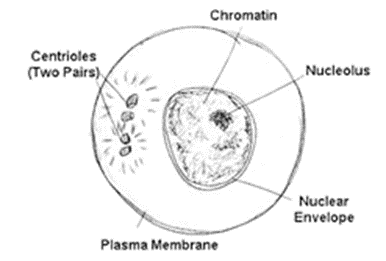
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Question 1: The Chromatin material is formed forms of
(a) DNA only
(b) DNA and histones
(c) Histones only
(d) Nucleotides
Solution :
DNA and Histones
Question 2: The term “chromosomes” literally means
(a) Inherited bodies
(b) Twisted threads
(c) Coloured bodies
(d) Shining threads
Solution :
Coloured bodies
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Questions 1: Name the following:
a) The repeating components of each DNA strand lengthwise.
b) The complex consisting of DNA strand and a core of histones.
c) The type of bond which joins the complementary nitrogenous bases.
d) The three components of a nucleotide.
Solution 1:
(a) Nucleotides.
(b) Nucleosome.
(c) Hydrogen Bond.
(d) Phosphate, Sugar and Nitrogenous base.
Short Answer Type Questions
Questions 1: What is the difference between chromatin fibre and chromosome?
Solution 1:
Unfolded, uncondensed, and stretched DNA is referred to as chromatin fibre. It can only be seen when a cell divides, whereas chromosomes are condensed DNA that can be seen when a cell divides.
Question 2: What are the rungs of the “DNA ladder” made of?
Solution 2:
The nitrogenous bases Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), and Thymine (T) make up the rungs of the DNA ladder (T).
Question 3: Correct the following statements if there is any mistake.
a) The four nitrogenous bases in the DNA are Guanine, Thiamine, Adrenaline and Cytosine.
b) Genes are specific sequences of bases on a chromosome.
c) A nucleotide is composed of a sulphate, a sugar (pentose) and a nitrogenous base.
d) Nucleosomes are groups of cysteine molecules surrounded by DNA strands.
e) If there are 46 chromosomes in a cell there will be 23 chromatin fibres inside the nucleus during interphase.
Solution 3:
(a) The four nitrogenous bases in the DNA ladder are Guanine, Thymine, Adenine and Cytosine.
(b) Genes are specific sequences of nucleotides on a chromosome.
(c) A nucleotide is composed of a phosphate, sugar (pentose) and a nitrogenous base.
(d) Nucleosomes are groups of histone molecules surrounded by DNA strands.
(e) If there are 46 chromosomes in a cell there will be 46 chromatin fibres inside the nucleus during interphase.
Long Answer Type:
Question 1: What is a nucleosome?
Solution 1:
The nucleosome is the most fundamental structural element of DNA. Each strand of DNA is wound around an eight-molecule core of histone molecules. This core like a football, around which a long rope with one or two loops is twisted. A nucleosome is the name for such a complicated structure. A million nucleosomes can be found on a single human chromosome.
Question 2: What are genes?
Solution 2:
Gene is a structural and functional unit of heredity and variations. Genes are specific sequences of nucleotides on a chromosome that encode particular proteins which express in the form of some particular feature of the body. In other words, the gene is the DNA segment of the chromosome and it controls the expression of characteristics.
Structured/Application/Skill Type
Question 1: Given below is a schematic diagram of a portion of DNA.

(a) How many strands are shown in the pic?
(b) How many nucleotides have been shown in each strand?
(c) Name the parts numbered 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 respectively.
(d) Name the DNA unit constituted by the parts 1, 2, 3 collectively.
Solution 1:
(a) 2
(b) 2 on each strand
(c) 1- Phosphate, 2- Sugar, 3- Nitrogen Base, 4- Hydrogen Bond, 5 – Base
(d) Nucleotide
Question 2:
The three sketches (A, B and C) are intended to represent the replication of DNA. What should be their correct sequence starting with the first and ending with the last? ……

