Students should refer to The Excretory System ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions provided below with solutions. These will help the students to understand the type of questions which have been asked in previous year examinations and the type of solutions which the student should give to get good marks. You should also refer to ICSE Class 10 Biology Sample papers for more practice
ICSE Class 10 Biology The Excretory System Important Questions
Students should learn the important questions and answers given below for Chapter The Excretory System in Biology for ICSE Class 10. These board questions are expected to come in the upcoming exams. Students of ICSE Class 10th should go through the Important questions and answers ICSE Class 10 Biology which will help them to get more marks in exams.
The Excretory System ICSE Class 10 Biology Board Exam Questions
The Excretory System ICSE Class 10 Biology
Question. Name the end products of metabolism removed from the body?
Ans. Metabolic wastes or nitrogenous waste.
Question. What happens if waste products are not eliminated from the body?
Ans. If waste products are not eliminated from the body, they accumulate in the body and may prove toxic and fatal to the body.
Question. What are excretory organs?
Ans. The organs which remove metabolic wastes from the body are called excretory organs.
Question. Name the knot of blood capillaries enclosed by Bowman’s capsule
Ans. Glomerulus
Question. What is the function of renal artery?
Ans. Renal artery brings oxygenated blood along with toxic nitrogenous wastes.
Question. What is ‘excretion’?
Ans. The process by which metabolic wastes are eliminated from the body is called excretion.
Question. Give the functions of kidney.
Ans. Functions of kidneys.
(a) Kidneys filter blood.
(b) Kidneys produce urine
(c) Osmoregulation – maintaining / regulation of osmotic pressure of blood (i.e., water and salt concentration)
(d) The kidney regulates water, electrolyte and acid-base content of the blood.
(e) The kidney removes the excess of foreign substances such as drugs, pigments, etc.
(f) The kidney regulates the chemical composition of body fluids by removing the substances which are in excess of immediate need.
Question. What are ureters?
Ans. The ducts that carry urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder or cloaca are called ureters.
Question. What is urinary bladder?
Ans. The urinary bladder is a hollow muscular bag situated in the lower abdominal cavity serving as a reservior for urine.
Question. What is the function of urinary bladder?
Ans. The urinary bladder stores the urine till it is released through urethra.
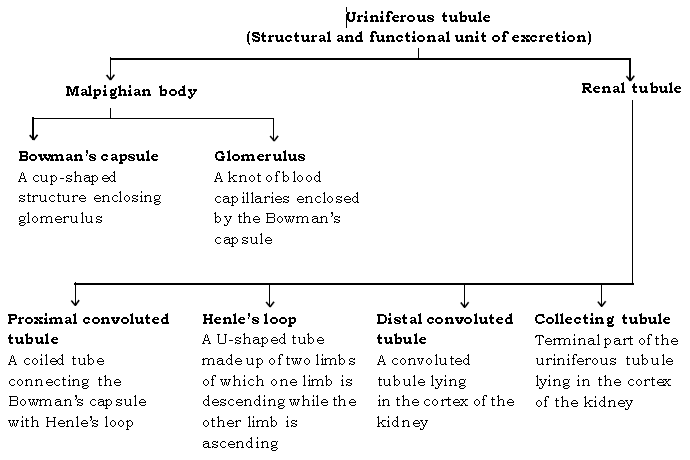
Question. What are the two major parts of uriniferous tubule?
Ans. The two major parts of uriniferous tubule are :
(1) Malpighian corpuscle, and (2) Renal tubule
Question. What are the functions of urethra?
Ans. (i) In males, the urethra extends up to the tip of the penis and serves as a common passage for both urine and sperms.
(ii) In females, the urethra is a short tube, opening separately in front of the vagina. In females, the urethra carries urine exclusively.
Question. Name the vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the kidney.
Ans. Renal vein
Question. Name the artery which enters the kidney
?Ans. Renal artery
Question. Name the constituents of cortex.
Ans. The cortex consists of glomeruli, renal corpuscles and part of nephrons.
Question. What is the approximate length of nephron in a human being?
Ans. 3 cm
Question. The afferent arteriole of the glomerulus is wider in diameter than the efferent arteriole. Give reasons.
Ans. (a) The wider diameter of the afferent arteriole allows the blood to enter the glomerulus with the great pressure. As a result, the ultrafiltration of blood occurs, through the glomerulus into the Bowman’s capsule
(b) Therefore, the afferent arteriole of the glomerulus has greater diameter than the efferent arteriole.
Question. What is the medulla composed of?
Ans. The medulla is composed of tubular parts of the nephrons and blood vessels which together form renal pyramids.
Question. What are the major excretory (waste) products of our body?
Ans. Carbon dioxide, nitrogenous compounds, bile pigments and acids, and salt and water are the major excretory products of our body.
Question. Name the structural and functional unit of kidney.
Ans. Nephron or uriniferous tubule.
Question. Give the function of Malpighian corpuscle.
Ans. Malpighian corpuscle maintains blood circulation under high pressure and promotes ultrafiltration.
Question. What is hilum?
