which a public company can issue ?
Ans. The following are the features of ordinary share :
(i) It is an indivisible part of the capital of a company.
(ii) It confers certain rights on its holder, e.g. dividend, voting power, return of capital, etc.
(iii) It creates certain liabilities on its holder.
(iv) Each share has a distire.
(v) Each share has a nominal
(vi) The holder of a share certificate under company.
(vii It is a movable proper transferred in the man the Articles of the company.
The following are the features of preference share :
(i) Preference shares have the characteristics of both equity shares and debentures. Like equity shares, dividend on preference shares is payable only when there are profits and according to the terms of issue.
(ii) Preference shares are similar to debentures in the sense that the rate of dividend is fixed and preference shareholders do not generally enjoy voting rights.
(iii) Therefore, preference shares are a hybrid form of financing.
Question: The directors of a company have decided to modernise the plant and machinery at an estimated cost of rupees one crore. State the merits and demerits of issuing equity shares for the purpose.
Ans. As a source of finance, equity shares offer the following benefits :
(i) Permanent Capital : Equity shareholders provide the permanent funds of a company. There is no obligation to return the money except at the time of winding up the company.
(ii) No Obligation as to Dividend : Equity shares do not impose an obligation to pay a fixed dividend. Dividends are payable only if the company has adequate profits. Equity shareholders stand by the company through thick and thin.
(iii) No Charge on Assets : For issuing equity shares. The company is not required to mortagage or pledge its assets.
(iv) Source of Prestige : A company with substantial equity capital has a high credit-standing. Creditors readily lend money to it because they regard equity capital as a safety sheild.
Equity shares suffer from the following limitations :
(i) No Trading on Equity : If a company issues only equity shares, it cannot obtain the benefits of trading on equity. The cost of equity shares is high.
(ii) Danger of Overcapitalisation : Equity share capital is not refundable during the lifetime of a company. A mistake in estimating financial requirements may, therefore, result in overcapitalisation, particularly when the company’s earning capacity declines.
(iii) Perpetuation of Control : Any new issue of equity shares must be offered first to the existing shareholders. As a result there is concentration of control in a few hands.
Question: What is a debenture ?
Ans. Debentures constitute the borrowed funds of a company. They are known as creditorship securities because debentureholders are the creditors of a company. Debenture capital may, therefore, be called debt capital.
Question: What are retained profits called “self financing” ?
Ans. Retained profits refer to the profits which have not been distributed as dividends but have been kept for use in business. Profits are usually retained in the form of general reserves and reused in business. A part of the profits is transferred to the reserves every year. After a few years, it becomes a large amout which is then employed for modernisation, expansion etc. of business. Therefore retained profits are also known as ploughing back of profits, self-financing.
Question: Explain the role of IDR, ADR and GDRs as sources of finance for Indian industries.
Ans. The role of GDRs are as under :
GDR stands for Globle Depository Receipts
(i) GDRs are denominated in US dollar.
(ii) GDRs can be listed on any American or European stock exchange.
(iii) One GDR can represent more than one share.
(iv) The holder of GDRs can get them converted into shares.
(v) The holder of GDRs has no voting rights in the company. But the shareholders do have voting rights.
(vi) Though GDRs represent the issuing company’s shares these have separate entity
The role of ADRs are as under :
ADR stands for American Depository Receipts
(i) ADRs are denominated in US dollar.
(ii) These are issued only to American investors.
(iii) ADRs can be listed on any stock exchange in USA.
(iv) A single ADR can represent more than one share e.g. one ADR = ten share.
(v) The holders of ADRs have no voting rights.
The role of IDRs are as under :
IDR stands for Indian Depository Receipts
(i) IDRs are denominated in Indian rupee.
(ii) These are issued by a foreign company in India.
(iii) IDRs can be listed on any stock exchange in India.
(iv) A single IDR can represent more than one share, e.g. one IDR = 10 shares.
(v) Holders of IDRs have no voting rights.
(vi) Holders of IDRs can get them converted into shares after one year from the date of issue.
(vii) The Indian Depository will distribute the dividend to the holders of IDRs
Question: Give the full forms of (a) ADRs (b) GDRs
Ans. (a) American Depository Receipts (ADRs)
(b) Global Depository Receipts (GDRs)

We hope you like the above provided Sources of Finance ICSE Class 10 notes and questions with solutions. In case you are searching for more study material then you can send us your comments in the box below. Our team of ICSE teachers will work to provide you the ICSE study material for free.


