Question 1: Why is cell division necessary?
Solution 1:
Cell division is necessary for an organism’s growth. It is also necessary for cells to divide in order to maintain their efficiency. Each organism needs new cells for growth, replacement, repair, and reproduction because all cells are formed by the division of pre-existing cells. Ability to grow and reproduce is the fundamental property of all living organisms.
Question 2: What do you understand by cell cycle?
Solution 2:
The seQuestionuence of events by which a cell duplicates it’s genome, synthesizes other constituents of the cell and eventually divides into two daughter cells is termed as cell cycle.
Question 3: How is interphase important?
Solution 3:
The cell cycle’s interphase is a prolonged resting phase under which the cell develops, DNA replication, RNA synthesis, and protein synthesis occurs. Interphase is essential in the cell cycle because it allows the cell to mature and grow into a mature cell before reproducing.It deals with the changes that occur in a cell and the nucleus before it enters into cell division.
Question 4: Which cell division results in formation of ova?
Solution 4:
The process of meiosis resulted in the formation of oocytes.
Question 5: Draw labeled diagram of different steps of mitosis.
Solution 5:



Question 6: Describe anaphase in mitosis.
Solution 6:
In anaphase, the two chromatids split at the centromere and start moving in opposing directions towards the poles. The spindle fibers attached to the kinetochore now shorten and daughter chromosomes begin to migrate towards the opposite poles formation of inter zonal fibres occur. The anaphase ends when the chromosomes reach the poles. Based on the length of the centromere’s arms, the chromosomes bend around it, forming a ‘V’, ‘J’, or ‘L’ shaped structure. It is the best stage to study shape of chromosomes.
Question 7: Write down the phases of mitosis.
Solution 7:
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase are the four stages of mitosis.
Question 8: Where does mitosis occur?
Solution 8:
Mitosis occurs in the somatic cell of the animals. It also occurs in the gonads for the multiplications of undifferentiated germ cell. In plants, it occurs in the dividing meristematic tissue and also a leaves flowers and fruits during growth.
Question 9: How is mitosis important?
Solution 9:
The importance of Mitosis because:
1. To growth and development of multicellular organism.
2. To Maintenance of cell size.
3. It helps in maintenance of chromosome number
4. It helps in replacing old dead and warm out cells buy the new cell
5. Helps in reproduction healing and regeneration.
Question 10: Mention characteristic features of mitosis.
Solution10:
Below are the characteristic features of mitosis:-
1. It takes place in somatic cells.
2. Chromosome number is remaining same.
3. Daughter cells produced are identical to the parent cell.
4. Increase in the number of cells.
Question 11: Give important characters of meiosis.
Solution 11:
Below are the few important characteristics of Meiosis are:
1. Meiosis is a process that happens only in germ cells.
2. Gametes are formed by this process.
3. The parent cell’s chromosome number is halved.
4. Daughter cells are distinct from their parents.
Question 12: With well labeled diagrams explain meiosis.
Solution 12:



Question 13: Where does meiosis take place in humans?
Solution 13:
In humans, meiosis occurs in the sexually reproducing organisms, testes, which produces sperm, and in the ovaries, which produces ova.
Question 14: What is the significance of meiosis?
Solution 14:
Below are the significance of Meiosis:
1. Formation of gametes.
2. Maintenance of chromosomes number.
3. Introduction of variation.
Question 15: What is the significance of crossing over?
Solution 15:
The exchange of genetic material (DNA) between non sister chromatids of the homologous chromosomes. The paternal and maternal homologous chromosomes of an organism pair up and exchange some sections of their chromatids as a result of crossing over, resulting in genetic differences. It makes each haploid cell’s genetic information
Question 16: Compare meiotic and mitotic telophase.
Solution 16:

Question 17: Is cytokinesis necessary after karyokinesis in meiosis I?
Solution 17:
No, cytokinesis is not necessary after karyokinesis in meiosis I.
Question 18: Define the following:
(i) Karyokinesis
(ii) Cytokinesis
(iii) Chiasmata
Solution 18:
1. Karyokinesis – the process of division of the nucleus that is the separation of the daughter chromosomes into two nuclei.
2. Cytokinesis – It is the division of cytoplasm, which follows karyokinesis.
3. Chiasmata – the point of attachment between homologous chromosomes after the parietal dissol of the synaptonemal complex is called chiasmata.
Question 19: How does cytokinesis differ in a plant and animal cell?
Solution 19:
In an animal cell, the division of the cytoplasm occurs by formation of furrow. Furrow starts at the periphery and the move inward, dividing the cell into two halves. In plant cells, the division of the cytoplasm occurs by formation of cell plate. Cell plate formation starts at the centre of the cell and grow outward, towards the lateral walls, dividing the cell into two halves
Question 20: Give five main differences between mitosis and meiosis.
Solution 20:
| Mitosis | Meiosis |
| 1. Karyokinesis and DNA replication occur once. | 1. Karyokinesis occurs twice, but DNA replicates once only. |
| 2. Prophase is short and is without sub-stages. | 2. Prophase I is prolonged with 5 different sub-stages. |
| 3. All chromosomes form a single plate in metaphase. | 3. Chromosomes form two parallel plates in metaphase I and one plate in metaphase II. |
| 4. Prophase chromosomes appear double from the very beginning. | 4. The chromosomes appear as single thread initially. |
| 5. On equatorial plate, chromosomes appear two threaded. | 5. On equatorial plate, chromosomes appear four threaded in metaphase I, while metaphase II is similar to metaphase of mitosis. |
Question 21: Why is reduction division important? Why is meiosis referred to as such?
Solution 21:
Reductional division is significant because it restores the number of chromosomes in a species. Meiosis is a reductional division as in meiosis the number of chromosomes of parent cell is reduced to half in the daughter cells.
Question 22: Is it right to say that meiosis is responsible for maintaining chromosome number of a species?
Solution 22:
Yes, meiosis is responsible for maintaining the chromosome number of a species as meiosis being a reductional division involves formation of daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes.
Question 23: How many daughter cells would you expect if 4 cells undergo
(i) Mitosis
(ii) Meiosis
(iii) Amitosis
Solution 23:
1. If four cells undergo mitosis, eight daughter cells will be produced.
2. Sixteen daughter cells will be produced.
3. Eight daughter cells will be produced if four cells undergo amitosis.
Question 24. Fill in the blanks:
(i) ______ takes place in body cells resulting in growth and development.
Solution:
Mitosis takes place in body cells resulting in growth and development.
(ii) The energy for cell division is stored as ______.
Solution:
The energy for cell division is stored as ATP.
(iii) Both ______ and heterotypic divisions occur in meiosis.
Solution:
Both Homotypic and heterotypic divisions occur in meiosis.
(iv) Meiotic division is also called ______ division.
Solution:
Meiotic division is also called Reduction division.
(v) ______ is the indirect cell division.
Solution:
Mitosis is the indirect cell division.
Question 25: The diagram given alongside represents a stage in cell division. Study the same and answer the Question that follow:
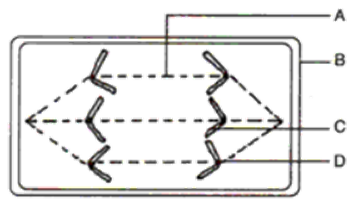
1. Identify the stage of cell division.
2. Name the parts labeled A, B, C and D.
3. What is the unique feature observed in the stage?
4. Where does this type of cell division usually occur?
5. How many daughter cells are formed from this type of cell division?
6. Is the dividing cell shown a plant or an animal cell?
Give a reason to support your answer.
Solution 25:
1. Anaphase in a plant cell
2. A – Spindle fibre
B – Cell wall
3. The homologous daughter chromatids or chromosomes begin to move towards opposite poles.
4. This type of cell division occurs usually in the somatic cells.
5. Two daughter cells are formed from this type of cell division.
6. The dividing cell shown is a plant cell because of the presence of cell wall and the absence of centriole.
Question 26: The fig. given alongside shows a certain stage in a cell division in a cell with four chromsomes

(i) Name the parts of the chromosome labeled A and B.
(ii) Name the structure C. What is its function?
(iii) Name the type of division. Give a reason.
(iv) Name the stage of division.
(v) Name the stage before and after the stage shown in the diagram.
Solution 26:
1. A – Duplicated chromosomes B – Centromere
2. The structure C is Spindle fibre. Its function is to help in the movement of chromosomes.
3. The type of cell division is mitosis because all chromosomes appear to be same as there is no crossing over.
4. Metaphase.
5. Prophase occurs before metaphase and after metaphase anaphase takes place.
Question 27: Choose the correct answer:
(i) Which division takes most time?
(a) mitosis
(b) amitosis
(c) meiosis
(d) none of these
Solution:
Meiosis
(ii) Somatic cells divide by
(a) mitosis
(b) meiosis
(c) both of these
(d) none of these
Solution:
Mitosis
(iii) Cytokinesis involves
(a) Constriction in animal cell
(b) plate formation in plant cell
(c) both of these
(d) none of these
Solution:
Both of these
(iv) In meiosis, chromosome number is reduced by
(a) 1/2
(b) 1/4
(c) 3/4
(d) 1/3
Solution:
1/2
(v) Mitosis results in
(a) gamete
(b) growth and repair
(c) both (a) & (b)
(d) none of these
Solution:
growth and repair
(vi) Centromere is related to:
(a) movement of chromosomes
(b) DNA replication
(c) all of these
(d) spindle formation
Solution:
movement of chromosomes
(vii) Crossing over is a feature of
(a) meiosis
(b) mitosis
(c) amitosis
(d) none of these
Solution:
meiosis
(viii) DNA replication takes place in
(a) mitosis
(b) amitosis
(c) meiosis
(d) both (a) and (c)
Solution:
both (a) and (c)
(ix) In an interphase cell chromosome are as
(a) microtubules
(b) chromatin
(c) flagella
(d) chromatid
Solution:
chromatin
(x) During mitosis which of the following disintegrate
(a) nucleolus
(b) nuclear membrane
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Solution:
both (a) and (b)
(xi) Chromosomes appear at equator in
(a) anaphase
(b) metaphase
(c) prophase
(d) telophase
Solution:
metaphase
(xii) Chromosomes number is halved in
(a) meiosis I
(b) meiosis II
(c) mitosis
(d) amitosis
Solution:
meiosis I
(xiii) If after karyokinesis, cytokinesis does not occur, then result would be:
(a) two nuclei, two cells
(b) one nucleus, two
(c) two cells, no nuclei
(d) one cell, two nuclei
Solution:
one cell, two nuclei
(xiv) Gametes are formed by
(a) meiosis
(b) mitosis
(c) amitosis
(d) none of these
Solution:
meiosis
(xv) Minimum coiling in chromosome is at:
(a) prophase
(b) metaphase
(c) anaphase
(d) telophase
Solution:
telophase
(xvi) Chromosome is most coiled at (in mitosis):
(a) telophase
(b) anaphase
(c) metaphase
(d) prophase
Solution:
prophase
(xvii) Nuclear membrane reappears in:
(a) metaphase
(b) prophase
(c) telophase
(d) anaphase
Solution:
telophase