Ans. The longitudinal opening seen on the concave side of each kidney is called hilum.
Question. Define afferent arteriole.
Ans. The branch of renal artery that enters the Malpighian corpuscle is called afferent arteriole.
Question. What is ultrafiltration?
Ans. The filtration of blood brought about under pressure in the kidney to remove nitrogenous waste in the form of urine, is known as ultrafiltration.
Question. What is urethra?
Ans. Urethra is a tube–like structure that arises from the urinary bladder.
Question. What does Malpighian corpuscle consist of?
Ans. Malpighian corpuscle consist of glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule.
Question. How are nitrogenous compounds formed as waste?
Ans. (i) The excess amount of proteins or amino acids are initially broken down into nitrogenous compounds like ammonia.
(ii) Ammonia is then transformed into less toxic substances such as urea and uric acid in the liver.
Question. How is glomerulus formed?
Ans. Glomerulus is formed by afferent arteriole, a branch of renal artery, which after entering the Bowman’s capsule breaks up into fine capillaries forming a knot (glomerulus).
Question. Name the artery which is formed by the fusion of glomerular blood capillaries
Ans. Efferent arteriole.
Question. What is Malpighian corpuscle?
Ans. Malpighian corpuscle is the anterior part of the uriniferous tubule.
Question. Which part of the nephron reabsorbs most of the glomerular filtrate?
Ans. Proximal convoluted tubule.
Question. Name the blood vessel through which filtered blood leaves the glomerulus.
Ans. Efferent arteriole.
Question. What is the source of urine formed in kindeys ?
Ans. Kidneys form urine from blood plasma.
Question. What are the substances, reabsorbed by the proximal convoluted tubule?
Ans. All of glucose, amino acids, vitamins, hormones and nearly 80% of the sodium chloride and water.
Question. Name the blood vessel which supplies blood to glomerulus.
Ans. Afferent arteriole.
Question. Which part of uriniferous tubule does the function of tubular secretion?
Ans. Distal convoluted tubule.
Question. Sketch and label the excretory organs of man
Ans.
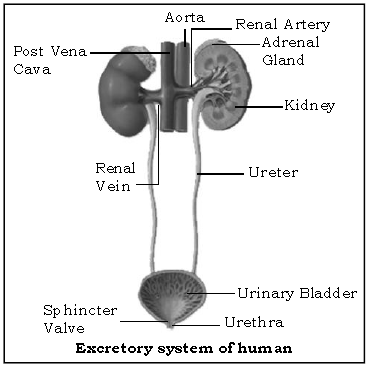
Question. In what form are nitrogenous wastes such as urea, uric acid and excess of water removed from our body?
Ans. Nitrogenous wastes such as urea, uric acid and excess of water are removed from our body in the form of urine.
Question. Name the blood vessel which supplies blood to different organs, from glomerulus.
Ans. Efferent arteriole.
Question. What is micturition?
Ans. The process leading to the removal of urine from the urinary bladder through the urethra under the impulse from the nevous system is called micturition or urination.
Question. Which part of the nephron shows the highest concentration of glucose
Ans. Bowman’s capsule
Question. Name the tube-like structure which runs through the kidney.
Ans. Renal tubule
Question. What do you mean by diuresis?
Ans. The process involving the secretion and passage of large quantities of urine is known as diuresis
Question. Name the part of kidney which acts as an ultrafilter.
Ans. Glomerulus, enclosed by Bowman’s capsule.
Question. What do you mean by tubular secretion?
Ans. Some substances such as the ions of potassium, ammonia, hydrogen, creatinine, etc., which escape ultrafiltration are absorbed by the cells of the uriniferous tubules which secrete them into the lumen of the uriniferous tubule. This process is called tubular secretion. These substances and also sometimes drugs like penicillin are passed into forming urine in the distal convoluted tubule.
Question. What are the various steps involved during the formation of urine?
Ans. The various steps involved during the formation of urine are :
(a) Ultrafiltration
(b) Selective reabsorption and
(c) Tubular secretion
Question. What is selective reabsorption?
Ans. The reabsorption of essential substances like glucose, water and certain salts by the cells of the uriniferous tubule from the glomerular filtrate, is called selective reabsorption. This reabsorption is only to the extent that the normal concentration of the blood is not disturbed. This is done by PCT and loop of Henle.
Question. Name the part of nephron that contains the least concentration of urea.
Ans. Renal (Bowman’s) capsule
Question. Sketch and label the V.S. of human kidney.
Ans.
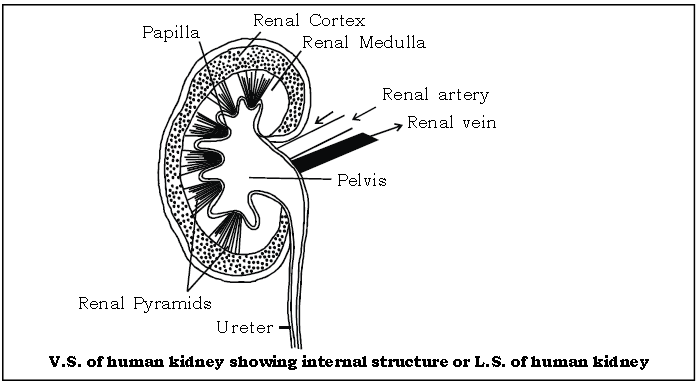
Question. Name the part of nephron that contains the least concentration of glucose.