Solution 2:
The correct sequences are as follows: B, C and A.
Exercise 2
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Question 1: The number of chromosomes in a certain type of cell division is halved. This kind of cell division occurs in.
(a) Only testis
(b) Only ovary
(c) Both ovary and testis
(d) All body cells
Solution :
Both ovary and testis
Question 2: In which one of the following options the two stages of mitosis have been given in correct sequence?
(a) Prophase, anaphase
(b) Metaphase, telophase
(c) Anaphase, telophase
(d) Telophase, anaphase
Solution :
Anaphase, telophase
Question 3: Synthesis phase in the cell cycle is called so for the synthesis of more of.
(a) RNA
(b) RNA and proteins
(c) DNA
(d) Glucose
Solution :
DNA
Very Short Answer Type
Question 1: Imagine one cell (A) has undergone one mitotic division and another cell (B) has completed its meiotic division. How many cells would the two produce?
Solution 1:
Cell A: 2
Cell B: 4
Question 2: Match the events given in column A with the phase in mitotic cell division in column B
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| a) Chromosomes get arranged in a horizontal plane at the equator. | Prophase |
| b) Daughter chromosomes move to the opposite poles of a spindle. | Anaphase |
| c) Chromosomes become visible as fine long threads. | Metaphase |
| d) Chromosomes lose their distinctiveness and gradually become transformed into a chromatin network. | Telophase |
Solution 2:
(a) Metaphase
(b) Telophase
(c) Prophase
(d) Anaphase
Fill in the blanks:
a) Mitosis occurs in our cells.
Solution:
Mitosis occurs in our Somatic (body) cells.
b) Mitosis produces two daughter cells whereas meiosis produces daughter cells.
Solution:
Mitosis produces two daughter cells whereas meiosis produces Four daughter cells.
c) Meiosis occurs only in cells.
Solution:
Meiosis occurs only in Reproductive cells.
d) Humans have 46 chromosomes: Their sperms and eggs will have chromosomes each.
Solution:
Humans have 46 chromosomes: Their sperms and eggs will have 23 and 23 chromosomes each.
e) During the pairing of chromosomes in meiosis, the chromosomes come to lie side by side.
Solution:
During the pairing of chromosomes in meiosis, the Homologous chromosomes come to lie side by side.
f) The (s) are surrounded by radiating rays called aster.
Solution:
The Centriole (s) are surrounded by radiating rays called aster.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1: State the difference between:
a) Chromosome and chromatid:
b) Centrosome and centromere:
c) Aster and spindle fibres:
d) Haploid and diploid:
Solution 1:
(a) In cells, a chromosome is an orderly structure comprising DNA and protein. A chromatid is one of the two copies of DNA that make up a duplicated chromosome, which are united at their centromeres for the process of cell division, whereas a genome is a single piece of coiled DNA containing numerous genes, regulatory elements, and other nucleotide sequences (mitosis or meiosis).
(b) Microtubules are formed in the centrosome, which is a part of the cell. The centrioles are a pair of tiny organelles found within the centrosome of an animal cell. The centrosome divides and the centrioles replicate (create new copies) during mammalian cell division, but each chromosome in its condensed state is made up of two chromatids linked at some point along its length. Centromere refers to the connection point.
(c) During mitosis in an animal cell, an aster is a cellular structure shaped like a star that forms around each Centrosome, whereas spindle fibres are aggregates of microtubules that move chromosomes during cell division.
(d) A haploid cell is one with one set of chromosomes. Meiosis produces gametes, which are haploid cells with two sets of chromosomes, whereas a diploid cell has two sets of chromosomes. Each parent contributes one set of chromosomes.
Question 2: “First meiotic division is the reduction division” what does the word ‘reduction’ refer to in this statement?
Solution 2: In this statement, reduction denotes that the number of chromosomes is cut in half, i.e., only one set of chromosomes is handed on to the sex cells out of the 23 pairs in humans.
Question 3: “Gametes must be produced by meiosis for sexual reproduction”. Why is it so?
Solution 3:
Because the number of chromosomes is reduced to half during meiosis and then restored during fertilisation, gametes must be created through meiosis for sexual reproduction.
Question 4: Mention whether the following statements are (T) Or (F). Give reason in support of your answer.
(a) As you grow from childhood to adulthood, your skin cells divide only to replace such cells that are lost from the surface.
Solution:
False
(b) The unfertilized human egg has half the number of chromosomes of the body cells.
Solution:
True
(c) Nuclear membrane in mitotically dividing cells remains intact up to the metaphase and disappears only in the telophase.
Solution:
False
(d) Mitotic cell division can be a mode of reproduction.
Solution:
True
(e) Crossing over between chromatids can occur only between homologous chromosomes.
Solution:
True
Structured / Application / Skill Type:
Question 1: Draw a labeled diagram to show the metaphase stage of mitosis in an animal cell having ‘6’ chromosomes.
Solution 1:

Question 2: The diagram below represents a stage during cell division. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:

a) Name the parts labeled 1, 2, and 3.
b) Identify the above stage and give a reason to support your answer.
c) Mention where in the body this type of cell division occurs.
d) Name the stage prior to this stage and draw a diagram to represent the same.
Solution 2:
(a) 1 – Centrosome
2 – Spindle fibres
3 – Chromatids
(b) The late anaphase of mitosis in an animal cell is depicted in the diagram. The existence of distinct chromatids at the cell’s two poles indicates the stage. Late anaphase is identified by the formation of a furrow in the cell membrane.
(c) Mitotic division occurs in all cells of the body except reproductive cells, and this type of cell division happens in all cells of the body save reproductive cells.
(d) Metaphase is the step preceding anaphase.

Question 3: The diagram given below represents a certain phenomenon which occurs during meiosis. Name and explain the phenomenon by using the terms – homologous chromosomes, chromatids, crossing over.
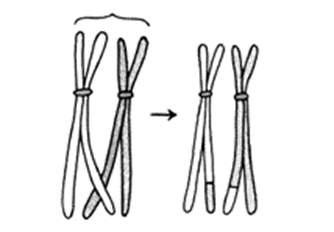
Solution 3:
Crossing-over is the transfer of chromatids between homologous chromosomes. This is the process of a homologous pair’s two chromosomes exchanging equal parts with each other.
The first division of meiosis is when cells cross over. Each chromosome has replicated into two strands known as sister chromatids at this point. A pair’s homologous chromosomes synapse, or join together. Breaks occur at corresponding places in two of the non-sister chromatids, i.e. in one chromatid of each chromosome, while the chromosomes are synapsed.
Because the chromosomes are homologous, breaks at corresponding places indicate that the broken segments contain corresponding genes, or alleles. The broken parts of the chromosomes are then exchanged between them to produce full new units, and each recombined chromosome of the pair can go to a different daughter sex cell. It causes recombination of related genes that are present on the same chromosome and would otherwise be transmitted together.
Question 4: Given below is a diagram representing a stage during mitotic cell division in an animal cell examines it carefully and answer the questions which follow.

a) Identify the stage. Give one reason in support of your answer.
b) Name the cell organelle that forms the ‘aster’
c) Name the parts labeled 1, 2 and 3.
d) Name the stage that follows the one shown above, how is that stage identified?
e) Mention two differences between mitosis and meiosis with regards to:
The number of daughter cells produced. The chromosome number in the daughter cells.
Solution 4:
a) Late prophase. Because the nuclear membrane and nucleolus have disappeared.
b) Centrioles
c) 1 – Centromere. 2 – Chromatids. 3 – Spindle fibre.
d) Metaphase. The centromeres of chromosomes are drawn to the equator by equal pull of two chromosomal spindle fibres that connects each centromere to the opposite poles, forming a metaphasic plate.
e) Differences between mitosis and meiosis:
| Mitosis | Meiosis |
| There are two daughter cells formed. | There are four daughter cells formed. |
| It is an equational division, which means that the number of chromosomes in the daughter or parent cells does not change. | It’s a reductional division, which means the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells is cut in half. |
Question 5: Given below are three diagrammatic sketches (A, B and C) of one and the same particular phase during mitotic type of cell division.

(a) Identify the phase
(b) What is the diploid number of chromosomes shown in them?
(c) Identify whether these are animal cells or plant cells?
(d) Which of these is/are shown in correct direction?
(i) Only A
(ii) Only B
(iii) Only A and C
(iv) All the three
Solution 5:
a) Metaphase.
b) 4
c) A – Animal, B – Animal, C – Plant
d) (iv) All the three
Question 6: Shown below are four stages (A, B, C, D) (not in sequence) of a certain kind of cell division.

(a) Is it a plant cell or an animal cell? Give two reasons
(b) Is it undergoing mitosis or meiosis?
(c) What should be the correct sequence of these four stages among themselves?
(d) Name the stage that should precede the earliest of these stages
(e) Draw the stage names above inside the blank space provided.
Solution 6:
(a) This is an animal cell since:
i) It has a circular outline (in plants, it would be angular, rectangular, or polygonal) and no cell wall.
ii) There Centrosomes or centrioles are present. (These can only be found in animal cells)
(b) Mitosis
(c) B, C, D, A.
(d) Interphase
(e)