Ans. Proximal convoluted tubule and collecting tubule.
Question. Which hormone regulates the urine output?
Ans. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secreted by the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland. It regulates the concentration of urine by water reabsorption in nephrons.
Question. What is dialysis? Explain the process.
Ans. (i) Dialysis is a process by which small molecules are separated from larger molecules using a semi-permeable membrane.
(ii) In cases of kidney disease or failure, the kidney machine which is used for cleansing the blood works on the dialysis principle. In this method, the arterial blood from the patient’s arm is pumped through the dialysis tube and then brought back into the vein of the recipeint.
(iii) Holes in the tubing of kidney machine allow small molecules such as glucose, salt and urea to diffuse out in a bath of water, salts and glucose while leaving behind larger molecules like protein as albumin in the blood.
(iv) Blood dialysis or Haemodialysis seperates smaller molecules like urea and other metabolic wastes from the blood while the large once like proteins are retained in the plasma.
(v) It is also called as Artificial kidney.
Question. What is haematuria?
Ans. The condition in which blood passes out in urine is called haematuria. It can be due to kidney stone or tumour or urinary tract infection.
Question. Draw a diagram of human excretory system and label the following : Renal cortex, Renal medulla, Renal pelvis, Ureter, Urinary bladder and Urethra.
Ans.
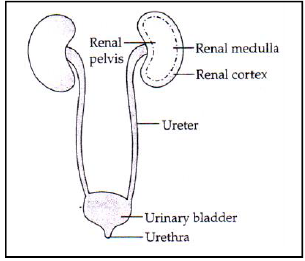
Question. What is glycosuria?
Ans. The condition in which excess glucose passes out in urine is called glycosuria. It can be due to diabetes mellitus.
Question. What are the abnormal constituents of urine?
Ans. Blood, Glucose, Bile pigments, Albumin.
Question. Name the part of nephron that contains the highest concentration of urea.
Ans. Collecting tubule.
Question. What is diuresis?
Ans. When ADH secretion is reduced, there is less reabsorption of water by nephrons and therefore more water in urine and there is an increased production of urine. This is called diuresis.
Question. What are diuretics and give examples of diuretics.
Ans. Diuretics are the substances that increase the production of urine. e.g., liquid diets, tea, coffee, alcohol etc., are examples of diuretics.
Question. What is gout?
Ans. Uric acid is relatively less soluble in water and may crystallize and get deposited in the joints of the body resulting in a condition called gout.
Question. What are kidney stones?
Ans. Excessive uric acid and some salts like calcium oxalate forms stones in the kidney and these are known as kidney stones.
Question. Draw a well-labelled diagram of nephron.
Ans.
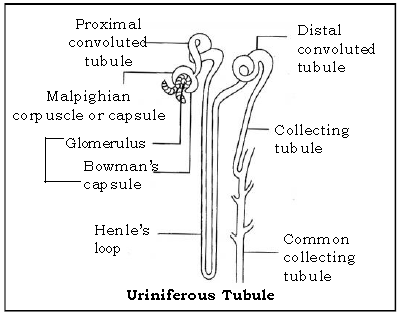
Question. What is osmoregulation?
Ans. Kidneys regulates the composition of blood i.e., percentage of water and salts in it. Thus it maintains the osmotic pressure of the blood. This process is known as osmoregulation.
Question. What is ureotelism?
Ans. Organisms that excrete out urea as their major nitrogenous waste products are called ureotelic organisms and their system is called ureotelism . e.g. Humans.
Question. What is uricotelism?
Ans. Excretion of uric acid as major nitrogenous waste product is called uricotelism. Such organisms are called uricotelic organisms. e.g. Birds and reptiles.
Question. What is ammonotelism?
Ans. Excretion of ammonia as major nitrogenous waste product is called ammonotelism. Such organisms are called ammonotelic organisms, e.g., Bony Fishes, Tadpole.
Question. Give reasons :
Question. Why a person urinates less and passes thicker urine in summer?
Ans. In summer, a considerable amount of water is lost in sweating/perspiration. So to maintain the osmotic pressure of blood, kidneys reabsorb more water from the glomerular filtrate and hence the urine becomes concentrated/thicker and also makes the person urinate less in summer.
Question. Why in cholera, a patient may die due to uremia?
Ans. In a disease cholera, the patient suffers from vomiting and watery bowels. His intestines are unable to absorb water into the blood. Because of this there is dehydration in the body. Due to which kidneys reabsorbs almost all the water from the urine formation and sometimes even urea. Ultimately there is reduced urination therefore accumulation of urea in the blood. This leads to toxicity and poisoing which is fatal. This condition is called as uremia.

Question. Draw a well-labelled diagram of Malpighian corpuscle.
Ans.








